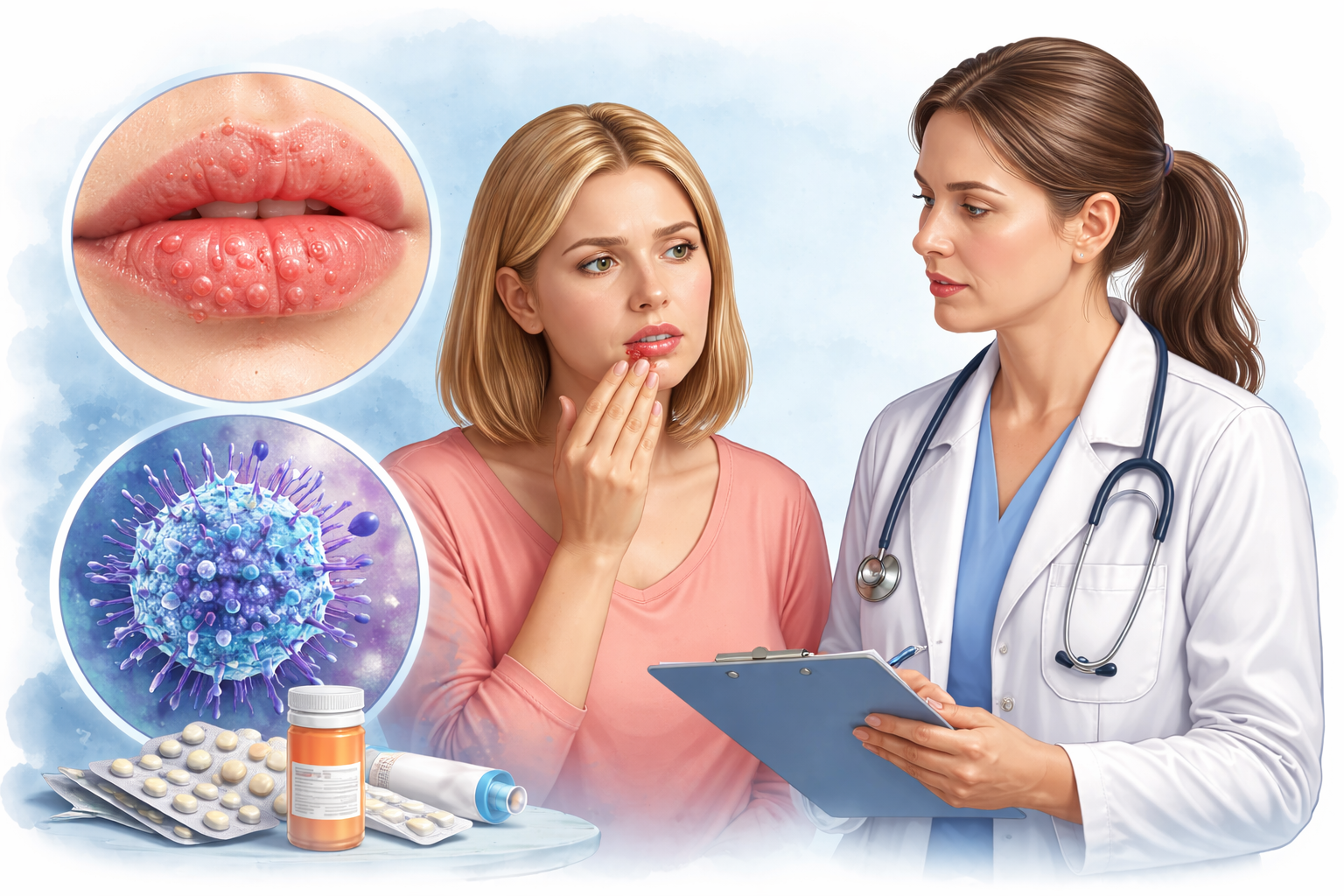
Herpes simplex is a common viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It affects people of all ages and is known for causing painful blisters on the skin or mucous membranes. Although herpes simplex is a lifelong infection, proper awareness, early diagnosis, and effective treatment can help control symptoms and reduce transmission.
What Is Herpes Simplex?
Herpes simplex is a viral disease caused by the herpes simplex virus, which remains dormant in the body after the initial infection. The virus can reactivate from time to time, leading to recurrent outbreaks.
There are two main types of herpes simplex virus:
- HSV-1 (Oral Herpes): Commonly affects the mouth and lips, causing cold sores.
- HSV-2 (Genital Herpes): Primarily affects the genital and anal areas.
Causes of Herpes Simplex
Herpes simplex spreads through direct contact with infected skin, saliva, or body fluids. Common modes of transmission include:
- Kissing or close personal contact
- Oral, vaginal, or anal sexual contact
- Sharing personal items like lip balm or razors
- Contact with active blisters or sores
The virus is most contagious during an active outbreak but can also spread when no symptoms are present.
Signs and Symptoms of Herpes Simplex
Symptoms vary from person to person. Some individuals may not experience any symptoms, while others develop painful outbreaks.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Tingling, itching, or burning sensation
- Small fluid-filled blisters
- Painful open sores after blisters rupture
- Redness and swelling
- Fever and body aches (during first infection)
- Swollen lymph nodes
Recurrent outbreaks are usually milder and shorter than the initial episode.
Diagnosis of Herpes Simplex
Herpes simplex is diagnosed through:
- Physical examination of sores
- Laboratory tests such as viral culture or PCR
- Blood tests to detect HSV antibodies
Early diagnosis helps in better symptom control and prevention of spread.
Treatment of Herpes Simplex
There is no permanent cure for herpes simplex, but treatment significantly reduces symptoms and outbreak frequency.
Medical Treatment Options
- Antiviral medicines (acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir)
- Pain relievers for discomfort
- Topical antiviral creams (for mild cases)
Antiviral therapy works best when started at the earliest sign of symptoms.
Home Care and Lifestyle Management
- Keep affected areas clean and dry
- Avoid touching or scratching sores
- Wash hands frequently
- Avoid close contact during active outbreaks
- Manage stress and maintain immunity
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet
Complications of Herpes Simplex
If untreated or poorly managed, herpes simplex may cause:
- Frequent painful outbreaks
- Secondary bacterial infections
- Emotional stress and anxiety
- Increased risk of HIV transmission
- Serious infection in newborns (neonatal herpes)
Prevention of Herpes Simplex
Preventive measures play a vital role in reducing transmission:
- Avoid contact during active outbreaks
- Use protection during sexual activity
- Do not share personal items
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- Take suppressive antiviral therapy if advised by a doctor
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare professional if:
- You experience frequent or severe outbreaks
- Sores do not heal properly
- Symptoms worsen or spread
- You are pregnant or immunocompromised
Conclusion
Herpes simplex is a manageable viral infection with proper medical care and lifestyle adjustments. Early diagnosis, regular treatment, and preventive measures can significantly improve quality of life and reduce complications. If you suspect herpes simplex infection, timely consultation with a healthcare provider is essential.