When it comes to cholesterol, many people immediately think of heart disease and blocked arteries. But not all cholesterol is harmful. In fact, HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) cholesterol is often called the “good cholesterol” because of its protective role in cardiovascular health. Understanding HDL, its functions, and ways to maintain healthy levels can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall well-being.
What is HDL Cholesterol?
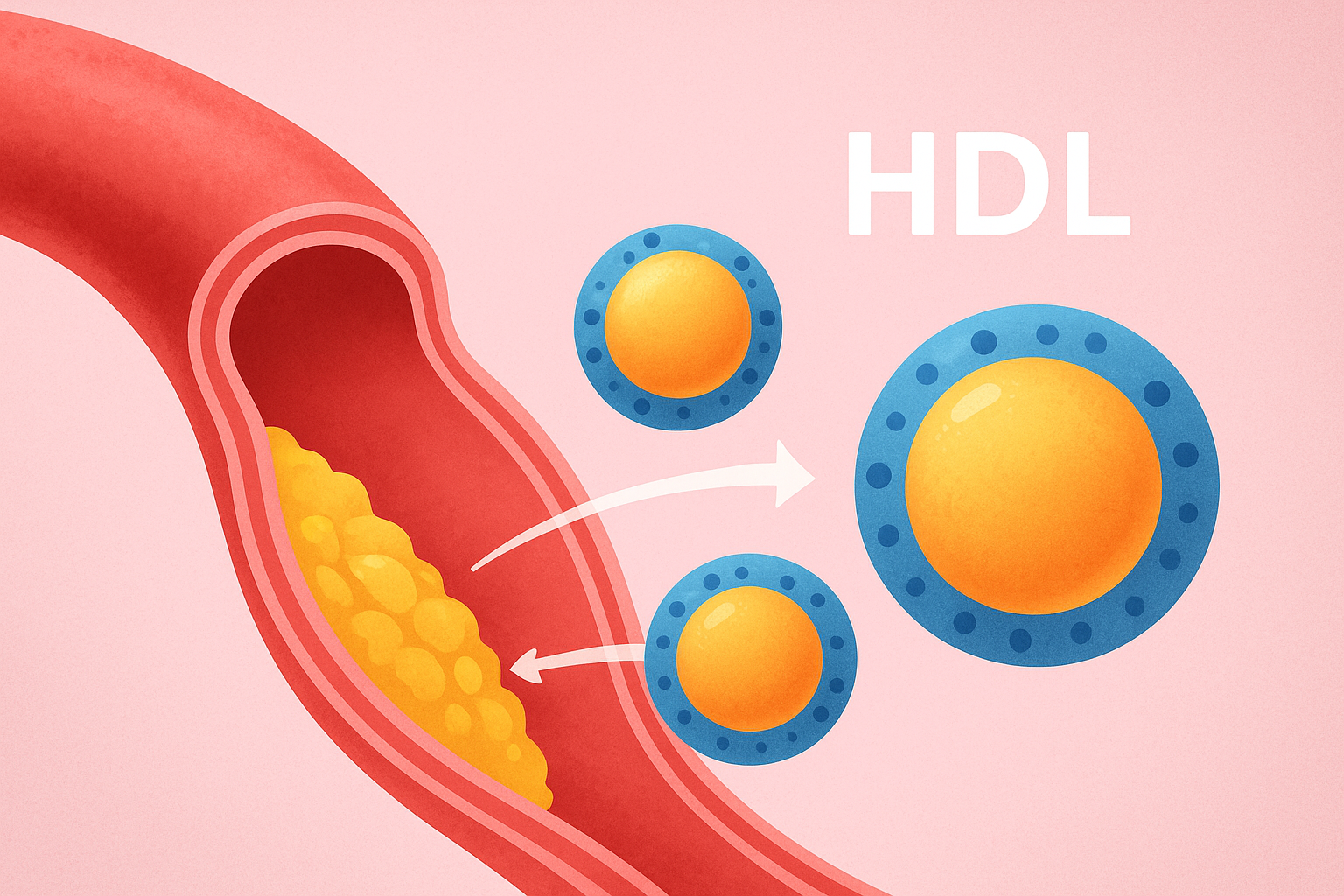
HDL stands for High-Density Lipoprotein, a type of lipoprotein that carries cholesterol through the bloodstream. Unlike LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein), which deposits cholesterol in the arteries, HDL works like a cleanup system. It transports excess cholesterol from the blood and arterial walls back to the liver for processing and elimination.
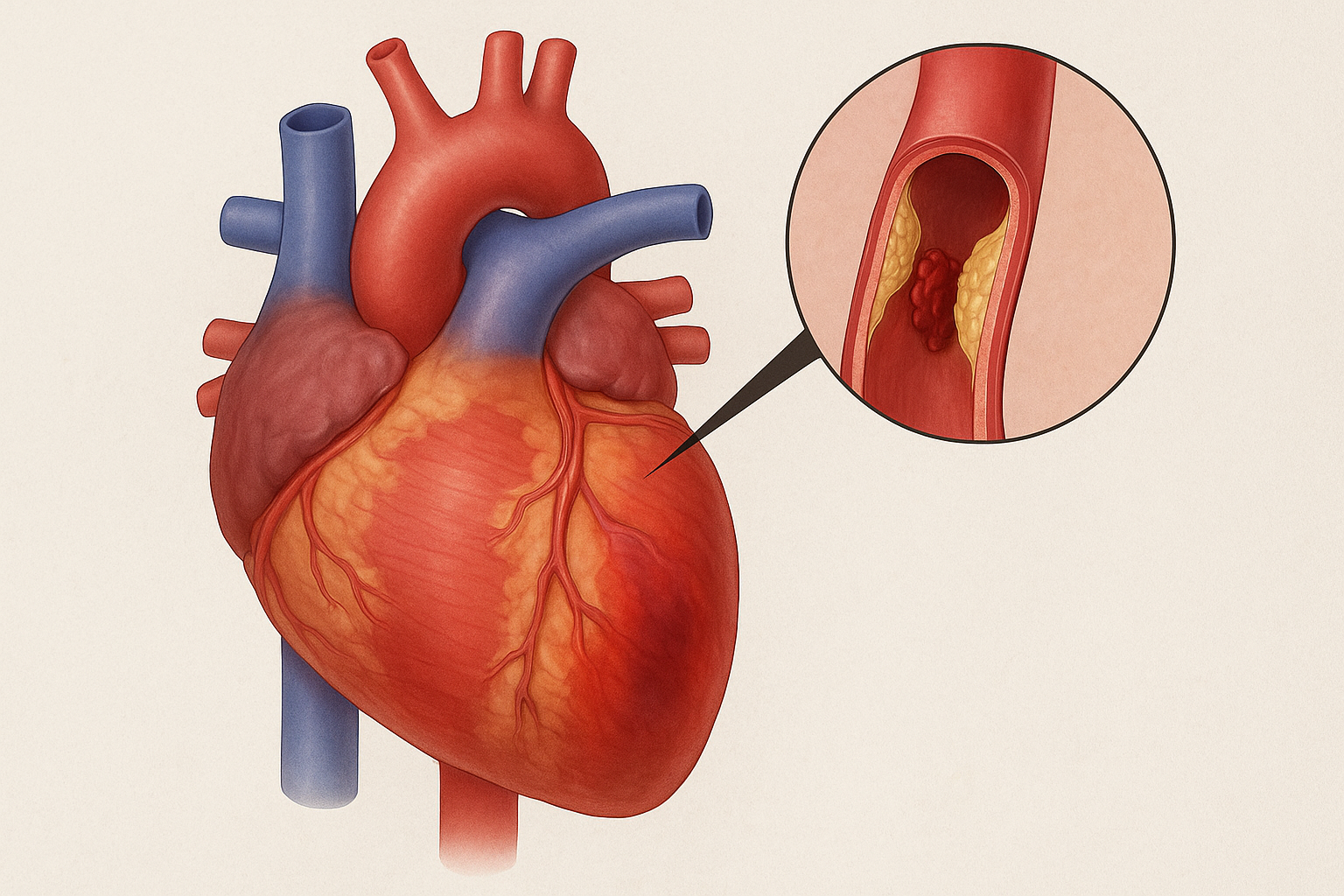
This unique function of HDL makes it a key player in preventing atherosclerosis, a condition where cholesterol plaques build up in arteries, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Normal HDL Levels
Maintaining healthy HDL levels is crucial for cardiovascular protection. According to international guidelines, including the American Heart Association (AHA) and World Health Organization (WHO):
- Men: HDL should be 40 mg/dL or higher
- Women: HDL should be 50 mg/dL or higher
- Above 60 mg/dL: Considered protective against heart disease
- Below recommended levels: Increases the risk of cardiovascular problems
Functions of HDL in the Body
- Reverse Cholesterol Transport – HDL removes excess cholesterol from arteries and tissues and transports it back to the liver.
- Anti-inflammatory Role – HDL reduces inflammation in the blood vessels, protecting against endothelial damage.
- Antioxidant Properties – HDL helps prevent oxidation of LDL cholesterol, which otherwise promotes plaque formation.
- Endothelial Protection – It supports healthy blood vessel function and improves circulation.
Causes of Low HDL Cholesterol
Several factors may contribute to low HDL levels, including:
- Unhealthy lifestyle habits (smoking, poor diet, lack of physical activity)
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Type 2 diabetes
- Certain medications such as beta-blockers, anabolic steroids, and progestins
- Genetic factors affecting lipid metabolism
Health Risks Associated with Low HDL
Low HDL is linked to:
- Increased risk of coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Greater chance of heart attacks and strokes
- Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance
- Accelerated progression of atherosclerosis
In other words, even if LDL cholesterol is normal, low HDL can still be dangerous.
How to Increase HDL Naturally
The good news is that lifestyle changes can significantly boost HDL cholesterol levels:
- Exercise Regularly
- Aerobic activities like walking, running, cycling, and swimming improve HDL.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week.
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
- Increase intake of omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, walnuts, flaxseeds).
- Include monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (olive oil, avocados, nuts).
- Reduce trans fats and refined carbs.
- Quit Smoking
- Smoking lowers HDL; quitting can quickly improve levels.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Even modest weight loss improves HDL and overall lipid balance.
- Limit Alcohol Intake
- Moderate alcohol consumption (e.g., a glass of red wine) may increase HDL, but excess drinking is harmful.
- Medication (if necessary)
- In some cases, doctors prescribe statins, niacin, or fibrates to manage cholesterol balance.
Key Takeaways
- HDL cholesterol is protective and helps prevent heart disease by removing excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
- Low HDL increases cardiovascular risk, even if LDL levels are normal.
- Lifestyle choices such as exercise, healthy eating, and avoiding smoking play a major role in maintaining good HDL levels.
- Regular lipid profile testing is essential for early detection and management of cholesterol imbalance.
Conclusion
HDL is rightfully called the “good cholesterol” because of its role in protecting the heart and blood vessels. By understanding its importance and adopting heart-healthy habits, individuals can improve their HDL levels, reduce cardiovascular risk, and enjoy a healthier life.
If you want to protect your heart, remember: raising HDL is just as important as lowering LDL.