The HbA1c test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, is one of the most important tools in diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. It provides a picture of the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), HbA1c is a reliable and standardized test that helps in both early detection and long-term management of diabetes.
In this blog, we will explore all aspects of HbA1c testing, including its purpose, procedure, interpretation, and role in diabetes care.
What is HbA1c?
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. When glucose circulates in the bloodstream, it can attach to hemoglobin, forming glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). The higher the blood sugar levels, the more HbA1c is formed.
Since red blood cells live for about 120 days, HbA1c reflects the average blood glucose level of the last 2–3 months.
Why is HbA1c Important?
The HbA1c test is essential because:
- It provides a long-term overview of blood sugar control (unlike daily glucose monitoring).
- It helps diagnose diabetes and prediabetes.
- It guides treatment adjustments in diabetic patients.
- It is linked to the risk of diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems.
IDF Guidelines for HbA1c Testing
The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) recommends HbA1c testing for both diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes.
1. Diagnostic Criteria
According to IDF guidelines:
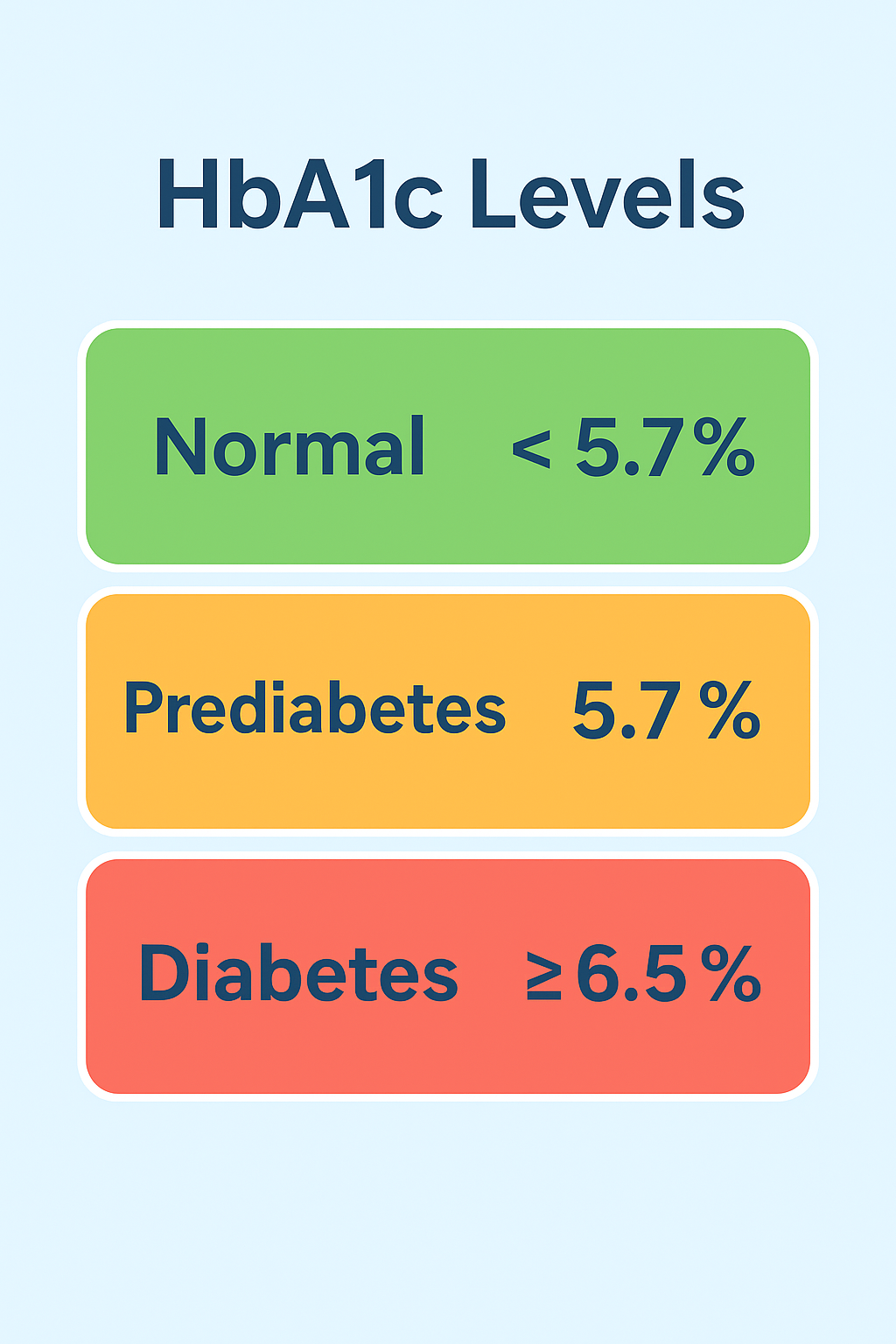
- Normal: HbA1c < 5.7%
- Prediabetes (Increased risk): HbA1c 5.7% – 6.4%
- Diabetes: HbA1c ≥ 6.5%
These ranges are widely accepted and used in clinical practice worldwide.
2. Target HbA1c for Diabetes Patients
- Most adults with diabetes: HbA1c < 7%
- For selected patients (e.g., younger individuals with no complications): HbA1c < 6.5% may be targeted.
- For elderly or patients with severe complications: HbA1c < 8% may be acceptable to avoid hypoglycemia and treatment risks.
3. Frequency of Testing
- At least twice a year for patients with stable blood glucose control.
- Every 3 months for patients whose therapy has changed or who are not meeting glycemic targets.
How the HbA1c Test is Performed
- The test is done through a simple blood sample (usually from a vein in the arm).
- Fasting is not required, making it more convenient than other blood sugar tests.
- Results are reported as a percentage (%).
Factors That May Affect HbA1c Results
While HbA1c is highly reliable, certain conditions can influence the results:
- Anemia or iron deficiency
- Recent blood loss or transfusion
- Hemoglobin disorders (e.g., sickle cell disease)
- Pregnancy
In such cases, doctors may use alternative tests like fructosamine to monitor blood sugar.
HbA1c and Risk of Complications
Research shows that higher HbA1c levels are strongly linked to the risk of diabetes complications. For example:
- Every 1% increase in HbA1c raises the risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and retinopathy.
- Maintaining HbA1c within target range significantly reduces the chances of long-term complications.
How to Improve HbA1c Levels
If your HbA1c is above target, lifestyle and medical management can help lower it:
- Healthy diet: Choose whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and avoid sugary foods.
- Regular physical activity: At least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Weight management: Even small weight loss improves glucose control.
- Medication adherence: Take prescribed medications (oral drugs or insulin) as directed.
- Regular monitoring: Keep track of blood sugar at home and follow up with your doctor.
Conclusion
The HbA1c test is a cornerstone of diabetes care, providing valuable information about long-term blood sugar control. According to IDF guidelines, it is crucial not only for diagnosing diabetes but also for setting treatment goals and preventing complications.
If you have risk factors for diabetes or already live with the condition, ask your doctor about regular HbA1c testing. Managing your levels effectively can greatly improve your quality of life and reduce future health risks.