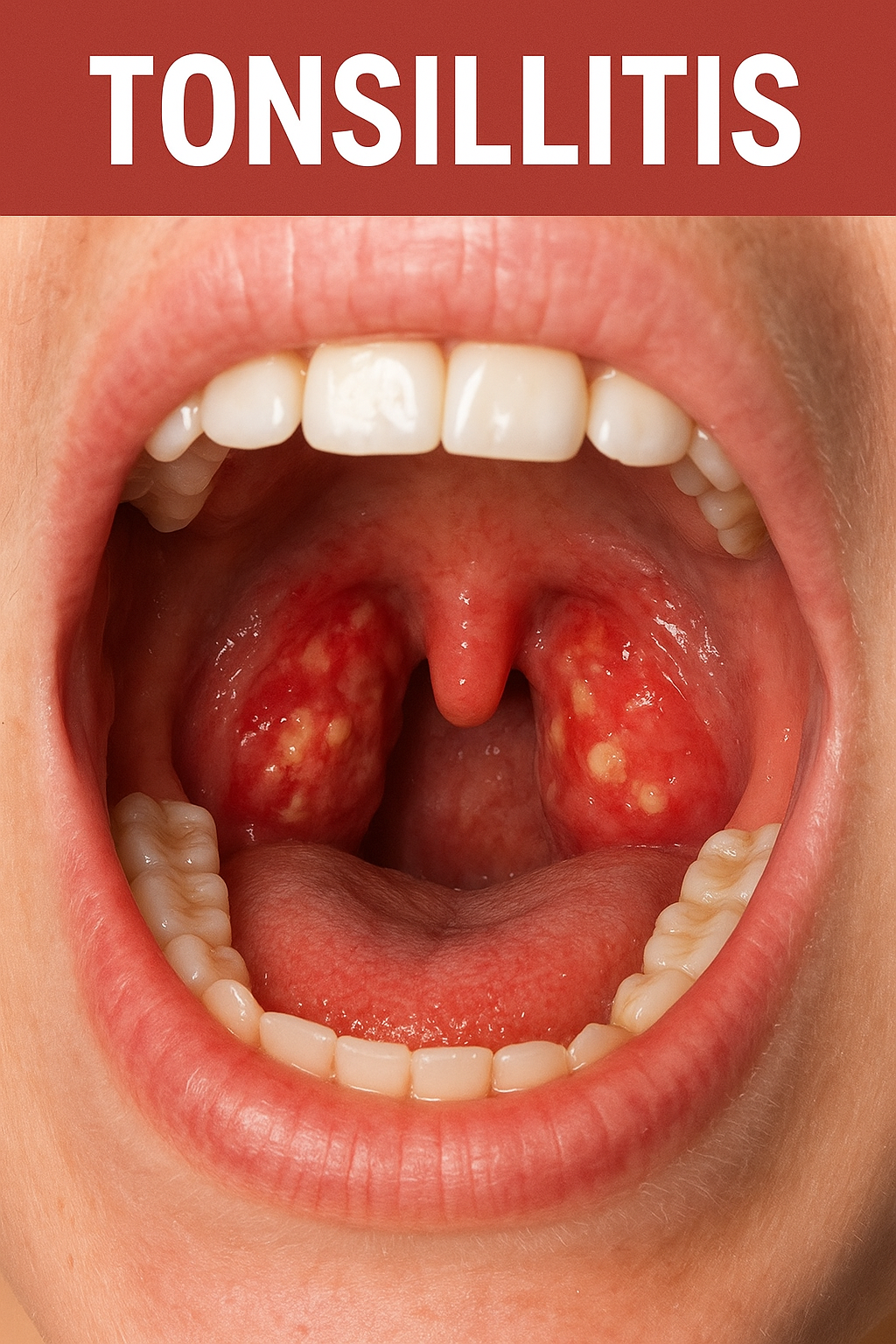
Tonsillitis is a common condition that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by the inflammation of the tonsils — two oval-shaped glands located at the back of the throat. Tonsils play an important role in fighting infections, but when they themselves become infected, they can cause throat pain, fever, and difficulty swallowing.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tonsillitis.
What is Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis refers to the infection and swelling of the tonsils. It may be acute (short-term), recurrent (repeated episodes), or chronic (long-lasting). While it can occur at any age, children are more prone due to their developing immune systems.
Causes of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis can result from viral or bacterial infections. The most common causes include:
- Viral Infections
- Adenovirus
- Influenza virus
- Epstein-Barr virus (causes mononucleosis)
- Rhinovirus (common cold virus)
- Bacterial Infections
- Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus) — the main cause of strep throat.
- Other less common bacteria can also cause tonsil infections.
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the cause, but common signs include:
- Sore throat
- Red, swollen tonsils
- White or yellow patches on tonsils (pus)
- Pain or difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness or muffled voice
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Fever and chills
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Headache and ear pain
Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
A doctor may diagnose tonsillitis through:
- Physical examination: Checking the throat, tonsils, and lymph nodes.
- Throat swab: To confirm if Streptococcus bacteria are present.
- Blood tests: In cases where mononucleosis or other viral infections are suspected.
Treatment of Tonsillitis
The treatment approach depends on whether the infection is viral or bacterial.
- Viral Tonsillitis
- Most cases resolve on their own.
- Supportive care includes:
- Rest and hydration
- Warm saltwater gargles
- Lozenges and warm fluids
- Pain relievers (acetaminophen or ibuprofen)
- Bacterial Tonsillitis (Strep Throat)
- Antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the infection.
- It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics to prevent complications.
- Chronic or Recurrent Tonsillitis
- If infections are frequent or severe, a doctor may recommend tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils).
Complications of Tonsillitis
If left untreated, especially in bacterial cases, tonsillitis can lead to complications such as:
- Peritonsillar abscess (pus around the tonsil)
- Rheumatic fever (affecting the heart and joints)
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (kidney inflammation)
Prevention of Tonsillitis
- Wash hands frequently to prevent infections.
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- Do not share utensils, cups, or towels.
- Strengthen the immune system with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Practice good oral hygiene.
Conclusion
Tonsillitis is a common throat infection that can be caused by both viruses and bacteria. While mild cases usually resolve with home care, bacterial infections require antibiotic treatment to prevent complications. Recurrent or chronic tonsillitis may need surgical intervention.
By practicing good hygiene and maintaining a strong immune system, the risk of tonsillitis can be reduced significantly.