Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer, originating from the hepatocytes (liver cells). It is a serious global health issue and a leading cause of cancer-related deaths, especially in regions with a high prevalence of chronic liver disease and hepatitis infections. Understanding its causes, early symptoms, and treatment options is essential for better outcomes.
What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
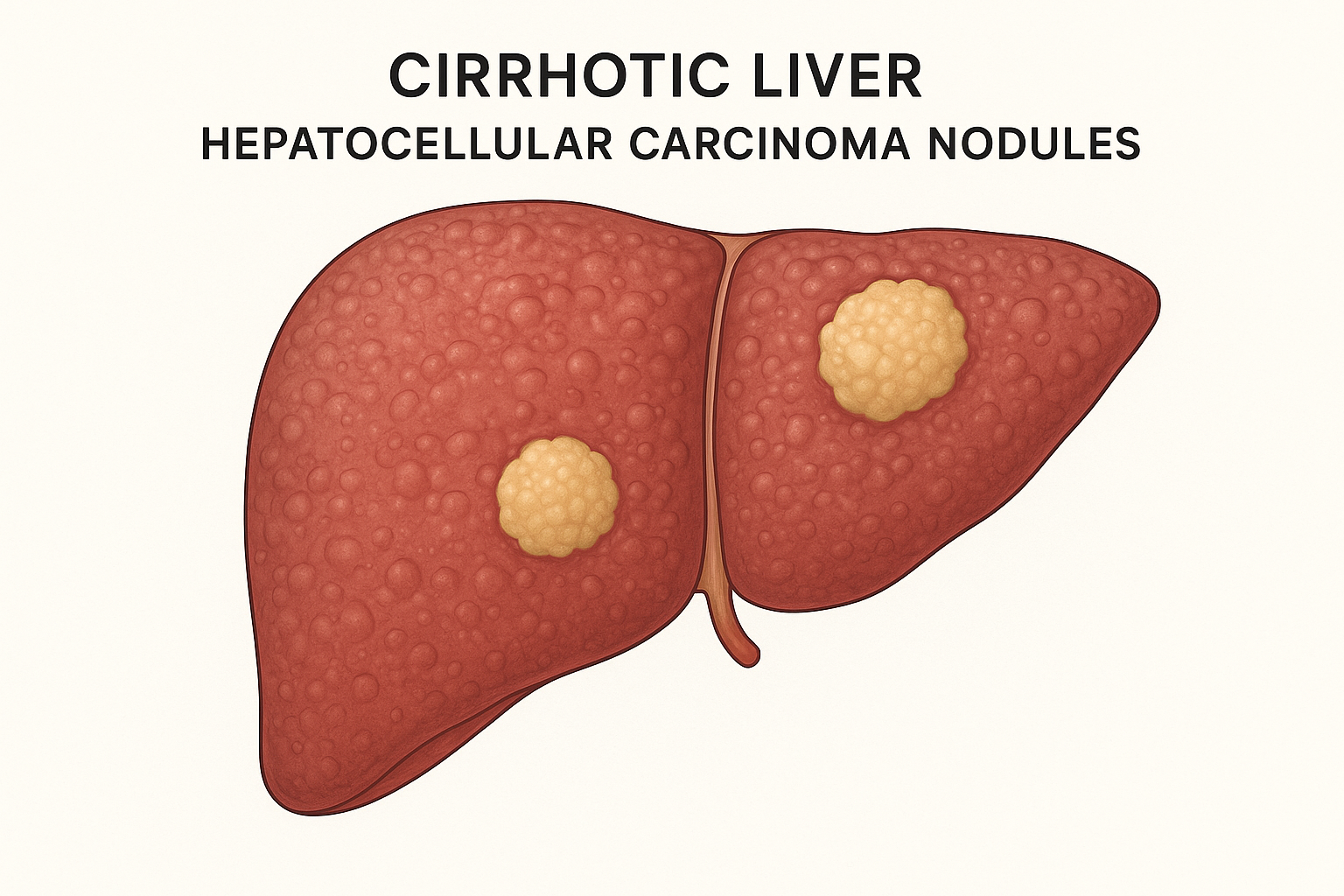
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a malignant tumor of the liver that usually develops in people with chronic liver damage, particularly cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B, hepatitis C, or long-term alcohol use. Unlike secondary liver cancers (metastatic cancers spreading to the liver from other organs), HCC begins within the liver itself.
Risk Factors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Several factors increase the risk of developing HCC:
- Chronic hepatitis B and C infections – major causes worldwide
- Cirrhosis of the liver due to alcohol abuse, fatty liver disease, or chronic viral hepatitis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) linked with obesity and diabetes
- Exposure to aflatoxins (toxins produced by mold on poorly stored grains and nuts)
- Family history of liver cancer
- Male gender and increasing age
Symptoms of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Early-stage HCC may remain asymptomatic, making regular screening crucial in high-risk individuals. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort (especially in the upper right side)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite and fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of eyes and skin)
- Nausea and vomiting
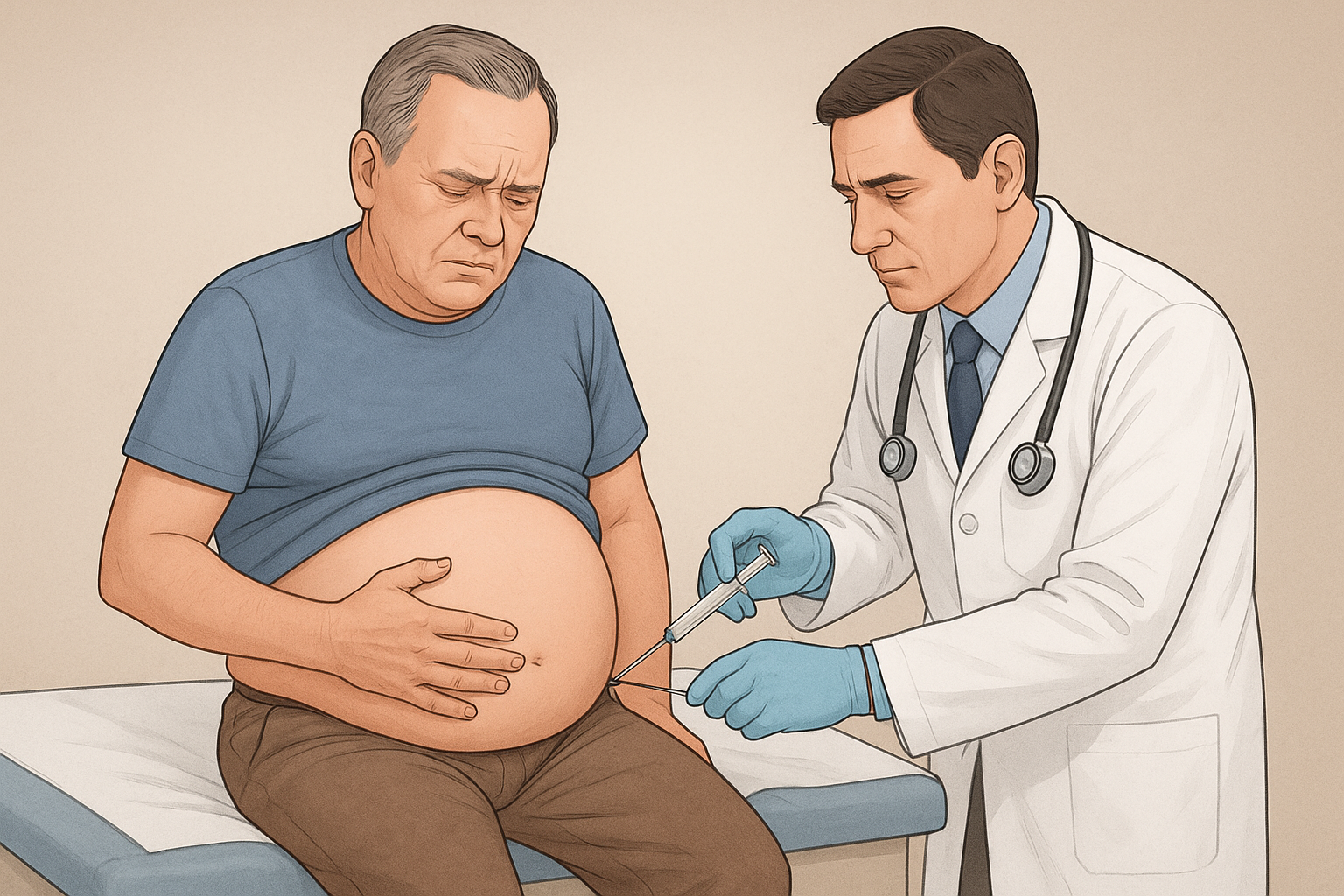
- Swelling in the abdomen (ascites)
- Enlarged liver or spleen
Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Accurate diagnosis requires clinical evaluation, blood tests, and imaging:
- Blood tests – Elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels can indicate HCC.
- Ultrasound of the liver – Often used for screening in high-risk patients.
- CT Scan and MRI – Detailed imaging to assess tumor size and spread.
- Liver biopsy – Confirms diagnosis under a microscope.
- Liver function tests – Evaluate the extent of liver damage.
Staging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
HCC is classified into stages to guide treatment:
- Early stage: Tumor confined to the liver, preserved liver function.
- Intermediate stage: Multiple tumors without spread outside the liver.
- Advanced stage: Tumor spread to blood vessels or other organs.
- End-stage: Severe liver damage with limited treatment options.
Treatment and Management of HCC
Treatment depends on the stage, overall liver function, and patient’s health status. Options include:
1. Surgical Resection
Removal of the affected liver portion in patients with good liver function.
2. Liver Transplantation
Best option for patients with cirrhosis and liver failure alongside HCC.
3. Locoregional Therapies
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA): Heat destroys cancer cells.
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE): Blocks blood supply to tumor and delivers chemotherapy.
- Radioembolization: Uses radioactive particles to target cancer cells.
4. Systemic Therapies
- Targeted therapies (sorafenib, lenvatinib) slow tumor growth.
- Immunotherapy strengthens the immune system to fight cancer cells.
5. Palliative Care
In advanced cases, focus is on symptom relief and improving quality of life.
Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Preventing HCC focuses on reducing risk factors:
- Vaccination against hepatitis B
- Effective treatment of hepatitis C
- Avoiding excessive alcohol use
- Maintaining a healthy weight and controlling diabetes
- Safe food storage to prevent aflatoxin contamination
- Regular screening (ultrasound and AFP tests) for high-risk individuals
Final Thoughts
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a life-threatening condition strongly associated with chronic liver disease. Early detection through regular screening, especially in high-risk individuals, offers the best chance for successful treatment. Preventive strategies such as hepatitis vaccination, healthy lifestyle practices, and timely medical care play a vital role in reducing the global burden of liver cancer.