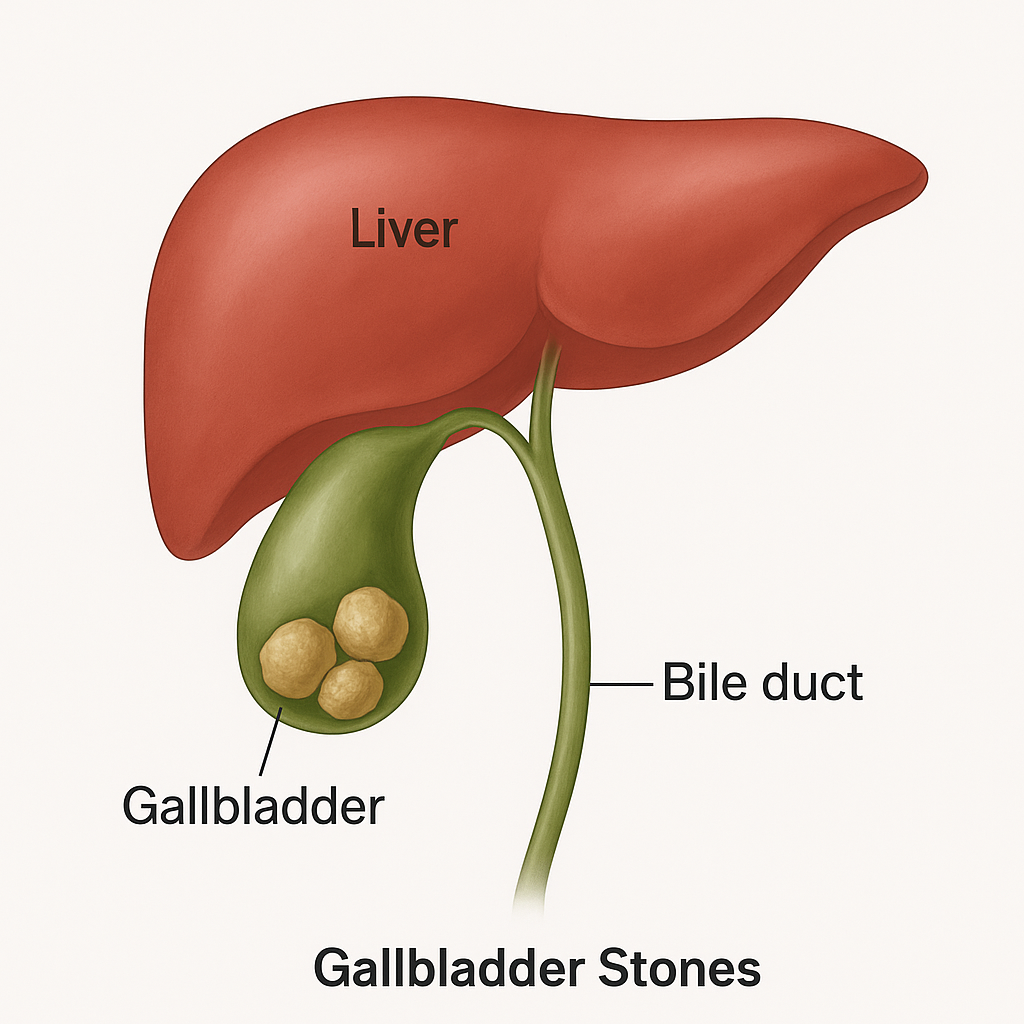
Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, are a common digestive disorder that can cause severe pain and complications if not managed properly. They are hardened deposits that form inside the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile. Understanding gallstones, their risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for better health and prevention.
What Are Gallbladder Stones?
Gallstones are solid particles made of cholesterol, bile salts, and other digestive fluids. They can vary in size, from tiny grains like sand to larger stones resembling pebbles. Some people may develop just one stone, while others can form multiple stones at the same time.
Types of Gallstones
There are mainly two types of gallstones:
- Cholesterol Gallstones – The most common type, formed when bile contains too much cholesterol.
- Pigment Gallstones – Made from excess bilirubin, more common in people with liver disease or blood disorders.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gallstones
Gallstones develop when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile. Several risk factors increase the likelihood of gallstone formation:
- Excess cholesterol in bile
- Excess bilirubin production (due to liver disease, infections, or blood disorders)
- Poor bile drainage (gallbladder does not empty completely)
Risk Factors:
- Being female (hormonal changes increase risk).
- Age above 40 years.
- Obesity and rapid weight gain.
- Rapid weight loss or prolonged fasting.
- Pregnancy.
- Family history of gallstones.
- Diet high in fats and cholesterol but low in fiber.
- Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, liver cirrhosis, or hemolytic anemia.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Some people with gallstones may have no symptoms (silent gallstones). However, when gallstones block bile ducts, they cause noticeable symptoms such as:
- Sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen (biliary colic).
- Pain in the right shoulder or back.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Indigestion, bloating, or gas after fatty meals.
- Fever and chills (if infection develops).
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
Complications of Gallstones
If untreated, gallstones can cause:
- Cholecystitis – inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Pancreatitis – inflammation of the pancreas.
- Cholangitis – infection of bile ducts.
- Gallbladder rupture (rare but serious).
Diagnosis of Gallstones
Doctors may use the following methods:
- Ultrasound – the most common and accurate method.
- Blood tests – to detect infection, liver function, or bile duct blockage.
- CT scan or MRI – to check complications.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) – both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Treatment Options for Gallstones
Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms:
1. No Symptoms (Silent Gallstones)
- Usually no treatment is needed.
- Regular monitoring may be advised.
2. Symptomatic Gallstones
- Medications – Oral bile acid pills may dissolve cholesterol stones (takes months to years, stones may recur).
- Surgery (Cholecystectomy) – The most effective and common treatment. It involves removing the gallbladder.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (keyhole surgery) – minimally invasive, faster recovery.
- Open surgery – for complicated cases.
- Endoscopic Procedures (ERCP) – To remove stones from bile ducts.
Prevention of Gallstones
Lifestyle and dietary changes can help reduce the risk of gallstones:
- Maintain a healthy weight – avoid crash diets.
- Eat a balanced diet with fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Reduce fatty, fried, and processed foods.
- Exercise regularly.
- Stay hydrated by drinking enough water daily.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe abdominal pain that does not improve.
- Persistent nausea and vomiting.
- Yellowing of skin or eyes.
- High fever with chills.
Conclusion
Gallstones are a common digestive problem that may remain silent or cause severe pain and complications. Early diagnosis and proper treatment, especially surgery when necessary, can provide permanent relief. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and balanced diet, you can lower your risk of gallstone formation and protect your digestive health.