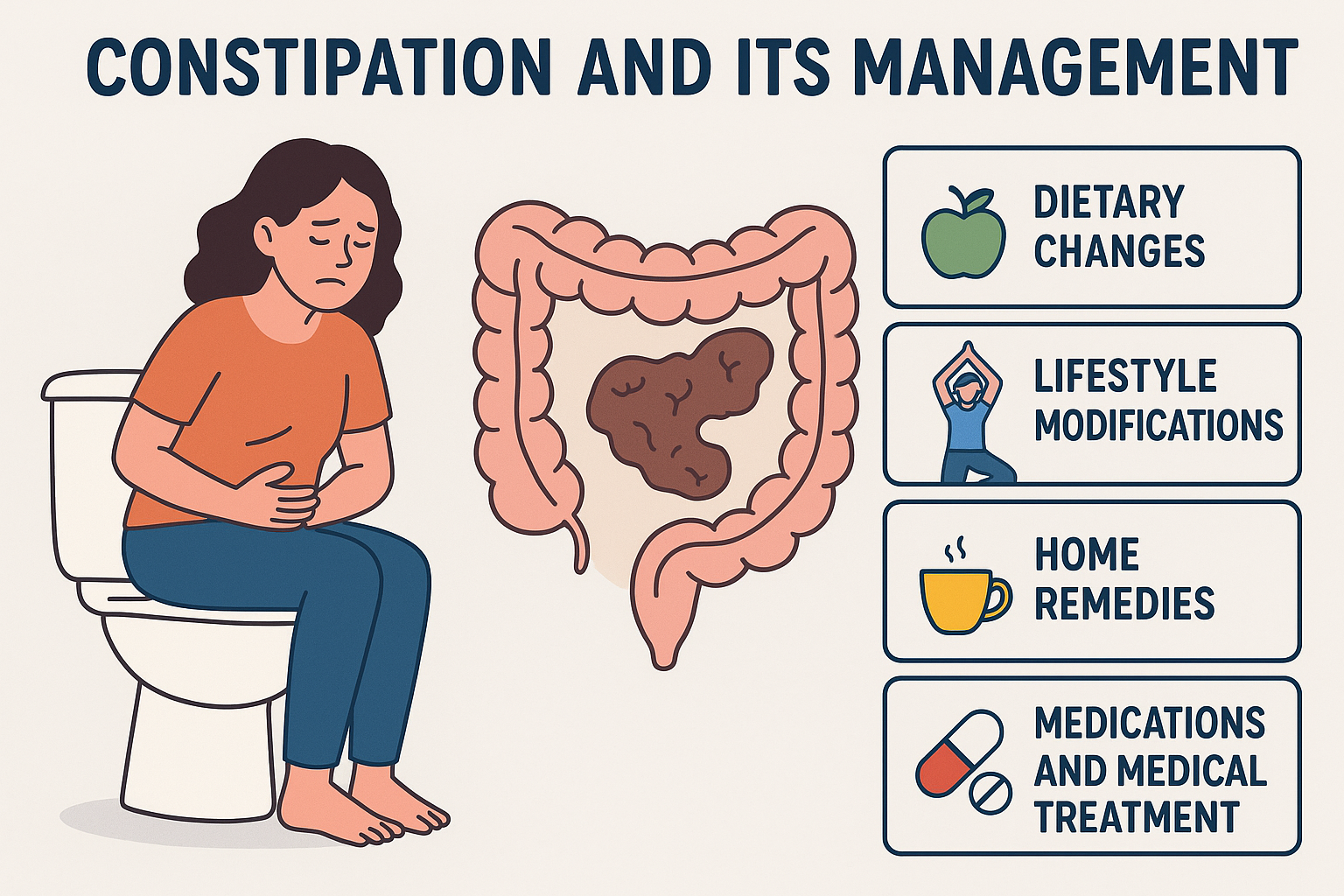
Constipation is a common digestive problem that affects people of all ages. It occurs when bowel movements become infrequent, hard, or difficult to pass. While occasional constipation is normal, chronic constipation can impact quality of life and may require medical attention. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
What is Constipation?
Constipation is typically defined as having fewer than three bowel movements per week, passing hard stools, or experiencing straining during defecation. It may be temporary or persistent, depending on underlying health and lifestyle factors.
Common Causes of Constipation
Several factors contribute to constipation, including:
- Low-fiber diet – Diets lacking in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains reduce stool bulk.
- Inadequate fluid intake – Dehydration can harden stools and slow bowel movements.
- Lack of physical activity – Sedentary lifestyle slows digestion.
- Medications – Painkillers, antidepressants, and iron supplements can cause constipation.
- Ignoring the urge to pass stool – Delaying bowel movements can lead to harder stools.
- Medical conditions – Hypothyroidism, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diabetes, or neurological disorders may cause chronic constipation.
Symptoms of Constipation
The main symptoms include:
- Infrequent bowel movements (less than three times per week)
- Hard or lumpy stools
- Straining during defecation
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation
- Abdominal discomfort, bloating, or cramps
If constipation is accompanied by blood in stool, unexplained weight loss, or severe pain, medical advice should be sought immediately.
Management of Constipation
1. Dietary Changes
- Increase fiber intake: Include fiber-rich foods such as whole grains, fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts.
- Stay hydrated: Drink at least 8–10 glasses of water daily to soften stools.
- Limit processed foods: Reduce intake of refined flour, fried items, and junk foods that slow digestion.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular physical activity: Walking, jogging, yoga, or light exercises stimulate bowel movements.
- Establish a routine: Train your bowel by setting regular times for defecation, preferably after meals.
- Avoid delaying stools: Respond promptly to the urge to pass stool.
3. Home Remedies
- Warm water with lemon in the morning may stimulate digestion.
- Prunes and figs act as natural laxatives.
- Flaxseeds or chia seeds can improve bowel regularity.
4. Medications and Medical Treatment
- Laxatives (used occasionally under medical guidance) may help in stubborn cases.
- Stool softeners and fiber supplements can be recommended.
- For chronic constipation, a doctor may investigate underlying medical causes and provide tailored treatment.
Preventing Constipation
Prevention is always better than treatment. Simple steps such as maintaining a high-fiber diet, drinking enough fluids, staying physically active, and developing healthy toilet habits can go a long way in keeping constipation away.
Final Thoughts
Constipation is a manageable condition, but ignoring it for long periods can lead to complications such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures. By making healthy lifestyle changes and seeking timely medical advice when needed, constipation can be effectively prevented and treated.