Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide, but the good news is that it is highly preventable and treatable when detected early. This article aims to raise awareness about cervical cancer, its risk factors, symptoms, and prevention methods. Understanding this condition can save lives and promote women’s health.
What is Cervical Cancer?
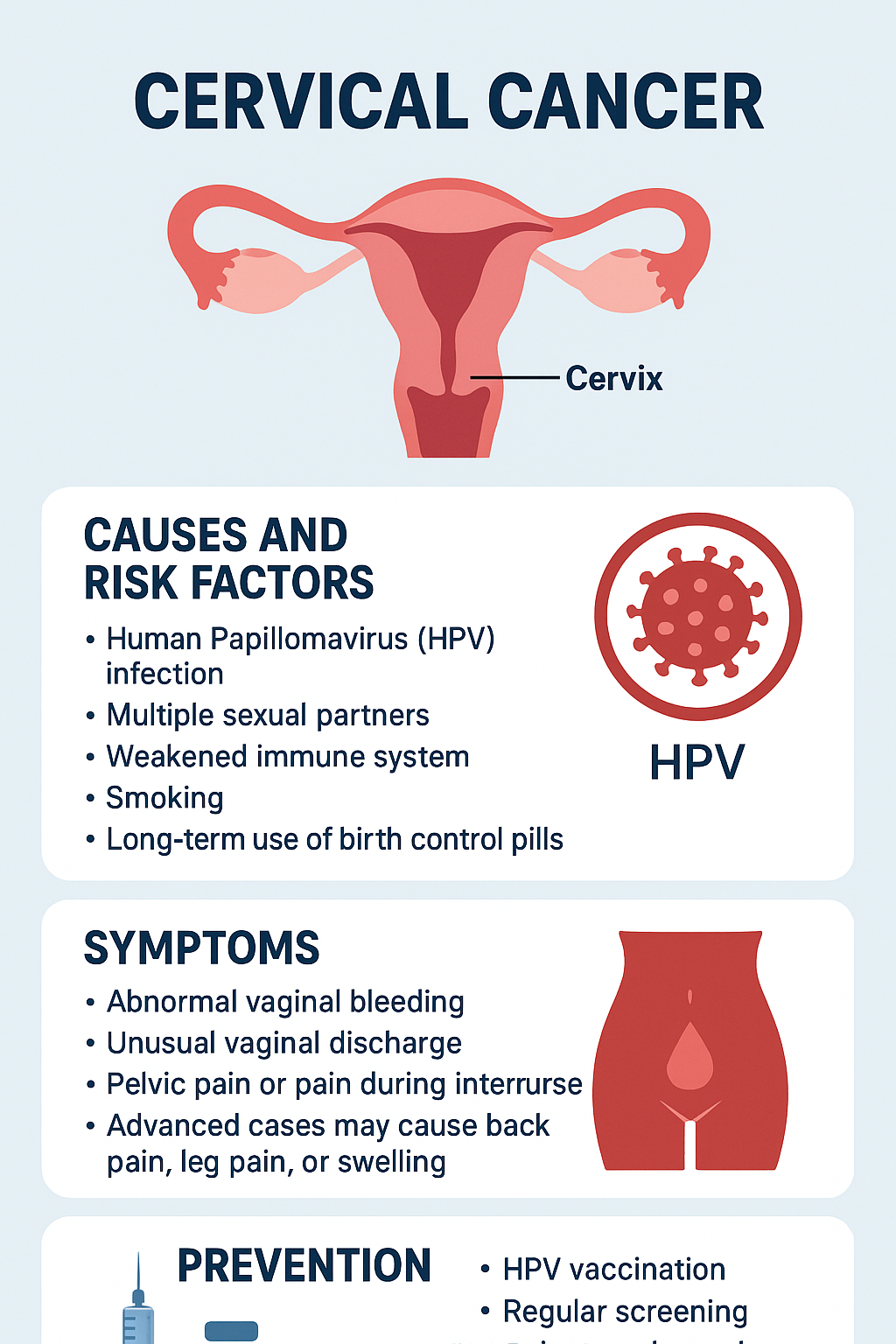
Cervical cancer develops in the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Most cases are caused by persistent infection with high-risk types of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection.
Causes and Risk Factors of Cervical Cancer
Several factors increase the risk of developing cervical cancer:
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection – the primary cause.
- Multiple sexual partners – increases exposure to HPV.
- Weakened immune system – due to conditions like HIV/AIDS.
- Smoking – linked to higher risk.
- Long-term use of birth control pills (more than 5 years).
- Family history of cervical cancer.
Common Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
In the early stages, cervical cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as it progresses, women may experience:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding (after intercourse, between periods, or after menopause).
- Unusual vaginal discharge (watery, bloody, or foul-smelling).
- Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse.
- Advanced cases may cause back pain, leg pain, or swelling.
If you notice these symptoms, consult a gynecologist immediately.
How is Cervical Cancer Diagnosed?
Early detection saves lives. The following tests are commonly used:
- Pap smear test (Pap test): Detects precancerous changes in the cervix.
- HPV DNA test: Identifies high-risk HPV strains.
- Colposcopy and biopsy: To confirm abnormal findings.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is largely preventable with the right measures:
- HPV Vaccination – Safe and effective in preventing HPV infection. Recommended for girls and boys from ages 9–14.
- Regular screening – Pap smears and HPV testing should be part of routine women’s health checkups.
- Safe sexual practices – Using condoms and limiting multiple partners reduces HPV risk.
- Quit smoking – Helps lower the risk of many cancers.
Treatment Options for Cervical Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage of the disease:
- Early stages: Surgery (hysterectomy or removal of abnormal cells).
- Advanced stages: Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy.
- Palliative care: For late-stage disease to improve quality of life.
Why Awareness Matters
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide, but with early detection and vaccination, thousands of lives can be saved each year. Raising awareness, promoting regular checkups, and encouraging HPV vaccination are key steps in fighting this disease.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is preventable, treatable, and curable if detected early. Women are encouraged to undergo regular Pap smears, get vaccinated against HPV, and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Awareness and education are powerful tools to reduce the burden of cervical cancer globally.