High LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” is one of the most common health issues worldwide. It plays a significant role in the development of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Understanding LDL cholesterol, its causes, and ways to manage it can help you protect your heart health and overall well-being.
What is LDL Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in your blood. It is essential for building cells, producing hormones, and aiding digestion. However, it travels through your bloodstream in particles called lipoproteins.
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Carries cholesterol to the arteries. High levels can lead to plaque buildup inside artery walls, causing them to narrow and harden (atherosclerosis).
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Known as “good cholesterol,” it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
When LDL levels become too high, the risk of cardiovascular disease increases.
Causes of High LDL Cholesterol
Several factors can contribute to elevated LDL cholesterol levels, including:
- Unhealthy Diet
- Eating foods high in saturated fats (red meat, full-fat dairy products) and trans fats (processed snacks, fried foods) can increase LDL cholesterol.
- Lack of Physical Activity
- Sedentary lifestyles lower HDL (good cholesterol) and may raise LDL.
- Genetics (Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
- Inherited conditions can cause high cholesterol even in young, healthy individuals.
- Excess Weight
- Being overweight or obese is linked to higher LDL levels.
- Medical Conditions
- Hypothyroidism, kidney disease, diabetes, and liver diseases can influence cholesterol metabolism.
- Smoking & Alcohol Consumption
- Smoking damages blood vessels, making it easier for LDL to accumulate. Excess alcohol can also increase cholesterol levels.
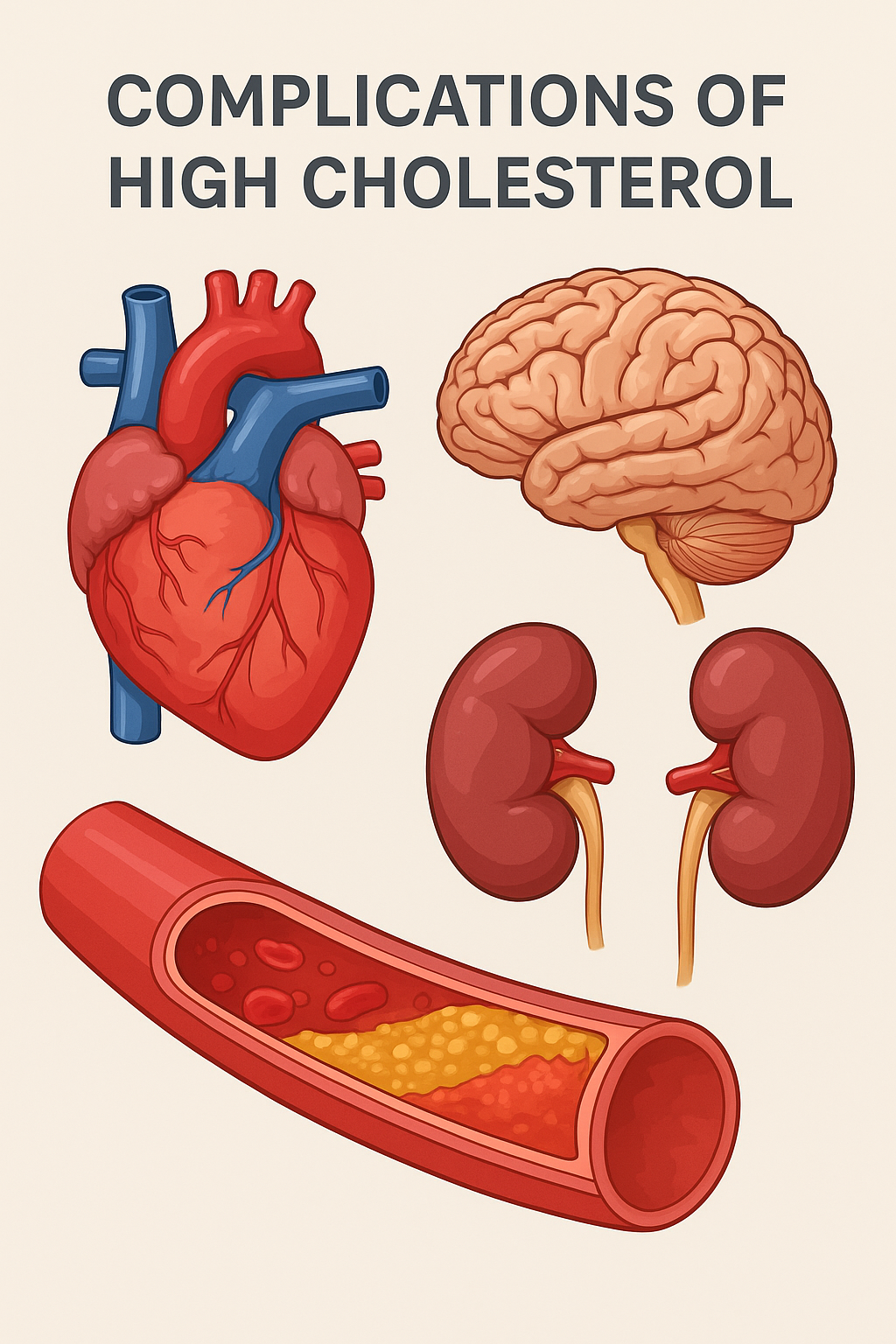
Health Risks of High LDL Cholesterol
High LDL cholesterol may not show immediate symptoms, but it silently damages your arteries over time, increasing the risk of:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Heart Attack
- Stroke
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
- Aneurysms
Diagnosis of High LDL Cholesterol
A lipid profile blood test is used to measure LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides.
LDL Cholesterol Levels (mg/dL):
- Optimal: Less than 100
- Near Optimal: 100–129
- Borderline High: 130–159
- High: 160–189
- Very High: 190 and above
How to Lower High LDL Cholesterol
1. Healthy Diet
- Increase: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, fatty fish (salmon, mackerel).
- Limit: Saturated fats, trans fats, processed foods, sugary drinks.
- Use: Healthy oils like olive oil or canola oil instead of butter or ghee.
2. Regular Exercise
- At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week (walking, cycling, swimming).
- Exercise raises HDL and lowers LDL.
3. Maintain Healthy Weight
- Losing even 5–10% of body weight can improve cholesterol levels.
4. Quit Smoking
- Improves HDL cholesterol and overall cardiovascular health.
5. Limit Alcohol
- Excess alcohol raises cholesterol and triglycerides.
6. Medications
- Statins, ezetimibe, bile acid sequestrants, and PCSK9 inhibitors may be prescribed for severe cases or if lifestyle changes are not enough.
Prevention Tips
- Get your cholesterol checked regularly (every 4–6 years for adults; more frequently if you have risk factors).
- Start heart-healthy habits early in life.
- Manage other health conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
Conclusion
High LDL cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease, but it’s manageable with the right lifestyle changes and, when needed, medications. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy habits can significantly reduce your risk. Early detection through routine blood tests is key to preventing serious complications.
Meta Description (SEO):
Learn about high LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) cholesterol, its causes, health risks, and effective ways to lower it naturally and medically for a healthier heart.