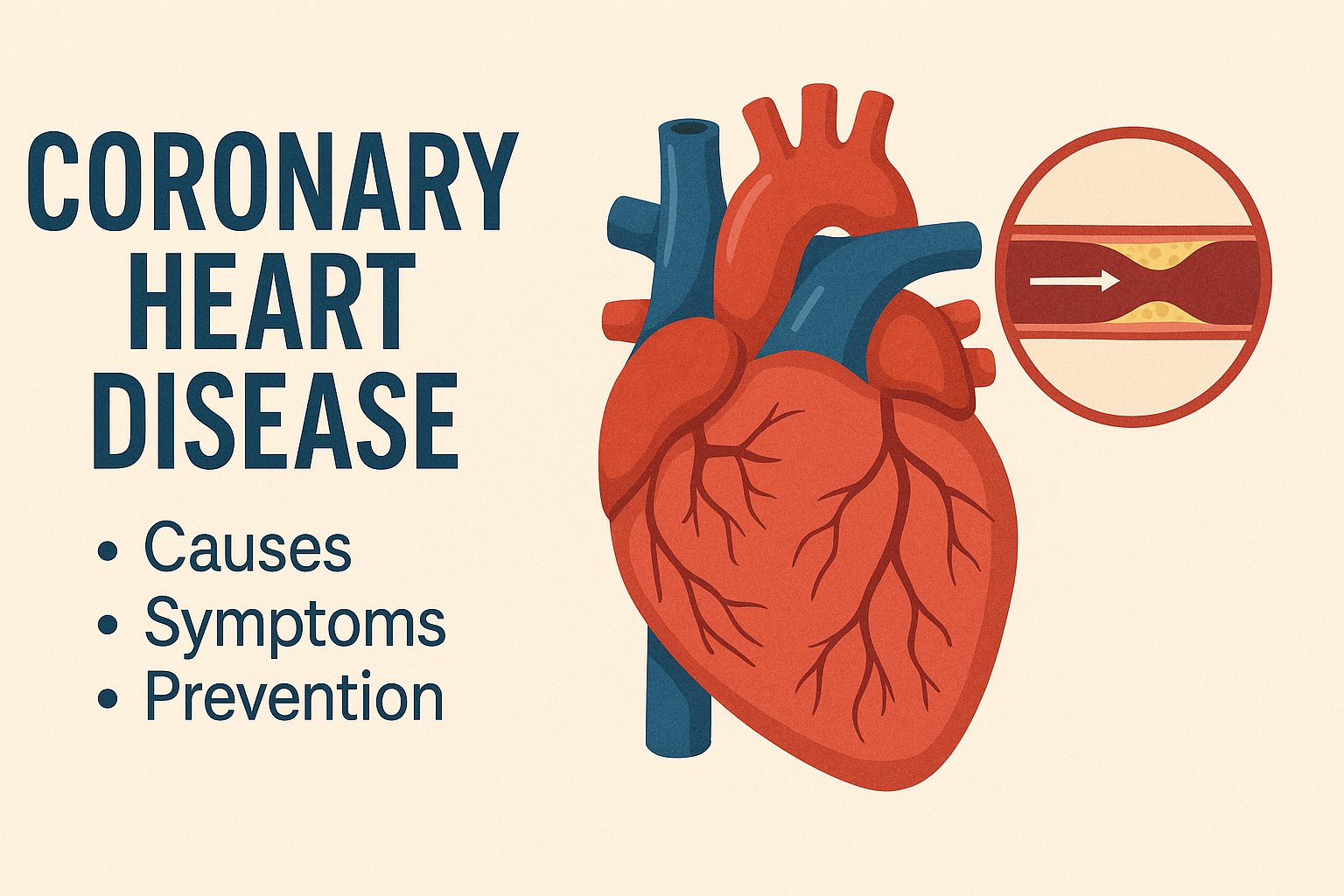
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) — also known as Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) — is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. As heart health becomes an increasingly urgent topic, understanding CHD is critical for prevention and effective management. In this blog, we will explore everything you need to know about coronary heart disease: its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and strategies for prevention.
What is Coronary Heart Disease?
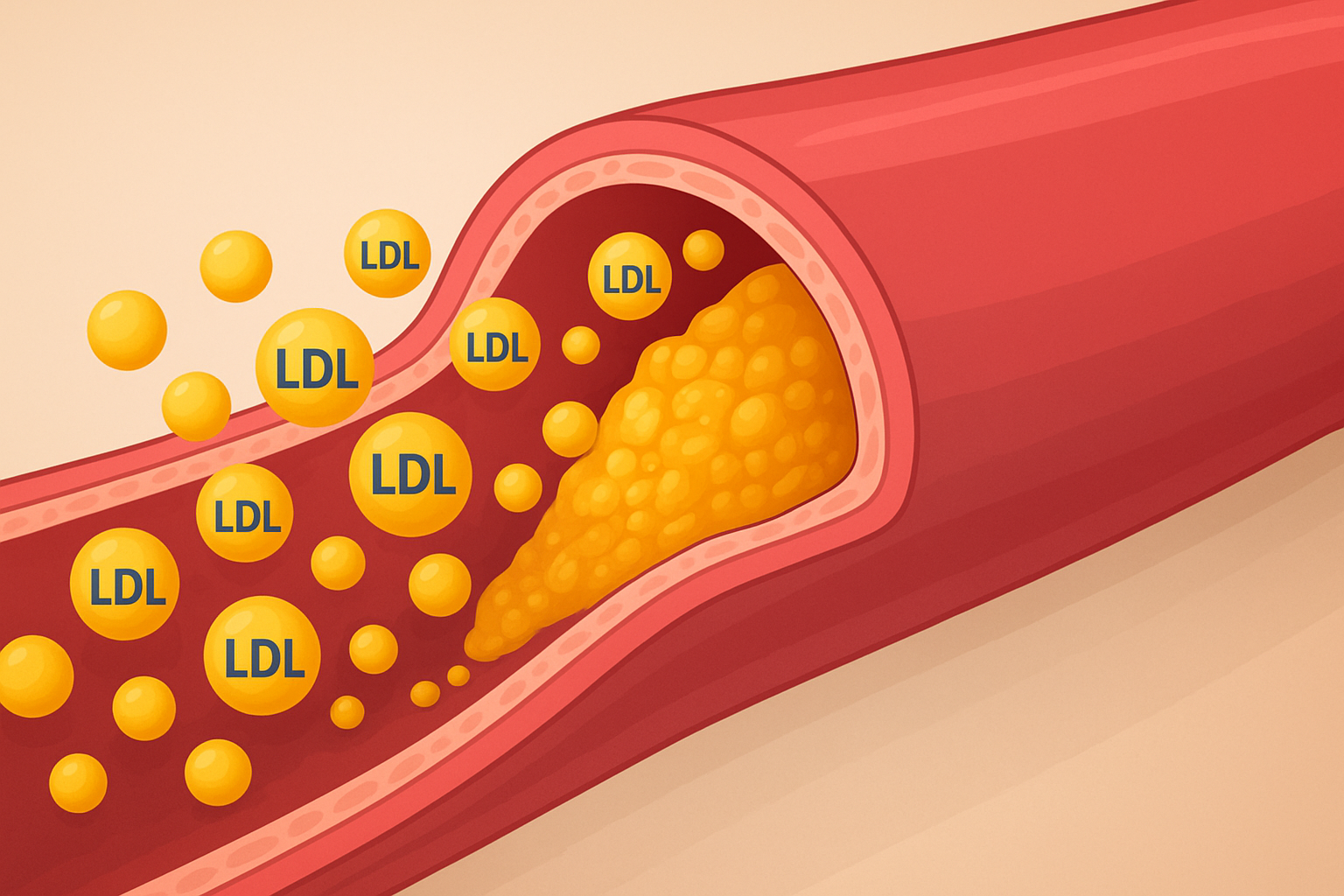
Coronary heart disease occurs when the major blood vessels supplying the heart — the coronary arteries — become damaged or diseased, usually due to the buildup of cholesterol-containing deposits (plaque). Over time, these plaques narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. This can lead to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even a heart attack if the artery becomes completely blocked.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early diagnosis of CHD can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical advice early can lead to better outcomes and an improved quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of coronary heart disease. These include:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Diabetes and insulin resistance
- Sedentary lifestyle
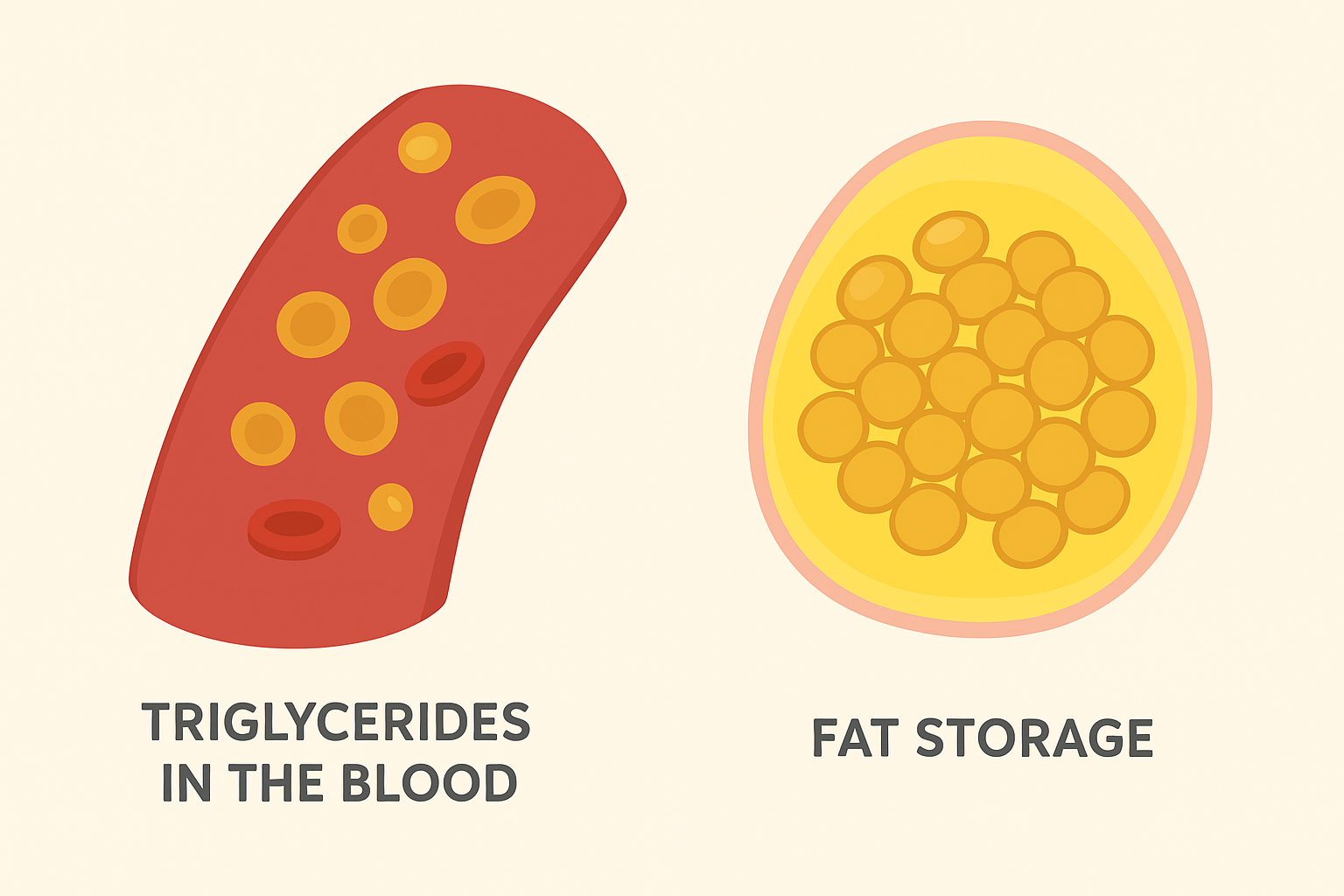
- Unhealthy diet rich in saturated fats and sugars
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Genetic predisposition
Each of these factors can damage the coronary arteries or contribute to plaque buildup, leading to reduced blood flow and increased risk of heart attacks.
Common Symptoms of Coronary Heart Disease
CHD can develop silently over decades. Some individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms until the disease has significantly progressed. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue, especially during exertion
- Pain in the neck, jaw, throat, upper abdomen, or back
- Heart palpitations
- Nausea or dizziness
In some cases, the first sign of CHD can be a heart attack. This is why regular medical checkups and attention to subtle symptoms are vital.
How is Coronary Heart Disease Diagnosed?
Doctors may use a variety of diagnostic tests to identify CHD, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
- Stress testing
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac catheterization and angiogram
- CT coronary angiography
These tests help assess the extent of artery blockage and the overall functioning of the heart.
Effective Prevention and Management Strategies
The good news is that coronary heart disease is often preventable. Here are some effective steps you can take:
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
- Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats (like those from nuts and olive oil).
- Limit the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugars.
2. Stay Physically Active
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight can significantly reduce the risk of CHD.
4. Quit Smoking
- Smoking cessation greatly improves heart health and lowers the risk of future cardiovascular events.
5. Manage Stress
- Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises.
6. Monitor and Control Health Conditions
- Keep blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels within the recommended ranges.
Treatment Options
When CHD is diagnosed, several treatment options are available:
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, quitting smoking)
- Medications to control cholesterol, blood pressure, or blood clots
- Surgical interventions such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the patient’s overall health.
Final Thoughts
Coronary heart disease remains a major public health issue, but with awareness, early diagnosis, and proactive lifestyle choices, it is possible to reduce the risk dramatically. Taking steps toward a healthier heart today can ensure a longer, more vibrant life tomorrow.
If you experience any symptoms or have risk factors for CHD, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for assessment and guidance.