Sleep is not just a period of rest — it’s a biological necessity. It plays a crucial role in supporting the brain, heart, metabolism, immune system, and overall well-being. Yet, in today’s fast-paced world, sleep is often sacrificed, especially among teens and adults.
In this comprehensive blog, we’ll cover:
- Recommended sleep duration by age
- Scientific benefits of normal, adequate sleep
- Dangers and disadvantages of decreased sleep
- Simple tips to improve sleep hygiene
Whether you’re a parent trying to regulate your child’s sleep or an adult struggling with your own, this guide is for you.
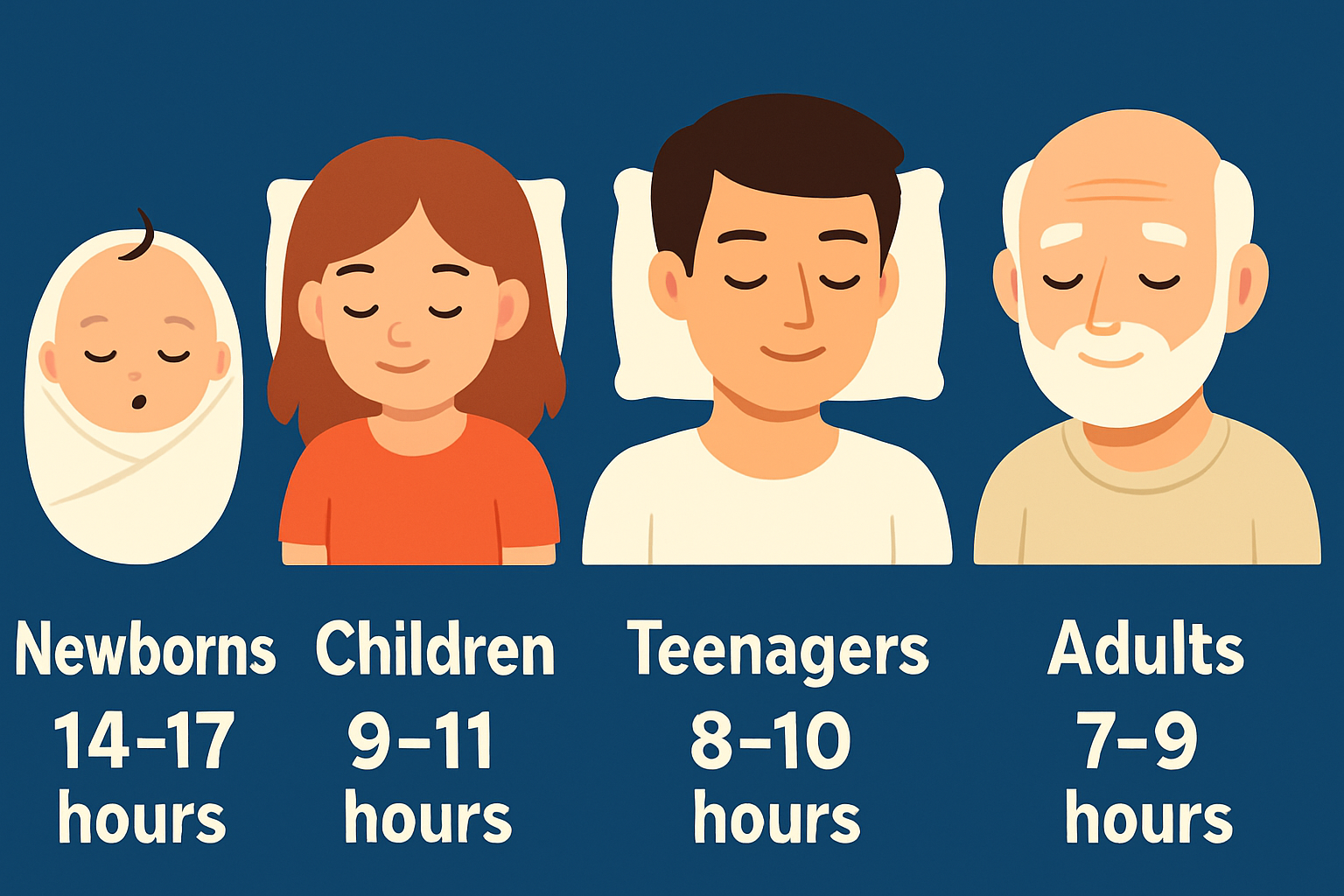
⏳ Sleep Duration According to Age
Sleep requirements vary depending on your stage of life. Babies need the most sleep due to rapid growth and brain development, while adults need consistent, quality rest to maintain mental and physical health.
| Age Group | Recommended Sleep Duration (per 24 hours) |
|---|---|
| Newborns (0–3 months) | 14–17 hours |
| Infants (4–11 months) | 12–15 hours |
| Toddlers (1–2 years) | 11–14 hours |
| Preschoolers (3–5 years) | 10–13 hours |
| Children (6–13 years) | 9–11 hours |
| Teenagers (14–17 years) | 8–10 hours |
| Young Adults (18–25 years) | 7–9 hours |
| Adults (26–64 years) | 7–9 hours |
| Older Adults (65+ years) | 7–8 hours |
📌 Note: While these are average recommendations, some people may function optimally with slightly more or less sleep.
✅ Benefits of Normal Sleep
Sleep is not just for energy — it has a profound impact on every organ system. Let’s dive into the science-backed benefits of getting adequate, high-quality sleep:
🧠 1. Improved Brain Function & Mental Clarity
- Enhances memory consolidation and learning.
- Boosts attention span, problem-solving skills, and creativity.
- Helps detoxify the brain, removing harmful waste like beta-amyloid (linked to Alzheimer’s).
🧬 2. Supports Physical Growth & Cellular Repair
- Growth hormone is primarily secreted during deep sleep (especially in children and teens).
- Cellular repair and muscle regeneration occur during sleep.
- Critical for athletes, gym-goers, and healing after injury or surgery.
💓 3. Heart and Metabolic Health
- Sleep regulates blood pressure and heart rate.
- Reduces inflammation in the cardiovascular system.
- Helps control blood sugar and improves insulin sensitivity — key for diabetes management.
🛡️ 4. Strengthens the Immune System
- Sleep boosts production of infection-fighting cytokines.
- People who sleep well are more resistant to common illnesses like flu and colds.
- Sleep also enhances vaccine effectiveness.
😌 5. Emotional Balance and Mental Health
- Reduces symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Improves mood and emotional control.
- Protects against stress-related disorders and burnout.
⚖️ 6. Weight Management
- Regulates hunger hormones (ghrelin and leptin).
- Poor sleep is linked to cravings for sugary, high-calorie foods.
- Inadequate sleep is a risk factor for obesity in both children and adults.
⚠️ Disadvantages of Decreased or Poor Sleep
Consistent lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation, leads to serious short-term and long-term health consequences.
❌ 1. Cognitive Impairment
- Decreased focus, slower reaction times, and poor decision-making.
- Increased risk of workplace and road accidents.
- Memory loss and confusion can become chronic with continued poor sleep.
💔 2. Higher Risk of Chronic Diseases
- Increases risk of:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Affects hormonal balance, increasing inflammation in the body.
😔 3. Mental Health Decline
- Strong link between insomnia and psychiatric disorders.
- Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety disorders.
- Can trigger or worsen episodes in people with mental health conditions.
🧘 4. Hormonal Imbalance & Reproductive Issues
- Irregular sleep disrupts menstrual cycles and fertility hormones.
- Affects testosterone production in men.
- Can lead to reduced libido and sexual dysfunction.
📉 5. Poor Productivity and Quality of Life
- Lack of motivation and energy.
- Reduced performance at work or school.
- Less interest in social and physical activities.
🛏️ Tips to Improve Sleep Hygiene
If you’re struggling with poor sleep, try incorporating these healthy sleep habits into your routine:
- Stick to a schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day — even on weekends.
- Create a calming bedtime routine: Reading, meditation, or soft music can help your body wind down.
- Avoid stimulants: Limit caffeine and nicotine, especially in the evening.
- Limit screen time: Avoid phones, TVs, and computers at least 1 hour before bedtime.
- Make your bedroom sleep-friendly:
- Cool temperature
- Dark curtains
- Noise-free or use white noise
- Avoid heavy meals late at night: They can cause indigestion and disturb sleep.
- Exercise regularly: But not too close to bedtime — aim for at least 4–5 hours earlier.
🧾 Conclusion
Sleep is one of the most powerful natural healing tools we have. From childhood to old age, the right amount of sleep keeps your mind sharp, your body strong, and your mood stable. Yet, millions of people overlook its value.
By understanding how much sleep is needed at each age, and recognizing the benefits and risks tied to sleep patterns, you can make informed decisions to live a healthier life.
So tonight, prioritize your rest — not just for tomorrow, but for your lifelong well-being.