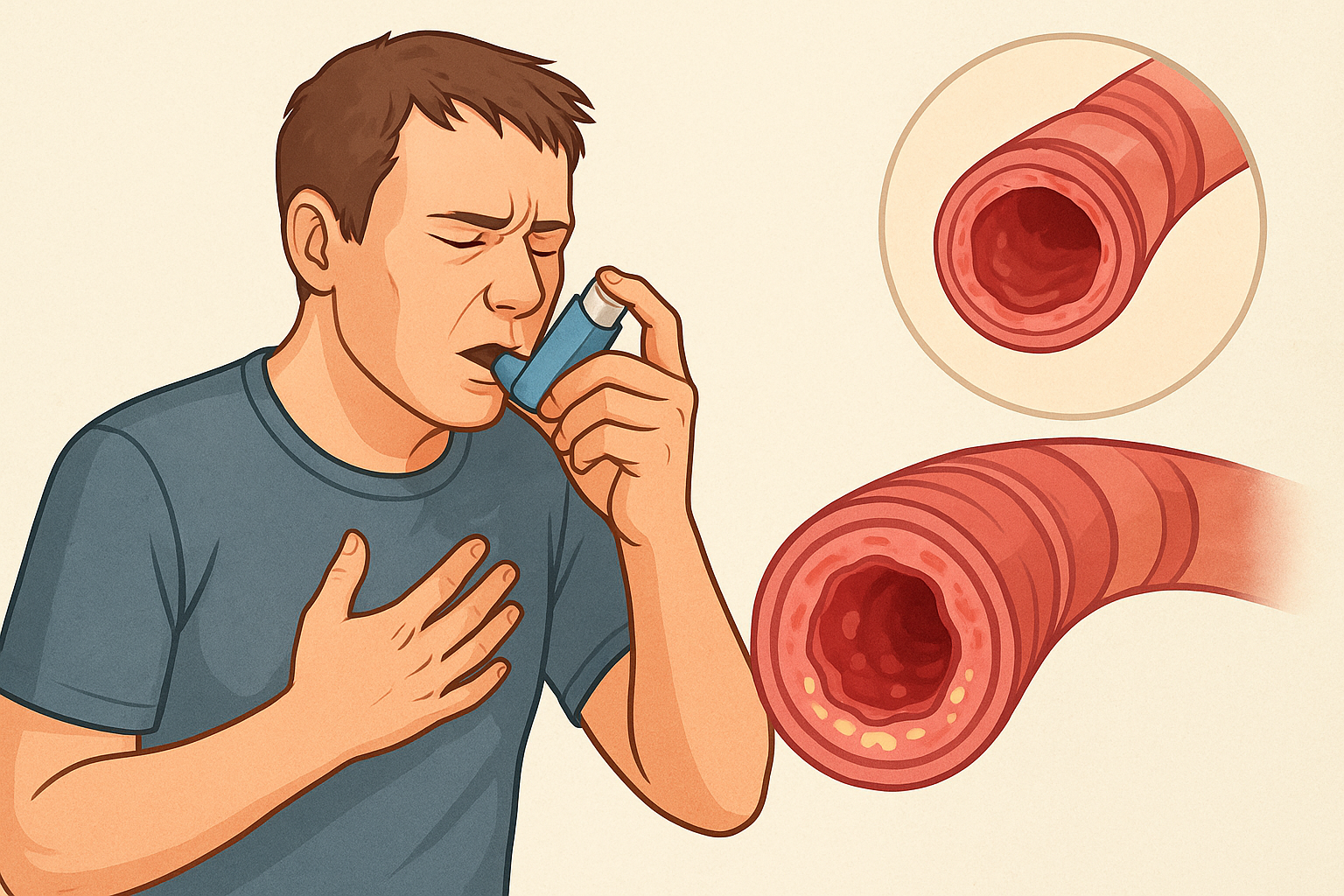
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects the airways, causing them to become inflamed and narrowed. This leads to breathing difficulties, coughing, and wheezing. Asthma can affect people of all ages, but it often begins in childhood. With proper management and treatment, most people with asthma can live a healthy and active life.
What Is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that causes them to become sensitive to various triggers such as allergens, pollution, cold air, or exercise. During an asthma attack, the airways swell and produce extra mucus, making it difficult for air to move in and out of the lungs.
Asthma can range from mild to severe and may be triggered by different factors in different individuals.
Types of Asthma
- Allergic Asthma:
Triggered by allergens such as pollen, dust mites, animal dander, or mold. - Non-Allergic Asthma:
Caused by factors like stress, exercise, or cold air. - Occupational Asthma:
Develops due to exposure to irritants in the workplace, such as chemicals or dust. - Exercise-Induced Asthma:
Symptoms appear during or after physical activity. - Cough-Variant Asthma:
Characterized mainly by a chronic dry cough without the classic wheezing.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of asthma isn’t fully understood, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors plays a role.
Common Causes and Triggers:
- Exposure to allergens (dust mites, pollen, pet dander)
- Air pollution and cigarette smoke
- Respiratory infections (cold, flu)
- Weather changes (especially cold air)
- Strong odors, perfumes, or chemical fumes
- Physical exercise
- Emotional stress or anxiety
Risk Factors:
- Family history of asthma or allergies
- Living in urban or polluted environments
- Obesity
- Exposure to tobacco smoke
- Occupational exposure to dust or chemicals
Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma symptoms vary from person to person. Some may experience symptoms occasionally, while others have them regularly.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing (whistling sound while breathing)
- Tightness or pain in the chest
- Persistent coughing, especially at night or early morning
- Difficulty breathing during exercise or exposure to cold air
Severe Asthma Attack Symptoms:
- Rapid breathing
- Difficulty speaking
- Bluish lips or fingers (lack of oxygen)
- Feeling anxious or panicked
If you experience severe symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis of Asthma
Asthma is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specific tests, including:
- Spirometry: Measures how much air you can breathe in and out.
- Peak Flow Test: Assesses how quickly you can exhale air.
- Allergy Testing: Identifies specific allergens that may trigger asthma.
- Chest X-ray: Helps rule out other respiratory conditions.
Treatment and Management
Asthma has no permanent cure, but with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications, it can be effectively controlled.
1. Medications:
- Reliever (Rescue) Inhalers: Provide quick relief during asthma attacks (e.g., Salbutamol).
- Controller (Preventive) Inhalers: Used daily to reduce inflammation and prevent attacks (e.g., Corticosteroids).
- Oral Medications: In some cases, doctors may prescribe oral steroids or leukotriene modifiers.
2. Lifestyle and Self-Care:
- Avoid known triggers (dust, smoke, strong odors).
- Maintain a clean, dust-free environment.
- Use an air purifier in polluted areas.
- Exercise regularly but consult your doctor about asthma-safe activities.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Manage stress with relaxation techniques like yoga or breathing exercises.
3. Asthma Action Plan:
Your doctor can help you create a personalized Asthma Action Plan that outlines:
- How to recognize early symptoms
- When to use medications
- When to seek emergency help
Complications of Untreated Asthma
If not properly managed, asthma can lead to:
- Frequent hospital visits
- Permanent airway damage (airway remodeling)
- Reduced ability to perform daily activities
- Respiratory failure (in severe cases)
Early diagnosis and consistent treatment significantly reduce these risks.
Prevention Tips
While asthma cannot be completely prevented, the following steps help reduce the risk of attacks:
- Avoid exposure to allergens and smoke.
- Stay updated with flu and pneumonia vaccinations.
- Monitor air quality and avoid outdoor activities when pollution levels are high.
- Keep inhalers accessible at all times.
- Regularly review your treatment plan with your doctor.
Conclusion
Asthma is a manageable chronic disease that requires consistent care and awareness. Understanding your triggers, using medications correctly, and following a doctor’s advice can help you live symptom-free. With proper control, asthma does not have to limit your quality of life.