Varicose veins are a common vascular condition that affects millions of people worldwide, especially women. These twisted, enlarged veins are most often seen in the legs and feet and can cause discomfort, pain, and cosmetic concerns. In this blog, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for varicose veins.
What Are Varicose Veins?
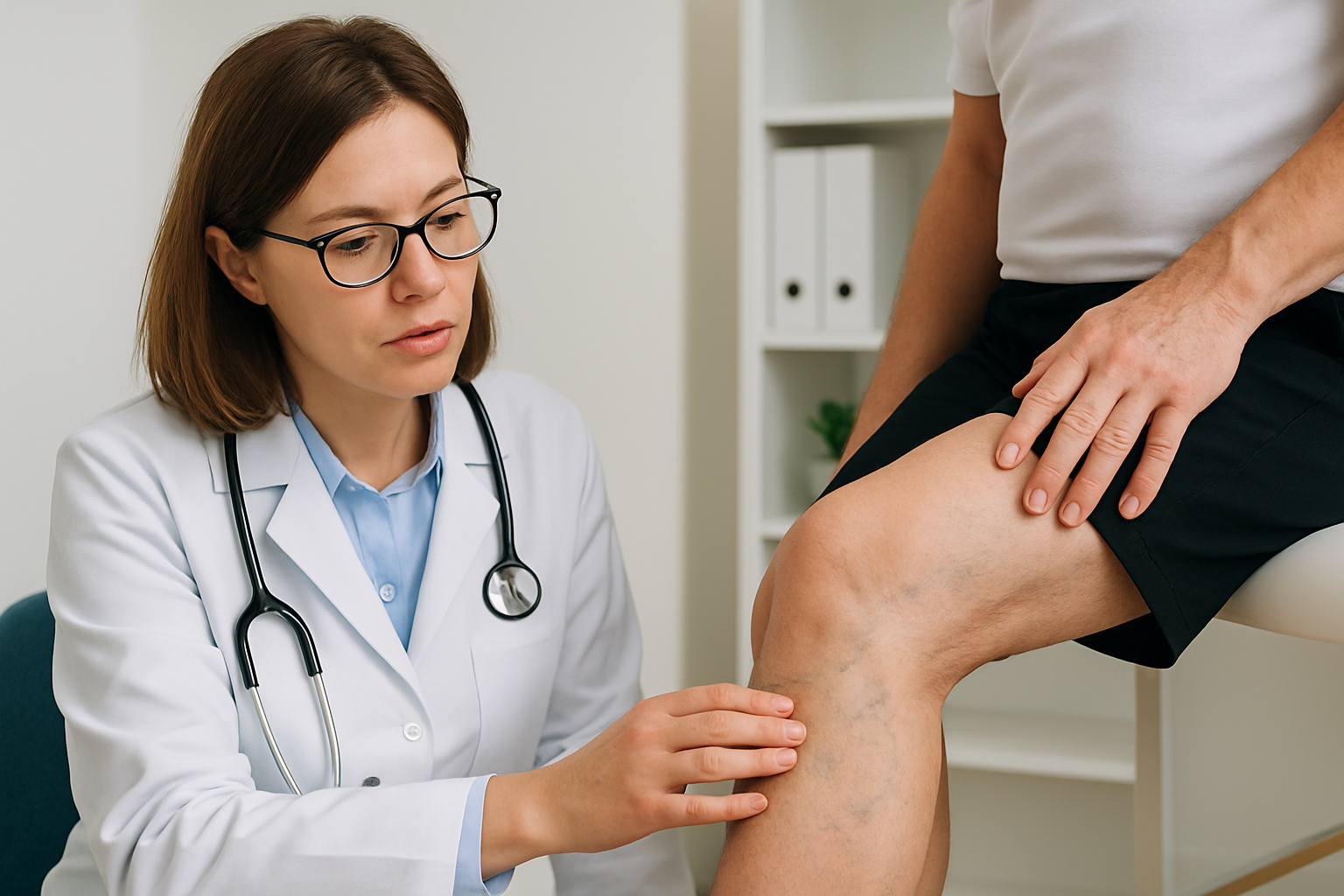
Varicose veins are swollen, bulging veins that appear just under the surface of the skin. They typically develop in the legs due to increased pressure in the veins when standing or walking. These veins appear blue or dark purple and often look twisted or rope-like.
Common Causes of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins occur when the valves in the veins weaken or become damaged, causing blood to pool instead of flowing back to the heart. The most common causes include:
- Genetics – A family history increases the risk.
- Age – Aging causes wear and tear on vein valves.
- Gender – Women are more prone due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause.
- Obesity – Excess weight puts added pressure on the veins.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting – This reduces blood circulation.
- Pregnancy – Increased blood volume and pressure on leg veins.
Signs and Symptoms
Some people with varicose veins may experience no symptoms, while others may have:
- Visible twisted or bulging veins
- Aching, heavy, or uncomfortable legs
- Burning, throbbing, or cramping sensations
- Swelling in the lower legs or ankles
- Itchy skin over the affected vein
- Skin discoloration or ulcers in severe cases
Who Is at Risk?
People who are more likely to develop varicose veins include:
- Women
- Older adults
- People with a family history
- Pregnant women
- Individuals who are overweight or obese
- Those who stand or sit for long periods
Complications of Varicose Veins
While varicose veins are often harmless, they can lead to complications if left untreated, such as:
- Chronic venous insufficiency
- Ulcers near the ankles
- Bleeding from burst veins
- Superficial thrombophlebitis (inflammation and clotting in the vein)
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider may perform a physical exam and ask about symptoms. An ultrasound may be recommended to check blood flow and rule out blood clots.
Treatment Options
There are several ways to manage or treat varicose veins:
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise
- Weight management
- Elevating the legs
- Avoiding long periods of standing or sitting
- Wearing compression stockings
2. Medical Procedures
- Sclerotherapy – A chemical is injected to close the vein.
- Laser Therapy – High-intensity light is used to close off veins.
- Radiofrequency or Endovenous Laser Ablation – Minimally invasive techniques using heat to seal veins.
- Vein Stripping and Ligation – Surgical removal of affected veins (rarely needed today).
Can Varicose Veins Be Prevented?
While not all varicose veins are preventable, you can reduce your risk with:
- Regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding high heels and tight clothing
- Taking breaks to move during long sitting/standing
- Elevating your legs whenever possible
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you notice:
- Persistent pain or swelling
- Skin changes or ulcers near the vein
- Bleeding from the veins
- Sudden leg swelling (may indicate a blood clot)
Conclusion
Varicose veins may be a cosmetic concern for some, but for others, they can cause significant discomfort and lead to complications. Fortunately, with early diagnosis and proper treatment, you can manage the symptoms effectively and improve your quality of life. If you’re experiencing symptoms, consult with a vascular specialist to explore the best treatment options for you.