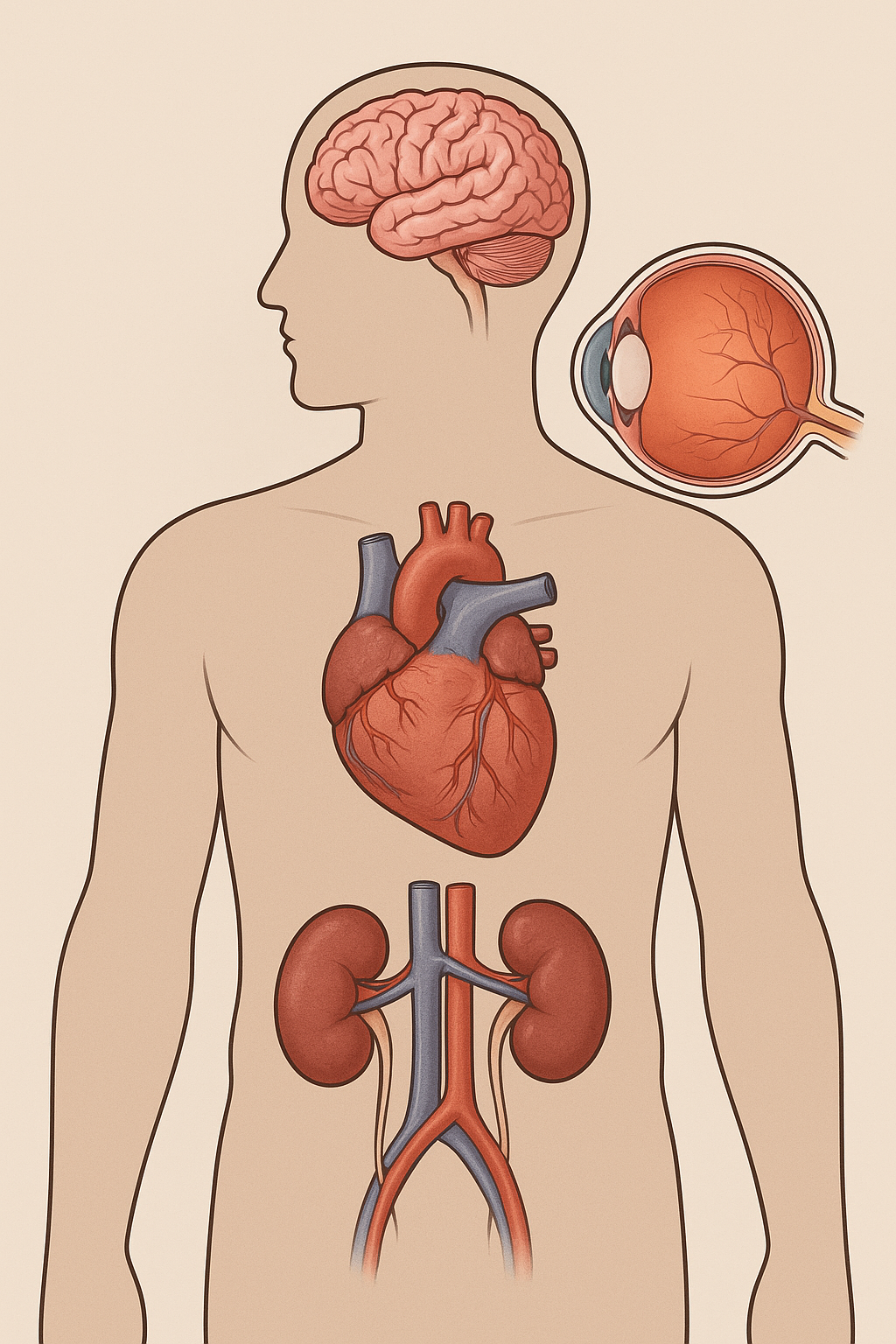
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a silent but serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Often called the “silent killer”, it may not show obvious symptoms for years but can cause severe damage to vital organs if left uncontrolled. Persistent high blood pressure puts extra strain on the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, brain, and eyes, leading to life-threatening complications.
In this blog, we will explore the major complications of hypertension, their risks, and how to prevent them.
Major Complications of Hypertension
1. Heart Complications
Hypertension is one of the leading causes of cardiovascular diseases. Long-term high blood pressure damages the arteries and increases the risk of:
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) – Narrowed or blocked arteries cut off blood supply to the heart.
- Heart Failure – The heart weakens and cannot pump blood effectively.
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy – Thickening of the heart muscle due to constant pressure load.
2. Stroke and Brain Damage
High blood pressure can weaken or block arteries in the brain, resulting in:
- Ischemic Stroke – Caused by blocked blood flow to the brain.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke – Occurs when a blood vessel bursts inside the brain.
- Vascular Dementia – Memory loss and cognitive decline due to reduced brain blood supply.
3. Kidney Damage (Hypertensive Nephropathy)
The kidneys filter waste from the blood, but uncontrolled hypertension damages the delicate blood vessels inside them, leading to:
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplant
4. Eye Complications (Hypertensive Retinopathy)
High blood pressure damages the tiny blood vessels in the retina, causing:
- Blurred vision
- Retinal hemorrhage
- Swelling of the optic nerve
- Permanent blindness if untreated
5. Aneurysm Formation
Persistent high blood pressure can weaken artery walls, creating a bulge called an aneurysm. If the aneurysm bursts, it can cause life-threatening internal bleeding.
6. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Hypertension narrows blood vessels in the arms and legs, reducing blood flow. Symptoms include:
- Leg pain while walking
- Numbness and weakness
- Slow wound healing, which may lead to infections
7. Metabolic and Cognitive Disorders
Uncontrolled hypertension also contributes to:
- Metabolic Syndrome – A combination of diabetes, obesity, and high cholesterol.
- Memory Problems and Dementia – Due to long-term brain damage.
How to Prevent Hypertension Complications
- Maintain Blood Pressure Control – Regularly monitor and follow prescribed medications.
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet – Limit salt, avoid fried foods, and increase fruits and vegetables.
- Exercise Regularly – At least 30 minutes of walking, jogging, or cycling daily.
- Quit Smoking and Reduce Alcohol – Lowers strain on heart and blood vessels.
- Manage Stress – Through relaxation techniques, yoga, or meditation.
- Routine Medical Checkups – Early detection of organ damage saves lives.
Conclusion
Hypertension is not just about numbers on a blood pressure monitor—it is a condition that can silently damage the heart, brain, kidneys, and eyes over time. The good news is that with early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and proper treatment, most of these complications can be prevented. Managing high blood pressure effectively is the key to living a longer, healthier life.