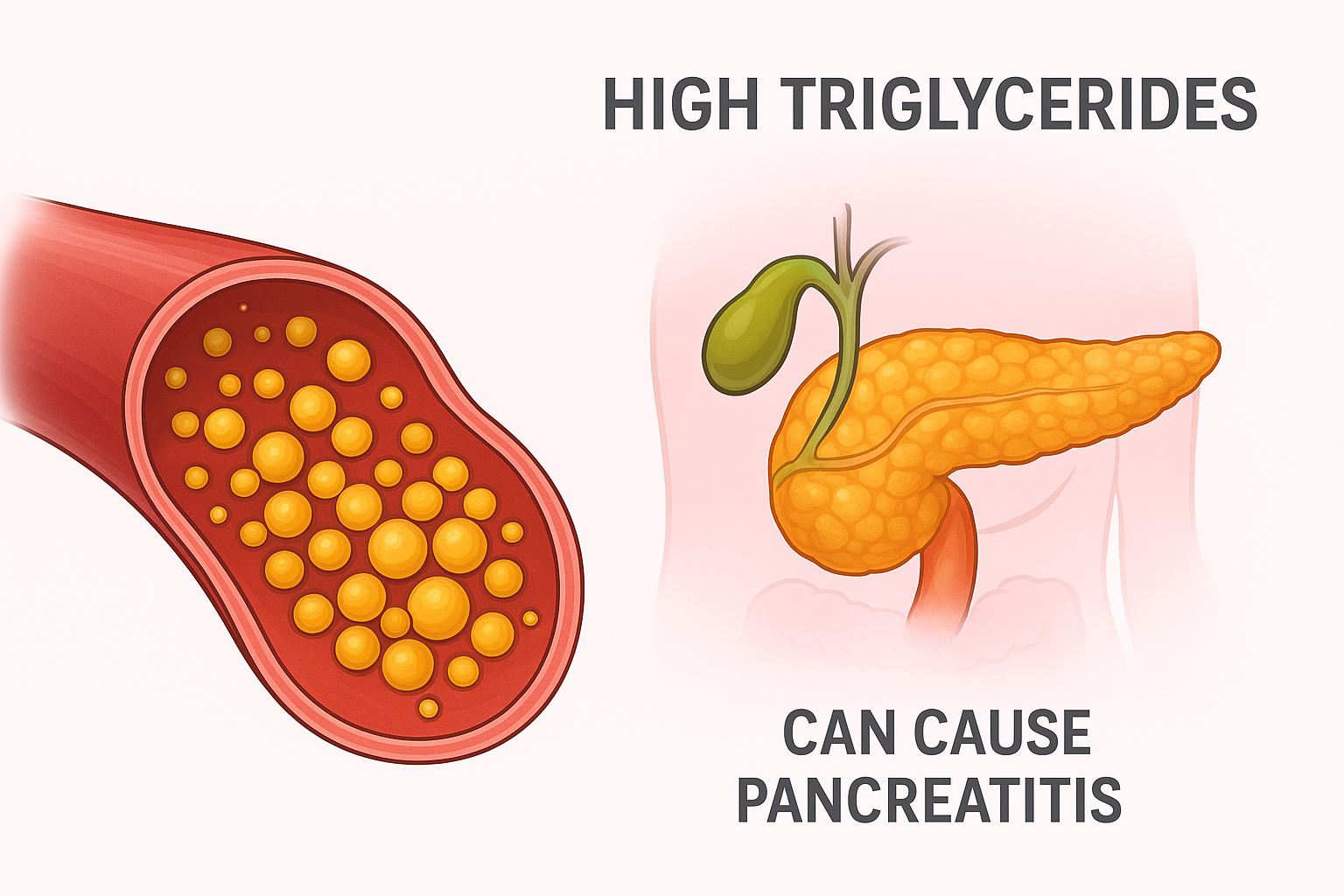
What Is Hypotension?
Hypotension is the medical term for low blood pressure, typically defined as a blood pressure reading below 90/60 mmHg. While it may seem like a good thing to have low blood pressure, when it drops too far, it can cause dizziness, fainting, and in severe cases, shock and organ damage.
📊 Types of Hypotension
1. Orthostatic (Postural) Hypotension
- Occurs when standing up from sitting or lying down
- Common in older adults
2. Postprandial Hypotension
- Drop in blood pressure after meals
- Seen in elderly or those with autonomic nervous system disorders
3. Neurally Mediated Hypotension
- Caused by emotional stress or standing for long periods
- Often affects young people
4. Severe Hypotension / Shock
- Life-threatening drop in blood pressure
- Often due to trauma, severe infection (septic shock), or blood loss
🔍 Common Causes of Hypotension
- Dehydration
- Heart conditions (bradycardia, heart failure)
- Endocrine disorders (adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism)
- Severe infection (sepsis)
- Blood loss or anemia
- Pregnancy
- Certain medications (diuretics, beta-blockers, antidepressants)
- Neurological disorders (Parkinson’s disease)
⚠️ Symptoms of Low Blood Pressure
While mild hypotension might not cause symptoms, moderate to severe cases can lead to:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Blurred vision
- Nausea
- Cold, clammy skin
- Fatigue or weakness
- Fainting (syncope)
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Confusion, especially in older adults
🧪 Diagnosis: How Is Hypotension Identified?
Your doctor may use several tools to diagnose hypotension:
- Blood pressure readings
- Tilt table test (to assess orthostatic hypotension)
- ECG/Echocardiogram (to check for heart issues)
- Blood tests (to rule out anemia, electrolyte imbalance, or hormone disorders)
🩹 Treatment of Hypotension
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and type of hypotension.
🧃 Immediate Remedies
- Drink water – hydrate if dehydration is the cause
- Lie down and elevate your legs – improves blood flow to the brain
- Eat small, frequent meals – prevents postprandial drops
💊 Medical Management
- Adjusting medications that lower blood pressure
- Fludrocortisone or midodrine may be prescribed in chronic cases
- Treating root causes like hormonal or cardiac problems
🍽️ Dietary Suggestions
- Increase salt intake (under doctor’s supervision)
- Drink more fluids
- Avoid alcohol
- Have caffeine in moderation
🧘 Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoid standing for long periods
- Stand slowly from sitting or lying positions
- Wear compression stockings to reduce pooling of blood in legs
🛡️ Prevention Tips
- Stay well-hydrated, especially during hot weather or exercise
- Avoid prolonged standing
- Monitor your blood pressure regularly
- Follow up with your doctor if symptoms persist
- Avoid sudden changes in posture
🚨 When to Seek Medical Help
Seek urgent medical attention if you experience:
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Confusion or trouble speaking
- Rapid pulse or breathing
- Pale or cold skin
These may indicate shock or serious cardiac conditions requiring immediate care.
✅ Final Thoughts
While hypotension is often less discussed than hypertension, it can be just as dangerous when left untreated. Knowing your blood pressure range and recognizing early symptoms can help prevent complications. With the right lifestyle changes and medical support, hypotension is manageable and often reversible.
🔗 Learn more about blood pressure health and related topics at medscapeus.com — your trusted source for reliable, physician-reviewed content.