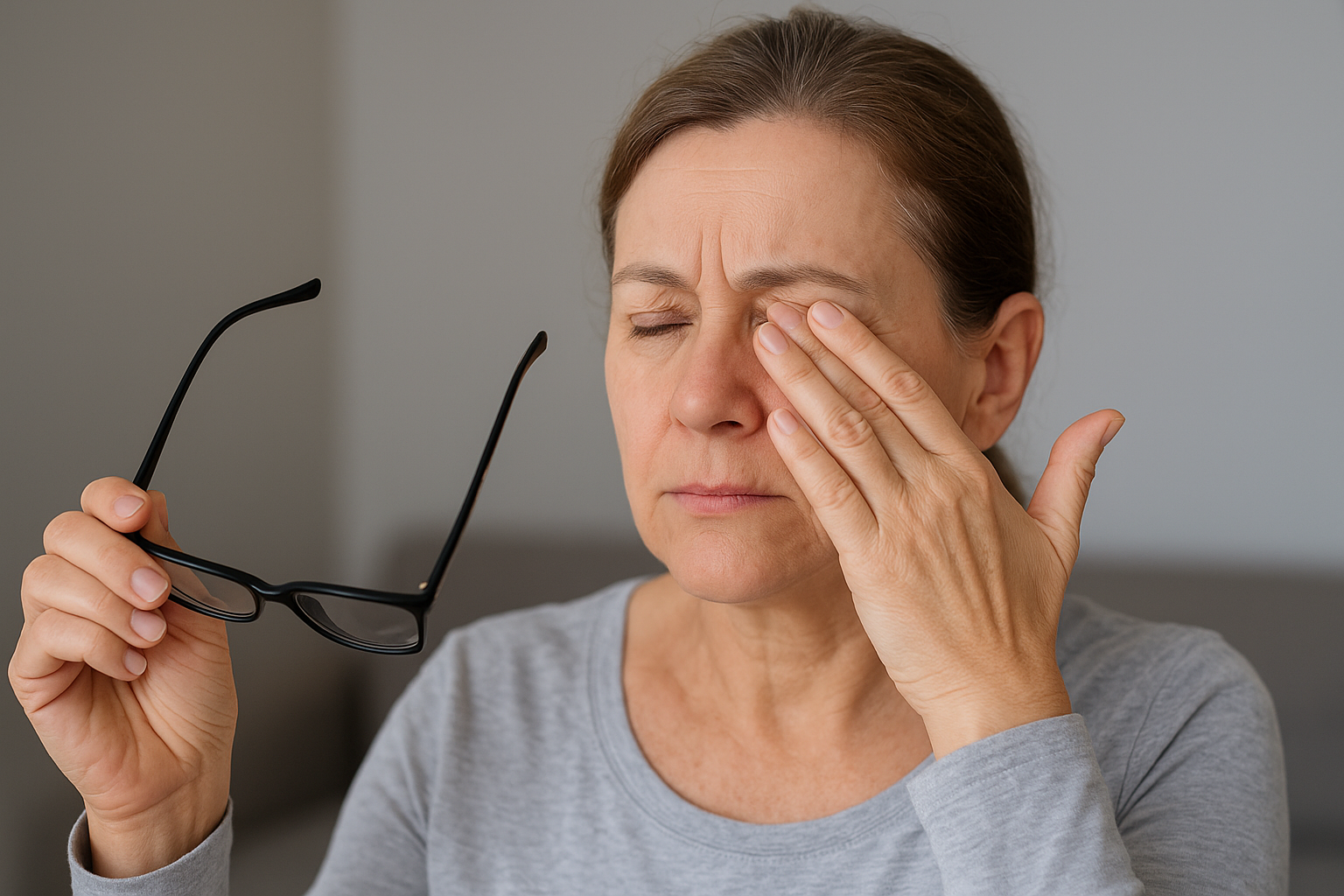
Near vision loss is a common eye problem in which a person struggles to see objects clearly at a close distance—such as reading a book, threading a needle, or using a mobile phone. This condition often develops gradually and affects people of all ages, although it is more common after the age of 40.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments helps in preventing complications and maintaining healthy vision.
What Is Near Vision Loss?
Near vision loss refers to difficulty focusing on close objects. The most common cause is presbyopia, a natural age-related change in the lens of the eye.
However, other factors such as refractive errors, medical conditions, and eye diseases can also lead to reduced near vision.
Common Causes of Near Vision Loss
1. Presbyopia (Age-Related Near Vision Loss)
- Usually starts after age 40
- Caused by the hardening of the eye’s lens
- Makes close-up tasks difficult
2. Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
A refractive error where distant objects appear clearer than near ones.
3. Eye Strain
Prolonged screen use, reading, or close-up work can temporarily affect near vision.
4. Cataracts
Clouding of the eye’s natural lens can reduce both near and distance vision.
5. Diabetes-Related Vision Problems
Poorly controlled diabetes can cause changes in the retina, affecting near vision.
6. Medications
Some drugs cause temporary blurred near vision (antihistamines, antidepressants, etc.).
7. Neuro-Ophthalmic Conditions
Rare conditions affecting the optic nerve or brain can impair focusing ability.
Symptoms of Near Vision Loss
- Difficulty reading small print
- Holding books or mobile phones farther away
- Eye strain or headache after near work
- Blurred or distorted close vision
- Increased need for bright light
- Frequent squinting
Diagnosis of Near Vision Loss
An eye specialist performs:
- Visual acuity test
- Refraction test to assess lens power needs
- Slit-lamp examination to check lens and cornea
- Retinal exam in case of diabetes or other diseases
Early diagnosis helps in selecting the correct treatment option.
Treatment Options
1. Reading Glasses
Most effective and simplest solution for presbyopia.
2. Bifocal or Progressive Lenses
Allow clear vision for both near and distance without switching glasses.
3. Contact Lenses
Options include:
- Multifocal lenses
- Monovision lenses (one eye for distance, one for near)
4. Refractive Surgery
Procedures include:
- LASIK
- Conductive keratoplasty
- Lens replacement surgery
Only suitable after evaluation by an ophthalmologist.
5. Treatment of Underlying Diseases
- Managing diabetes
- Treating cataracts surgically
- Adjusting medications that affect vision
Lifestyle Tips for Better Near Vision
- Use adequate lighting for reading
- Take breaks using the 20-20-20 rule
- Maintain normal blood sugar levels
- Avoid prolonged screen exposure
- Keep reading material at a comfortable distance
- Regular eye checkups after age 40
Complications of Untreated Near Vision Loss
If neglected, near vision problems can lead to:
- Frequent headaches
- Eye strain
- Difficulty performing daily tasks
- Decreased productivity
- Risk of accidents due to poor vision
Prevention
While presbyopia cannot be prevented, early detection and proper correction make daily activities easier.
Healthy lifestyle practices such as controlling diabetes, staying hydrated, and reducing screen strain can help protect eye health.
Conclusion
Near vision loss is a widespread condition that usually develops with age but can also result from medical issues, refractive errors, or lifestyle factors. Fortunately, it is highly manageable with reading glasses, contact lenses, surgery, and lifestyle adjustments.
Regular eye examinations remain the most effective strategy for maintaining clear and healthy vision throughout life.