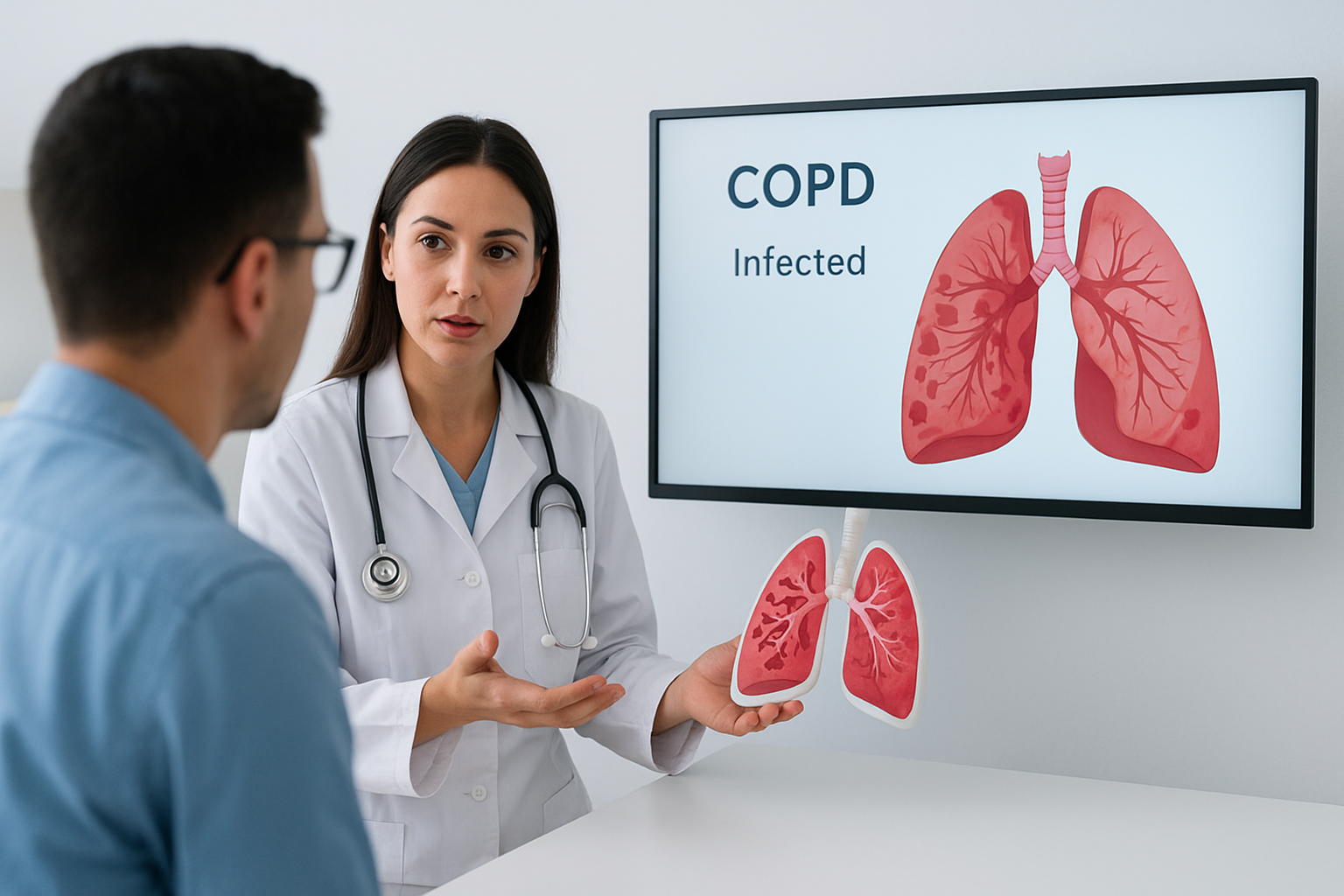
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a long-term lung condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes breathing difficulties due to airflow obstruction and lung damage, most often resulting from smoking or long-term exposure to air pollutants.
Raising awareness about COPD is essential because early detection and management can greatly improve the quality of life and reduce disease complications.
What is COPD?
COPD is a progressive lung disease that makes it hard to breathe. It includes two main conditions:
- Chronic Bronchitis – Long-term inflammation of the bronchial tubes causing cough and mucus production.
- Emphysema – Damage to the tiny air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs that impairs oxygen exchange.
Most people with COPD have a combination of both conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors
The most common cause of COPD is long-term exposure to irritants that damage the lungs and airways.
Key causes and risk factors include:
- Smoking (the leading cause of COPD worldwide)
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Air pollution and chemical fumes in workplaces
- Genetic factors (such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency)
- Frequent lung infections during childhood
Symptoms of COPD
Symptoms of COPD usually develop gradually and worsen over time.
Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough with mucus
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Wheezing (whistling sound while breathing)
- Chest tightness
- Fatigue and weakness
- Repeated respiratory infections
If left untreated, COPD can lead to complications such as heart disease, respiratory failure, or pneumonia.
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is crucial to slow disease progression. Your doctor may recommend:
- Spirometry (Pulmonary Function Test) – Measures lung capacity and airflow.
- Chest X-ray or CT scan – Detects lung damage and emphysema.
- Blood tests – To check oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
Treatment and Management
Although COPD cannot be cured, proper management can control symptoms and improve breathing.
1. Smoking Cessation
The most important step in COPD management is quitting smoking. It helps prevent further lung damage and improves overall health.
2. Medications
- Bronchodilators – Help open airways and make breathing easier.
- Steroid inhalers – Reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Antibiotics – Used during infections or exacerbations.
3. Oxygen Therapy
For patients with severe COPD and low oxygen levels, supplemental oxygen can help relieve symptoms.
4. Pulmonary Rehabilitation
A structured program that includes exercise, breathing training, and nutrition advice to strengthen lungs and body function.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.
- Engage in light exercise, such as walking or breathing exercises.
- Avoid exposure to dust, fumes, and pollutants.
Prevention
While COPD is largely preventable, awareness and lifestyle choices play a key role in prevention:
- Avoid smoking or exposure to tobacco smoke.
- Wear masks in polluted environments or workplaces with chemicals.
- Get vaccinated against flu and pneumonia to prevent infections.
- Regular check-ups for people with persistent cough or breathing issues.
Living with COPD
People with COPD can still live full and active lives with proper care and support.
Joining support groups, staying physically active, and following medical advice help patients maintain better control over symptoms and mental well-being.
Conclusion
COPD is a preventable and manageable condition if diagnosed early and treated properly.
Raising awareness about its causes, symptoms, and prevention can save lives.
If you experience persistent cough, shortness of breath, or chest tightness, consult your doctor immediately for assessment and early management.