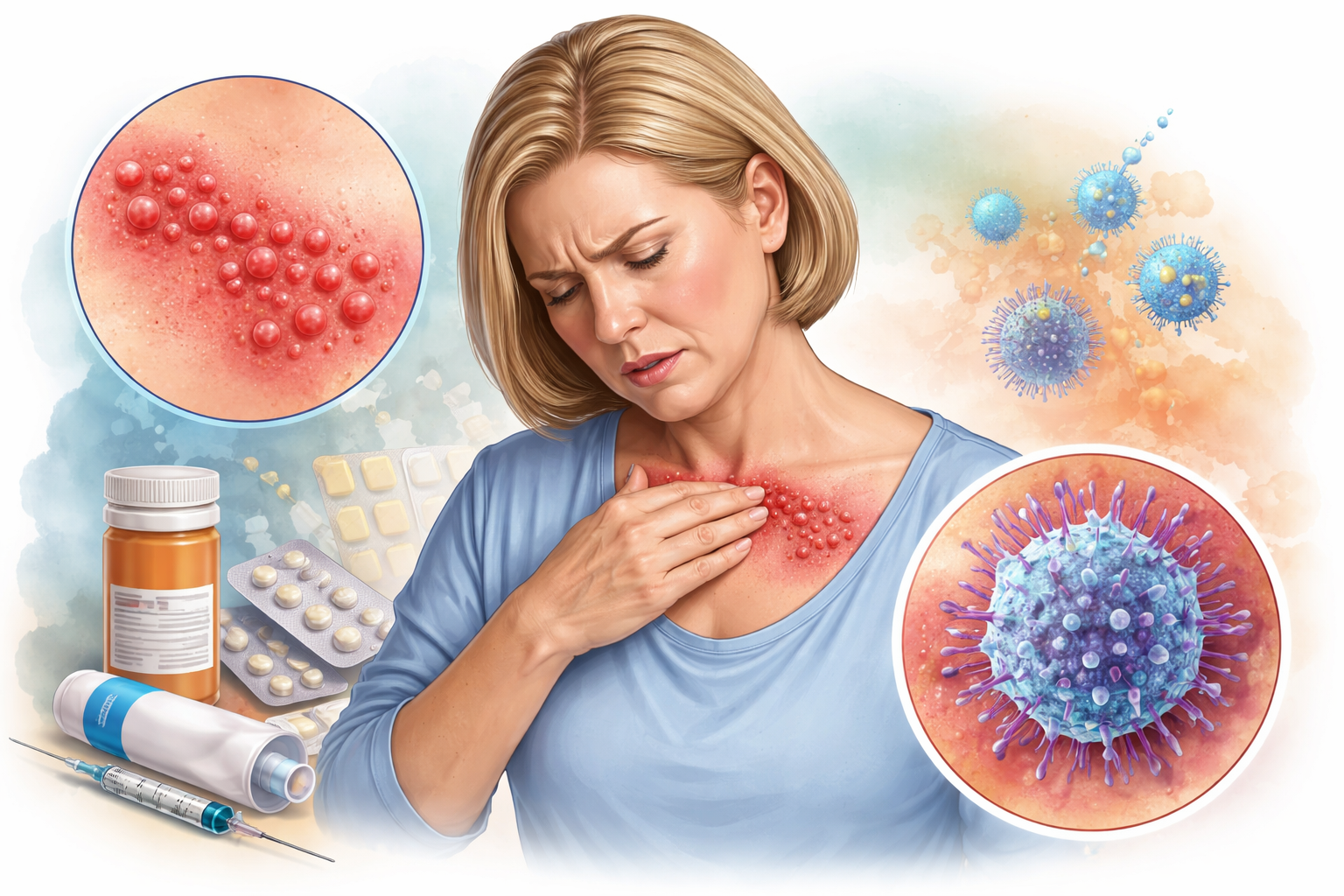
Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles, is a painful viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide, especially older adults and individuals with weak immune systems. It is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox. Understanding herpes zoster, its symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures can help reduce complications and improve quality of life.
What Is Herpes Zoster?
Herpes zoster is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with fluid-filled blisters, usually appearing on one side of the body. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains inactive in nerve tissues and may reactivate years later as shingles.
Causes of Herpes Zoster
The main cause of herpes zoster is the reactivation of dormant varicella-zoster virus. Factors that increase the risk include:
- Aging (especially above 50 years)
- Weak immune system
- Chronic illnesses (diabetes, cancer)
- Stress and fatigue
- Use of immunosuppressive medicines
Signs and Symptoms of Shingles
Symptoms usually develop in stages and may include:
- Burning, tingling, or stabbing pain
- Sensitivity to touch
- Red rash appearing after pain
- Fluid-filled blisters that crust over
- Itching
- Fever and headache
- Fatigue and body weakness
The rash typically follows the path of a nerve and appears on the chest, back, face, or neck.
Complications of Herpes Zoster
If not treated timely, shingles may lead to serious complications such as:
- Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) – long-lasting nerve pain
- Eye infection (herpes zoster ophthalmicus)
- Vision problems
- Skin infections
- Nerve damage
Early diagnosis significantly reduces the risk of complications.
Diagnosis of Herpes Zoster
Doctors usually diagnose herpes zoster based on:
- Clinical examination of the rash
- Patient’s medical history
- Laboratory tests (if needed), such as PCR or viral culture
Treatment Options for Herpes Zoster
Although herpes zoster cannot be cured completely, early treatment helps control symptoms and speed recovery.
Medical Treatment
- Antiviral medicines (acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir)
- Pain-relieving medicines
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Topical creams to soothe itching
Treatment is most effective when started within 72 hours of rash appearance.
Home Care and Lifestyle Tips
- Keep the rash clean and dry
- Avoid scratching the blisters
- Apply cool compresses
- Get adequate rest
- Maintain a healthy, balanced diet
- Manage stress effectively
Prevention of Herpes Zoster
The most effective way to prevent shingles is vaccination. Shingles vaccines significantly reduce the risk and severity of the disease, especially in older adults.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
- Adults above 50 years
- People with chronic medical conditions (as advised by a doctor)
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention immediately if:
- Rash appears near the eyes
- Severe pain persists
- Fever accompanies the rash
- Symptoms worsen despite treatment
Conclusion
Herpes zoster is a painful but manageable condition when diagnosed early and treated properly. Awareness of symptoms, timely medical care, and vaccination play a crucial role in preventing complications. If you or a loved one experiences signs of shingles, consult a healthcare professional without delay.