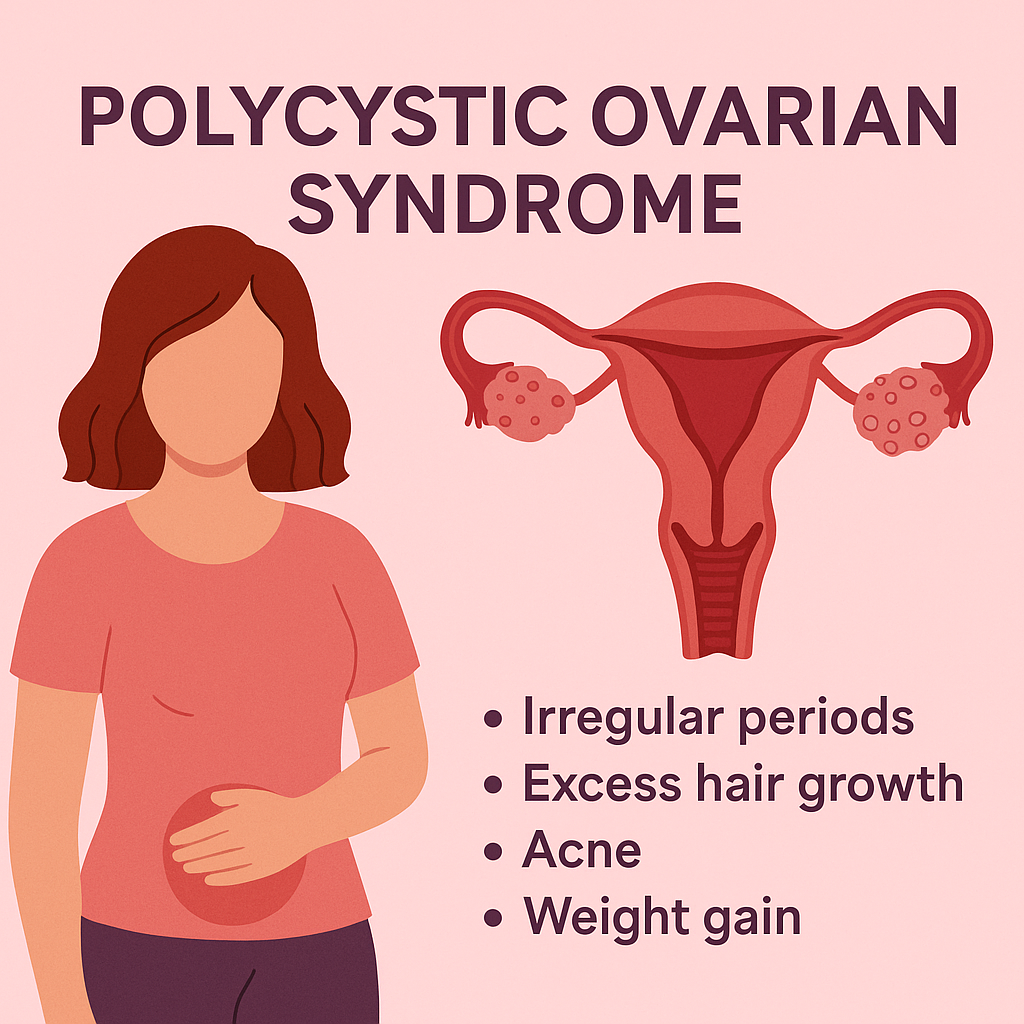
What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)?
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels (male hormones), and cysts in the ovaries. PCOS can lead to infertility, weight gain, acne, and other long-term health issues if left unmanaged.
According to research, PCOS affects approximately 1 in 10 women globally, making it one of the leading causes of female infertility.
🔍 Common Signs and Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS can vary, but the most common include:
- Irregular or missed periods
- Excess facial and body hair (hirsutism)
- Acne and oily skin
- Weight gain, especially around the abdomen
- Thinning hair or hair loss on the scalp
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Dark patches of skin (especially around the neck or underarms)
⚠️ Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of PCOS is unknown, several factors may contribute:
- Insulin resistance: High insulin levels can lead to increased androgen production.
- Hormonal imbalance: Elevated androgens interfere with ovulation.
- Genetics: PCOS can run in families.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation can also contribute to hormonal imbalance.
🧪 How is PCOS Diagnosed?
PCOS is usually diagnosed based on a combination of:
- Medical history and symptoms
- Physical exam
- Blood tests to check hormone levels
- Ultrasound to detect ovarian cysts
Doctors often follow the Rotterdam criteria, which require at least two of the following:
- Irregular periods
- Signs of excess androgens
- Polycystic ovaries on ultrasound
🩺 Health Risks Linked to PCOS
If not managed, PCOS can lead to several long-term health complications:
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Infertility
- Sleep apnea
- Endometrial cancer
- Anxiety and depression
🌿 Managing PCOS: Lifestyle and Medical Treatments
While there’s no cure for PCOS, the condition can be managed effectively through lifestyle changes and medication.
✅ 1. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced, low-glycemic index (GI) diet is beneficial for managing PCOS. Include:
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats)
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, legumes)
- Healthy fats (nuts, olive oil, avocado)
- Non-starchy vegetables (spinach, broccoli, cucumbers)
Avoid:
- Sugary snacks and drinks
- Processed and fried foods
- Excess red meat
✅ 2. Regular Physical Activity
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Walking, swimming, yoga, or strength training can improve insulin sensitivity and aid weight management.
✅ 3. Medical Treatments
- Hormonal birth control to regulate periods
- Anti-androgen medications to reduce excess hair and acne
- Metformin to improve insulin resistance
- Fertility treatments if trying to conceive
👩⚕️ PCOS and Mental Health
PCOS can affect mental well-being due to its visible symptoms and impact on fertility. If you feel overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to seek support from a counselor or therapist.
📌 Final Thoughts
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is a manageable condition with the right combination of medical care, dietary changes, and regular physical activity. Early diagnosis and proactive treatment can significantly improve a woman’s quality of life and reduce the risk of complications.