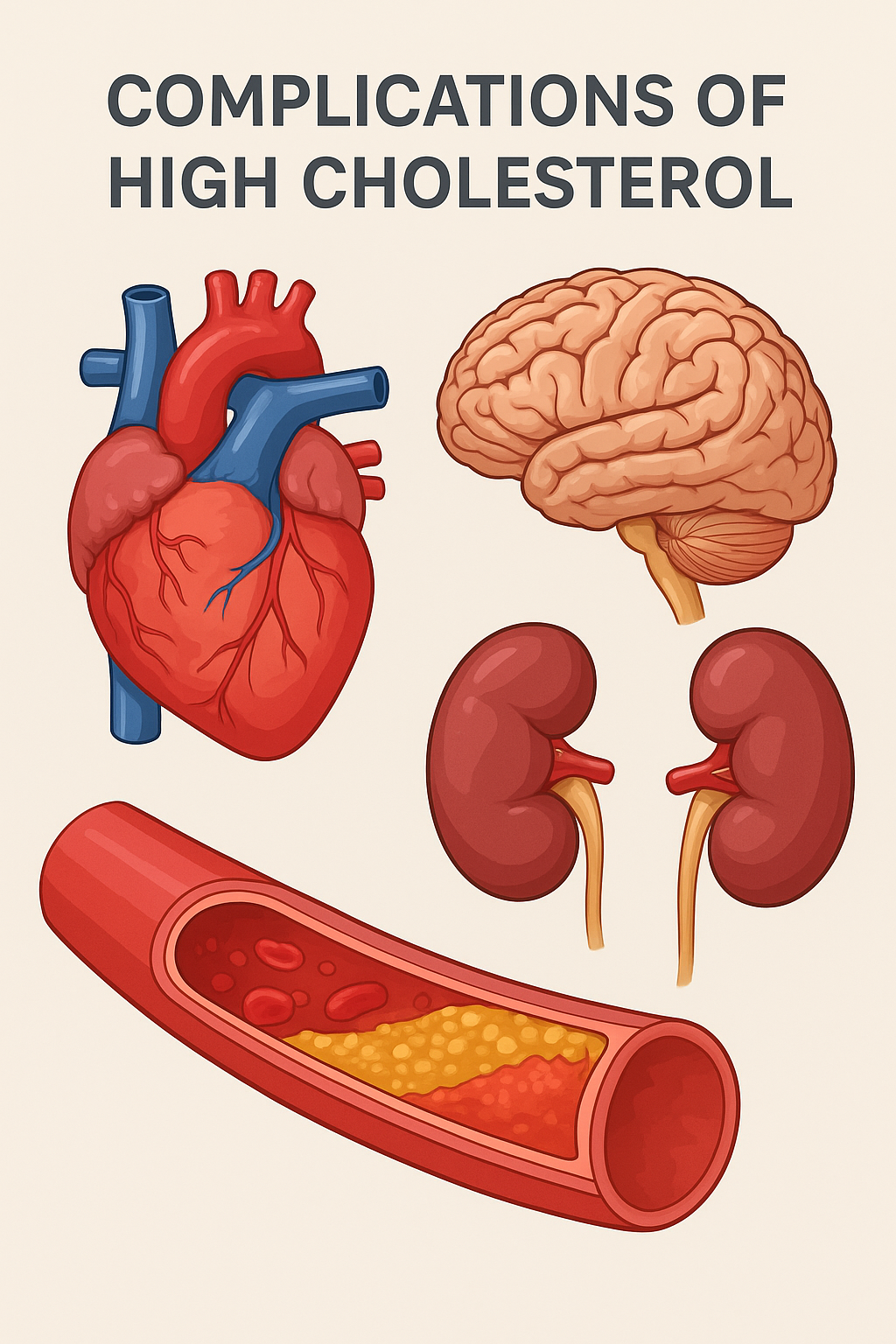
High cholesterol is a common health issue that develops when the body has excessive amounts of fatty substances (lipids) in the blood. Cholesterol is essential for building cells and producing hormones, but too much of it can silently damage arteries and increase the risk of life-threatening diseases.
Often called a “silent risk factor,” high cholesterol usually does not cause symptoms until complications appear. Understanding these complications is key to preventing long-term health problems.
Major Complications of High Cholesterol
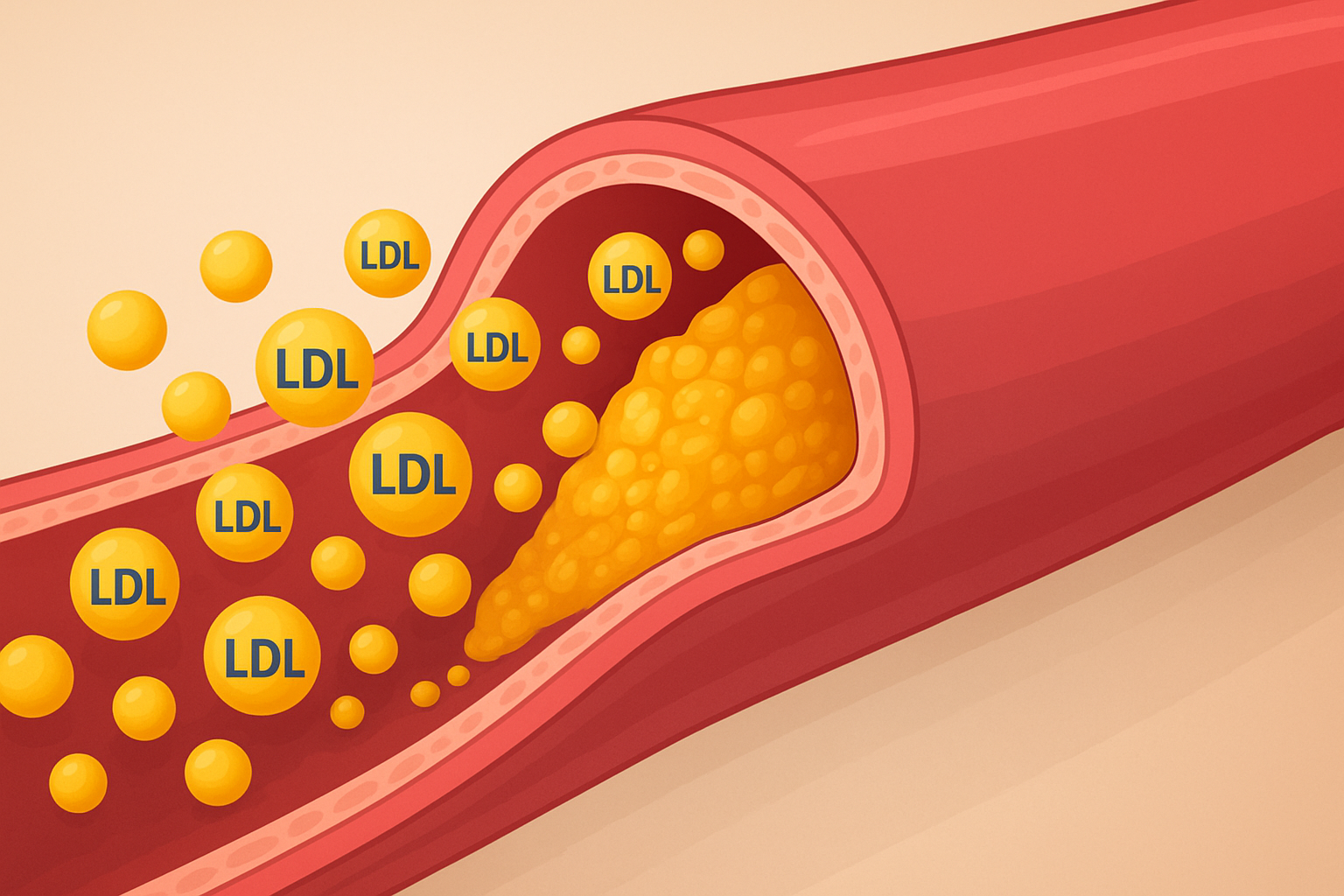
1. Atherosclerosis (Narrowing of Arteries)
Excess cholesterol gets deposited on the walls of arteries, forming plaques. Over time, these plaques harden and narrow the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow. This process, known as atherosclerosis, is the root cause of many cardiovascular complications.
2. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Plaque buildup in the coronary arteries (which supply blood to the heart) can cause:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Increased risk of heart attack
3. Stroke
If plaques rupture or a blood clot forms, blood flow to the brain can be blocked, leading to an ischemic stroke. High cholesterol also increases the risk of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), often called mini-strokes.
4. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
High cholesterol reduces circulation in the legs and arms, causing:
- Pain during walking (claudication)
- Coldness or numbness in legs and feet
- Poor wound healing, which may lead to infections or amputations
5. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
Plaque buildup makes arteries stiff and narrow, forcing the heart to pump harder. This results in hypertension, which further increases the risk of heart attack, kidney disease, and stroke.
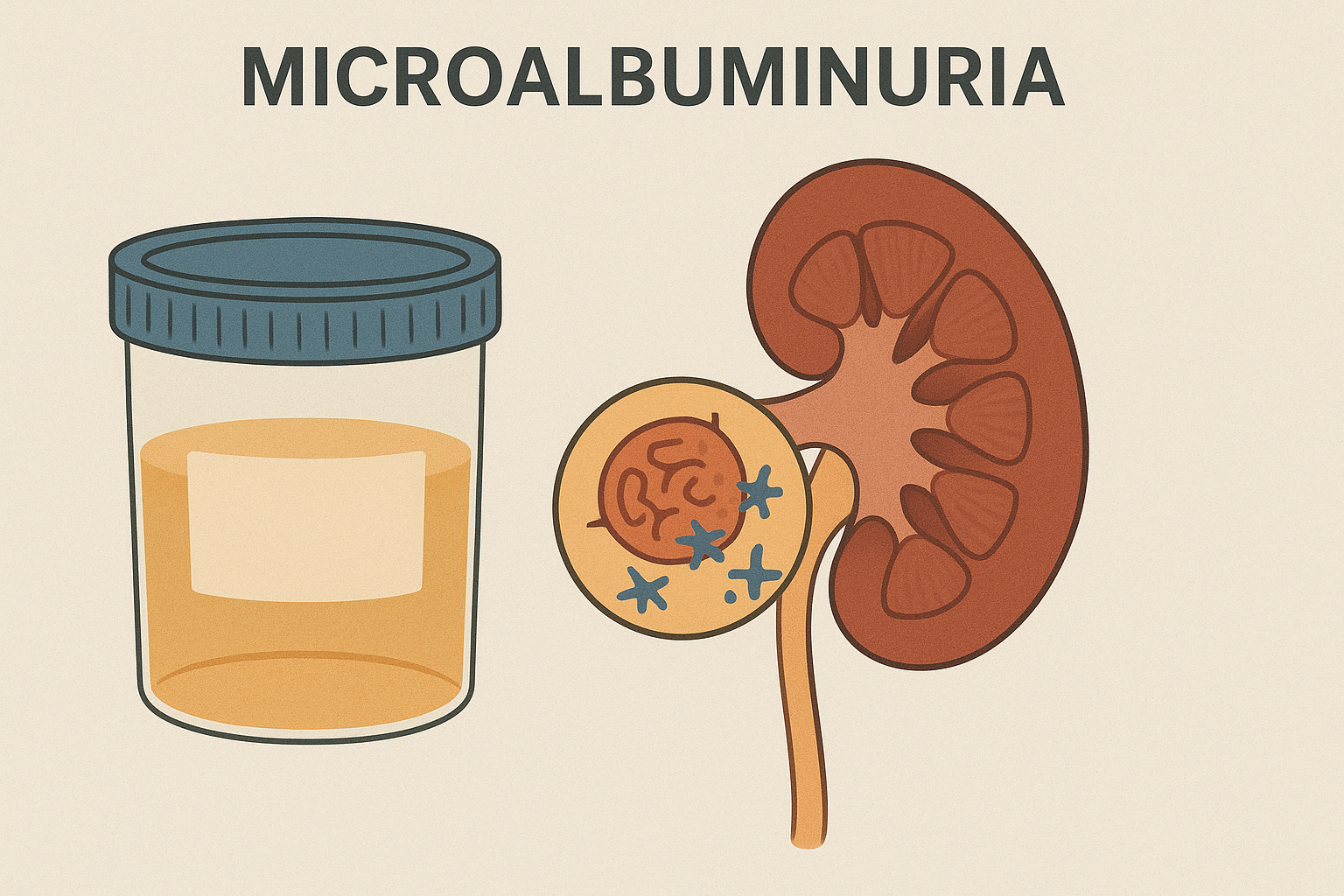
6. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Cholesterol plaques may block blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste effectively. Over time, this can lead to chronic kidney damage and failure.
7. Pancreatitis
Extremely high levels of triglycerides (a type of blood fat) can trigger inflammation of the pancreas, known as acute pancreatitis. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
How to Prevent Complications of High Cholesterol
- Healthy Diet – Reduce intake of fried foods, processed snacks, and trans fats. Eat more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Regular Exercise – At least 30 minutes of physical activity daily improves cholesterol balance.
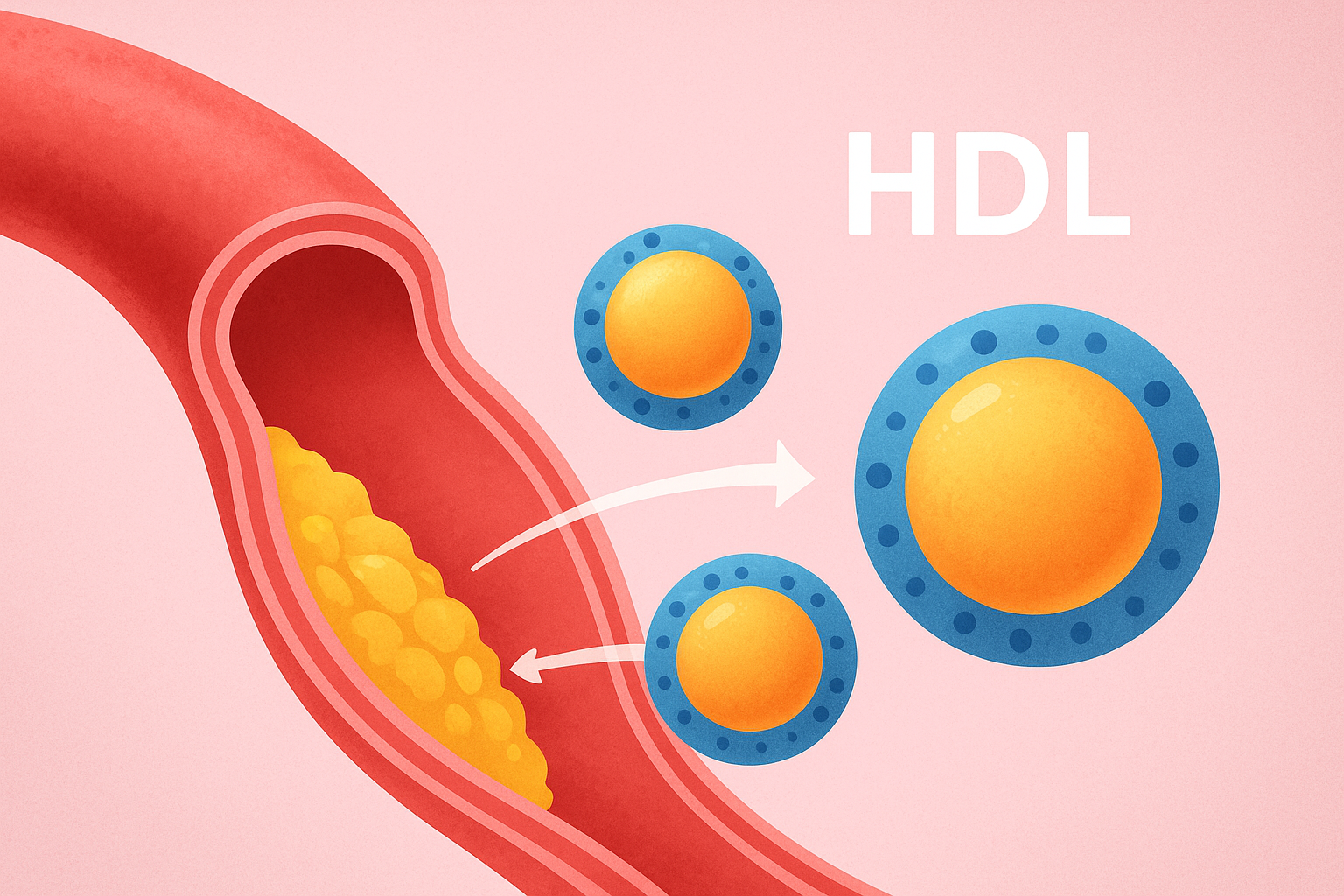
- Weight Management – Maintain a healthy weight to lower LDL (bad cholesterol) and increase HDL (good cholesterol).
- Quit Smoking – Smoking lowers HDL and accelerates artery damage.
- Limit Alcohol – Excess alcohol raises triglycerides and cholesterol levels.
- Routine Screening – Regular blood tests help monitor cholesterol levels and catch problems early.
- Medication (if needed) – Statins or other prescribed drugs can effectively lower cholesterol and prevent complications.
Conclusion
High cholesterol may not show symptoms, but it silently increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, and peripheral artery problems. The good news is that lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and proper treatment can significantly reduce these risks. By managing cholesterol levels effectively, you can protect your heart, brain, and overall health for years to come.