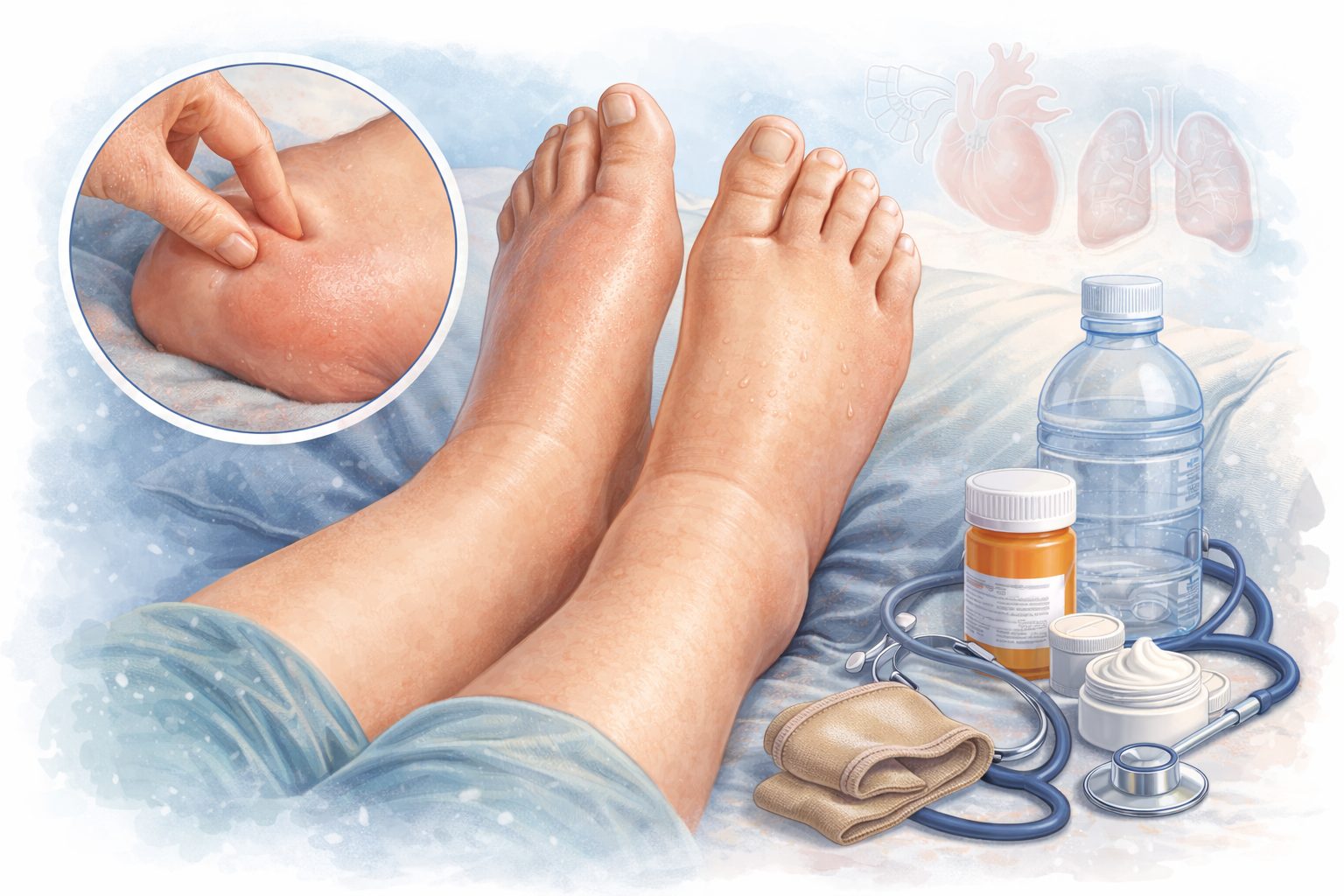
Feet swelling, medically known as pedal edema, is a common condition in which excess fluid accumulates in the tissues of the feet and ankles. It can occur temporarily due to lifestyle factors or indicate an underlying medical condition. Understanding the causes of feet swelling and seeking timely care can help prevent complications and improve comfort.
What Is Feet Swelling?
Feet swelling occurs when fluid builds up in the lower extremities, causing the feet, ankles, or legs to appear puffy or enlarged. The swelling may affect one or both feet and can range from mild to severe.
Common Causes of Feet Swelling
There are many possible causes of pedal edema, including:
Lifestyle and Temporary Causes
- Prolonged standing or sitting
- Long-distance travel
- Excessive salt intake
- Hot weather
- Pregnancy
Medical Causes
- Heart disease or heart failure
- Kidney disease
- Liver disorders
- Varicose veins
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Infections or injuries
- Diabetes-related complications
- Side effects of certain medications (e.g., blood pressure drugs)
Symptoms Associated with Feet Swelling
Feet swelling may be accompanied by:
- Puffiness or tightness in the feet and ankles
- Shiny or stretched skin
- Pain or heaviness
- Reduced flexibility
- Skin indentation when pressed (pitting edema)
If swelling is sudden or painful, medical attention is required.
Diagnosis of Feet Swelling
Doctors diagnose pedal edema by:
- Physical examination
- Reviewing medical history
- Blood and urine tests
- Imaging studies (ultrasound, X-ray)
- Heart, liver, or kidney function tests
Identifying the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment.
Treatment of Feet Swelling
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of swelling.
Medical Treatment
- Diuretics (only if prescribed)
- Treatment of underlying heart, kidney, or liver conditions
- Antibiotics for infections
- Adjustment of medications causing swelling
Home Care and Lifestyle Management
- Elevate feet above heart level
- Reduce salt intake
- Wear comfortable shoes
- Use compression stockings (if advised)
- Avoid standing or sitting for long periods
- Maintain a healthy body weight
Feet Swelling in Diabetes
People with diabetes are at higher risk of foot swelling due to poor circulation and nerve damage. Regular foot examination and proper glucose control are essential to prevent complications.
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical care if:
- Swelling is sudden or severe
- One foot is swollen and painful
- You experience shortness of breath
- Skin becomes red, warm, or infected
- Swelling does not improve with rest
Prevention of Feet Swelling
Preventive measures include:
- Staying physically active
- Managing chronic diseases
- Drinking enough water
- Limiting salt consumption
- Wearing supportive footwear
Conclusion
Feet swelling is often harmless but can sometimes indicate serious health issues. Early identification of the cause, proper treatment, and healthy lifestyle choices can effectively manage pedal edema. If swelling persists or worsens, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial.