Dyslipidemia is a medical condition characterized by abnormal levels of lipids (fats) in the blood, including cholesterol and triglycerides. It is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (CVD) such as heart attack and stroke. Understanding the causes, prevention, and treatment of dyslipidemia is essential for maintaining heart health and overall well-being.
Understanding Dyslipidemia
The condition involves:
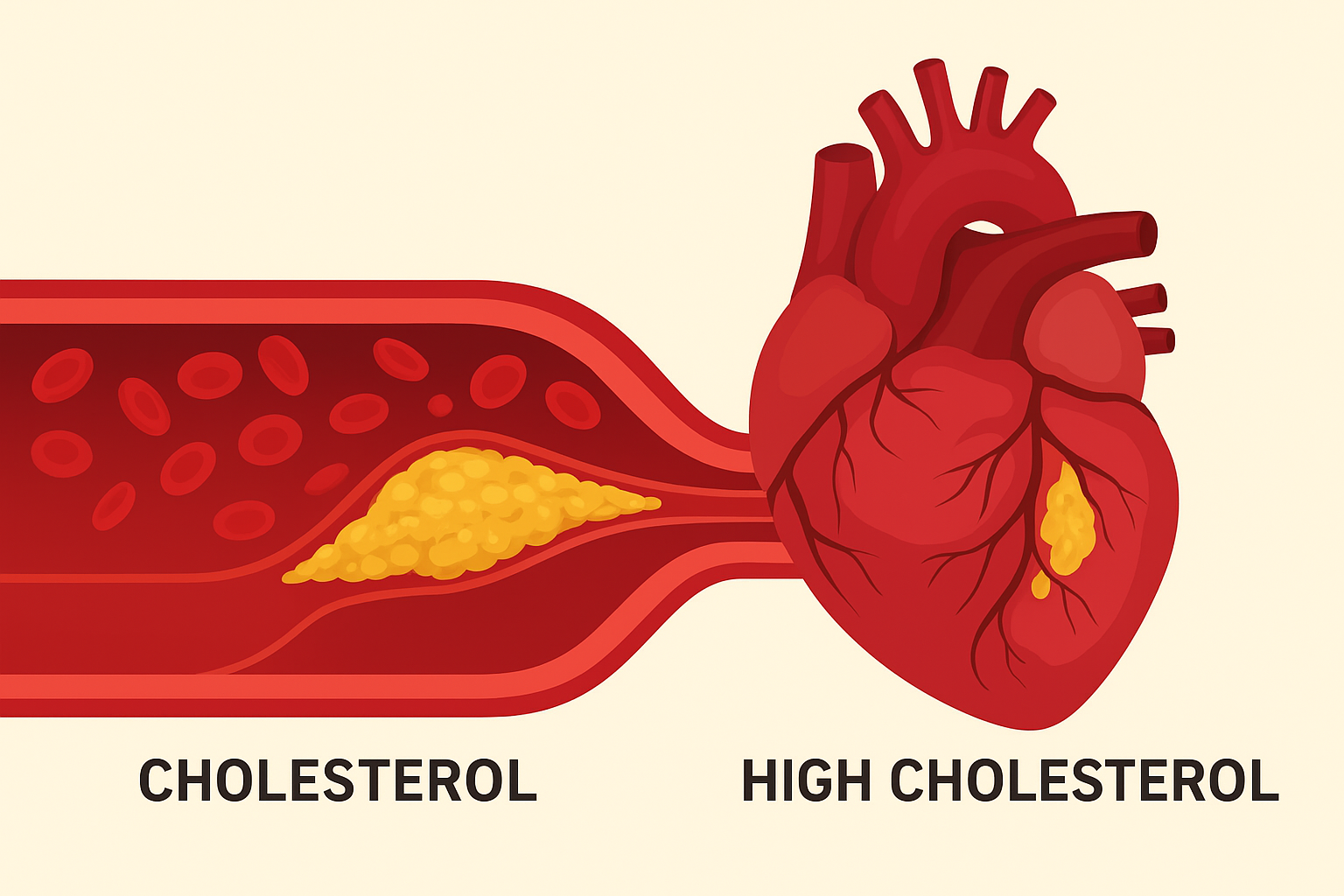
- High LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) cholesterol – “bad” cholesterol that contributes to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Low HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) cholesterol – “good” cholesterol that helps remove excess cholesterol.
- High triglycerides – a type of fat that increases heart disease risk when elevated.
Causes and Risk Factors
Dyslipidemia may be caused by:
- Unhealthy diet high in saturated fats and trans fats.
- Physical inactivity and sedentary lifestyle.
- Obesity or being overweight.
- Genetic predisposition (familial hypercholesterolemia).
- Certain medical conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol intake.
Symptoms
Dyslipidemia is often called a “silent” condition because it may not present noticeable symptoms until complications occur. Routine blood tests (lipid profile) are essential for early detection.
Management Strategies
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are the first line of defense against dyslipidemia.
- Healthy diet: Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Reduce saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugars.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly.
- Weight management: Maintain a healthy weight to improve lipid levels.
- Quit smoking: Increases HDL cholesterol and reduces CVD risk.
- Limit alcohol: Excessive alcohol raises triglyceride levels.
2. Medical Management
If lifestyle changes are insufficient, your healthcare provider may recommend medications, such as:
- Statins: Lower LDL cholesterol.
- Fibrates: Reduce triglycerides and increase HDL cholesterol.
- Niacin: Improves all lipid parameters.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Help lower triglycerides.
3. Regular Monitoring
- Perform a lipid profile every 4–6 months (or as recommended) to track progress.
- Monitor blood pressure, blood sugar, and other cardiovascular risk factors.
Prevention Tips
- Start healthy habits early in life.
- Engage in daily physical activity.
- Choose heart-friendly foods like oily fish, olive oil, and legumes.
- Avoid processed and fried foods.
- Have regular health check-ups.
Conclusion
Dyslipidemia management requires a balanced approach combining lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and, if needed, medications. Early detection and proactive treatment significantly lower the risk of heart disease and improve overall quality of life.