Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to inadequate insulin production or ineffective use of insulin. While diabetes can be controlled with proper management, if left untreated, it can lead to serious short-term and long-term complications. Understanding these complications is vital for patients, families, and healthcare providers to prevent disability and improve quality of life.
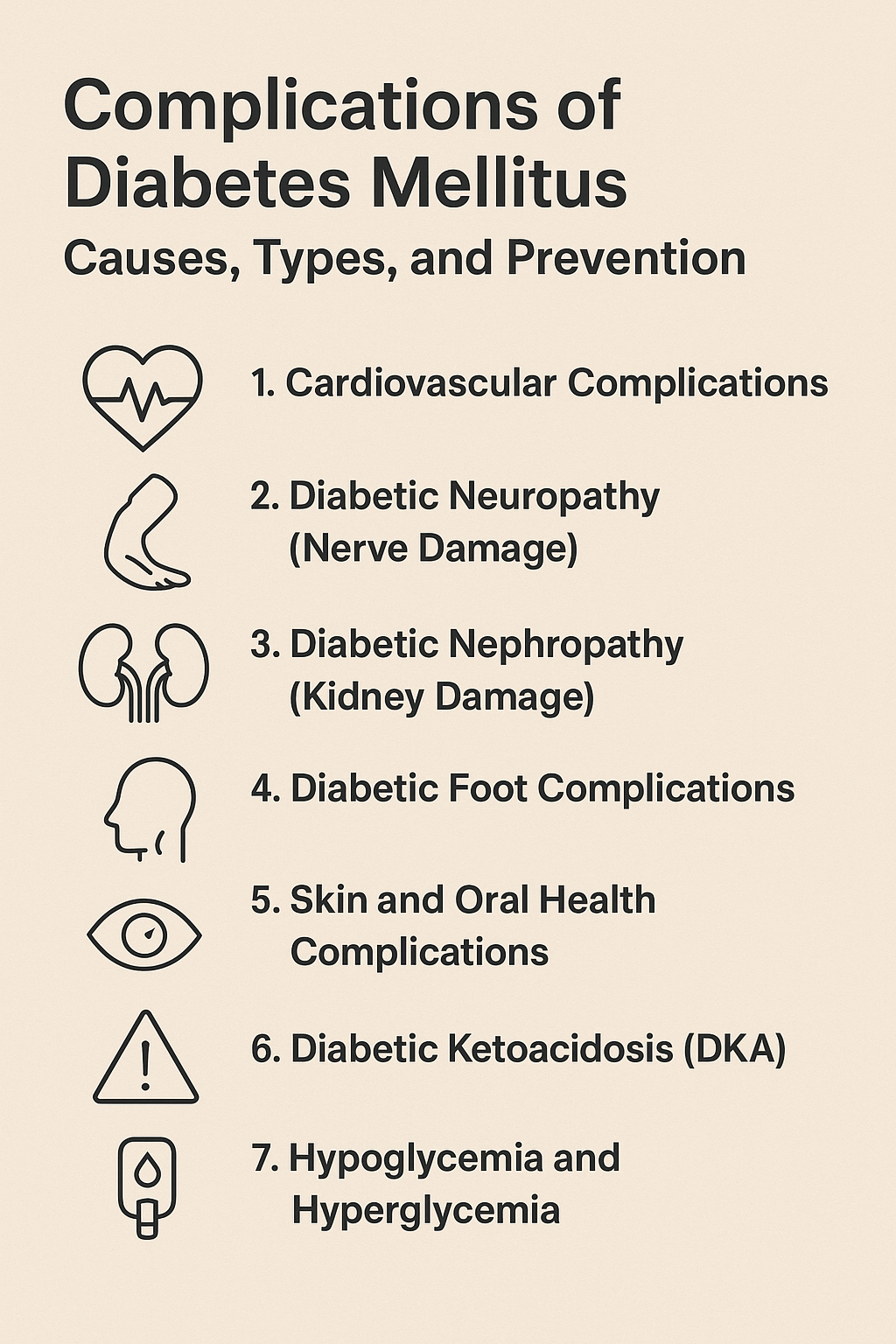
Common Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
1. Cardiovascular Complications
One of the most serious consequences of diabetes is its impact on the heart and blood vessels. People with diabetes are at higher risk of:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
- High blood pressure and high cholesterol
Uncontrolled blood sugar damages blood vessels, accelerating atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries).
2. Diabetic Neuropathy (Nerve Damage)
High glucose levels damage nerves throughout the body, leading to:
- Numbness and tingling in hands and feet
- Burning pain or sensitivity in legs
- Erectile dysfunction in men
- Digestive issues like gastroparesis
Diabetic neuropathy increases the risk of foot ulcers and infections, which may lead to amputations.
3. Diabetic Nephropathy (Kidney Damage)
The kidneys filter waste from the blood, but prolonged high blood sugar can damage these filters. This condition, called diabetic nephropathy, can cause:
- Protein in the urine (proteinuria)
- Swelling in legs and feet
- High blood pressure
- Chronic kidney disease and even kidney failure
4. Diabetic Retinopathy (Eye Complications)
Diabetes damages the small blood vessels in the retina, leading to:
- Blurred vision
- Cataracts and glaucoma
- Retinal detachment
- Complete blindness if not treated early
5. Diabetic Foot Complications
Poor circulation and nerve damage make the feet highly vulnerable. Patients may develop:
- Non-healing ulcers
- Infections
- Gangrene
- Risk of amputation
6. Skin and Oral Health Complications
People with diabetes often face:
- Fungal and bacterial infections
- Slow wound healing
- Gum disease and tooth loss
7. Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
This is an acute, life-threatening complication seen mostly in Type 1 diabetes. It occurs when the body breaks down fat excessively due to lack of insulin, producing ketones that make the blood acidic. Symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion and unconsciousness
8. Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): Causes sweating, dizziness, and fainting.
- Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar): Leads to frequent urination, thirst, and fatigue.
Both conditions require urgent medical management.
How to Prevent Diabetes Complications
- Maintain Blood Sugar Control – Regular monitoring and adherence to medications.
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle – Balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight control.
- Regular Medical Checkups – Eye exams, kidney tests, and foot inspections.
- Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol – Prevents heart and vascular complications.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol – Reduces risk of cardiovascular and kidney disease.
Conclusion
Diabetes mellitus is not just about high blood sugar—it can silently damage multiple organs over time. The good news is that most of these complications can be prevented or delayed with early diagnosis, strict glucose control, and lifestyle modifications. Patients should work closely with healthcare professionals to ensure a healthier, complication-free life.