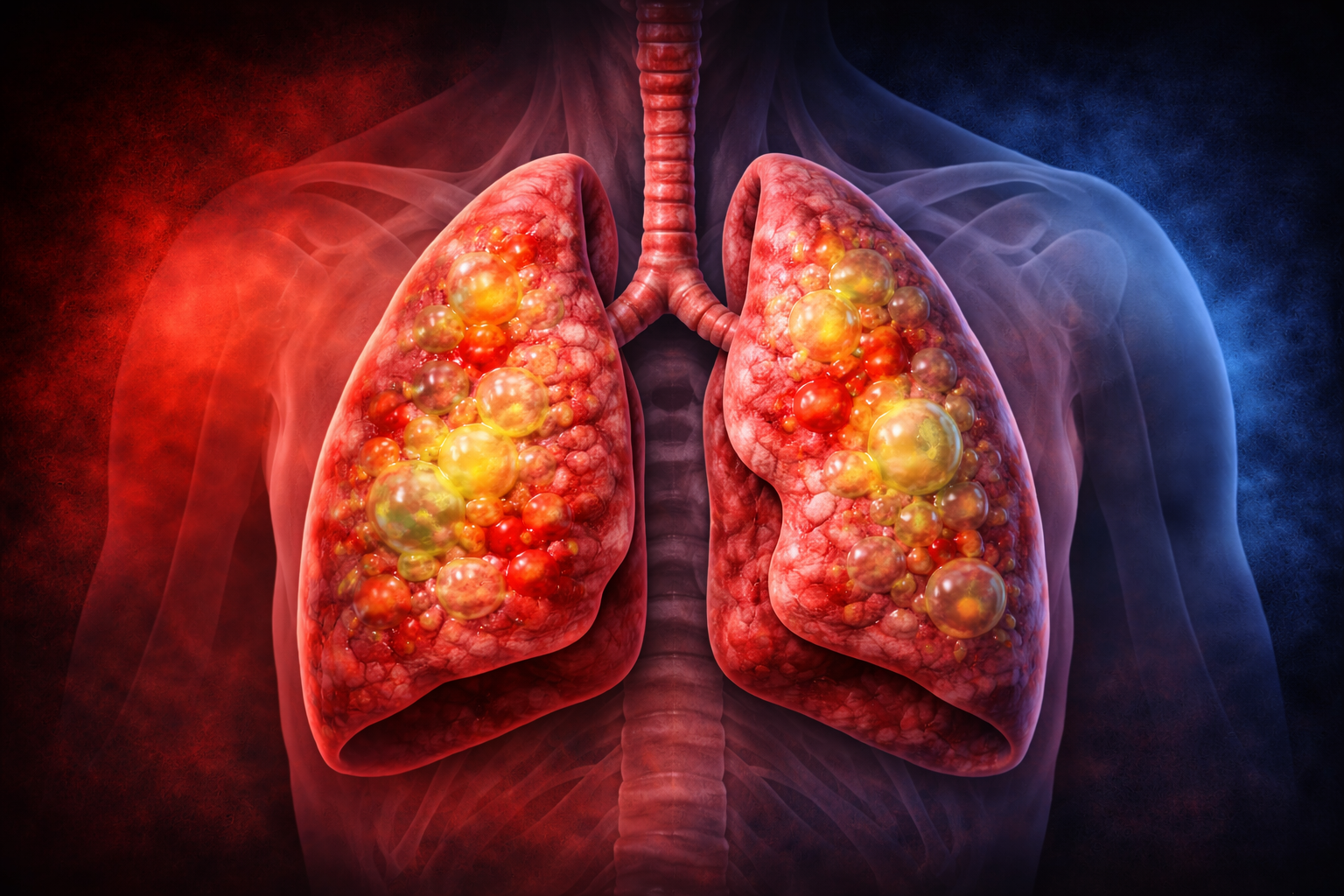
Double pneumonia is a serious lung infection in which both lungs are affected by inflammation and fluid-filled air sacs. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and may range from mild to life-threatening, especially in older adults, children, and people with weak immune systems. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for recovery.
What Is Double Pneumonia?
Double pneumonia refers to bilateral pneumonia, meaning infection is present in both lungs simultaneously. Unlike single-lung pneumonia, double pneumonia can significantly reduce oxygen exchange, making breathing more difficult and increasing the risk of complications.
Causes of Double Pneumonia
Double pneumonia can be caused by various infectious agents, including:
- Bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae)
- Viruses (such as influenza or COVID-19)
- Fungi (more common in immunocompromised patients)
- Aspiration of food, liquids, or vomit
- Hospital-acquired infections
Risk factors include smoking, chronic lung disease, diabetes, weakened immunity, and advanced age.
Symptoms of Double Pneumonia
Symptoms may be more severe compared to single-lung pneumonia and can include:
- High fever and chills
- Persistent cough (with or without mucus)
- Shortness of breath
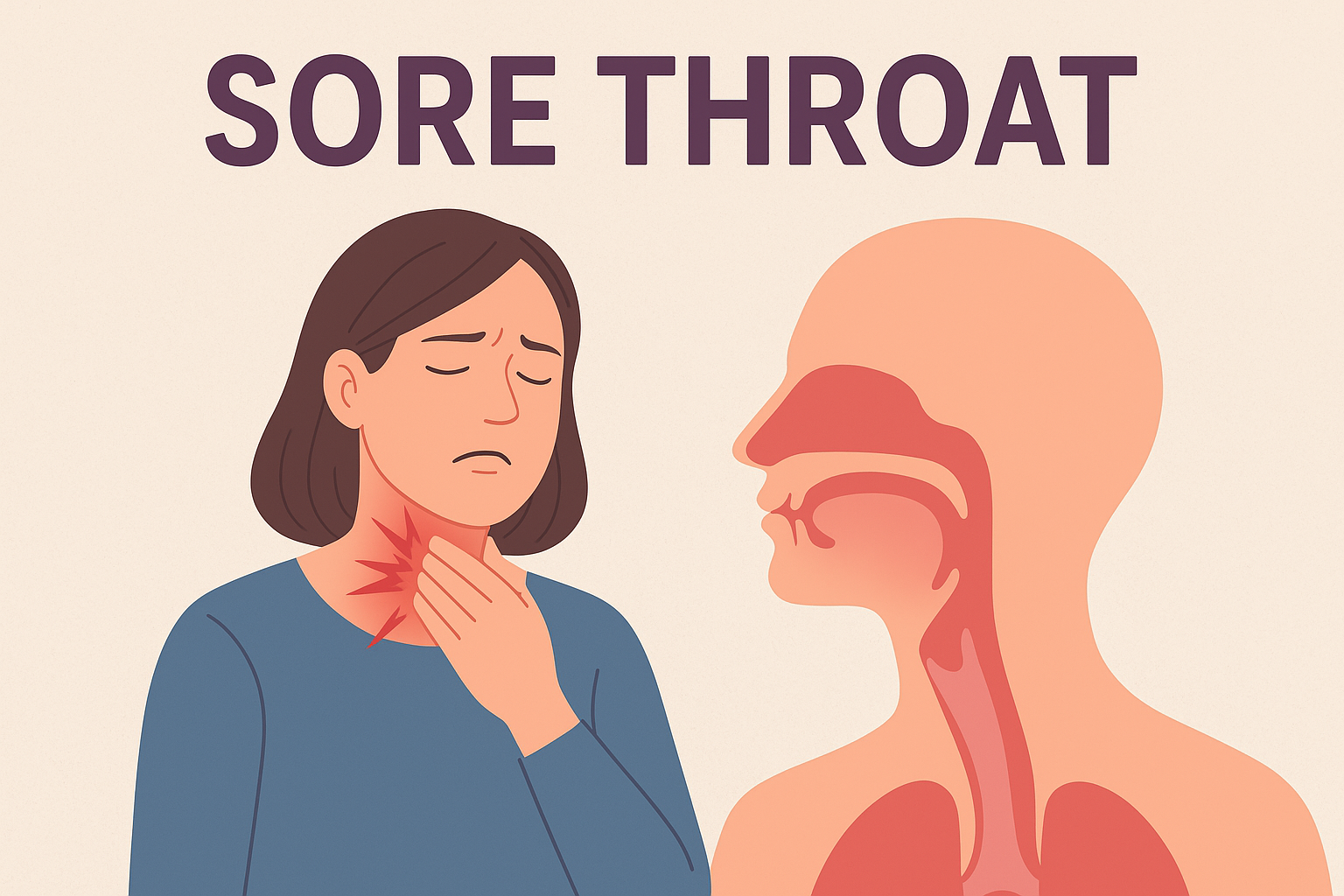
- Chest pain during breathing or coughing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Rapid breathing or heartbeat
- Bluish lips or nails (in severe cases)
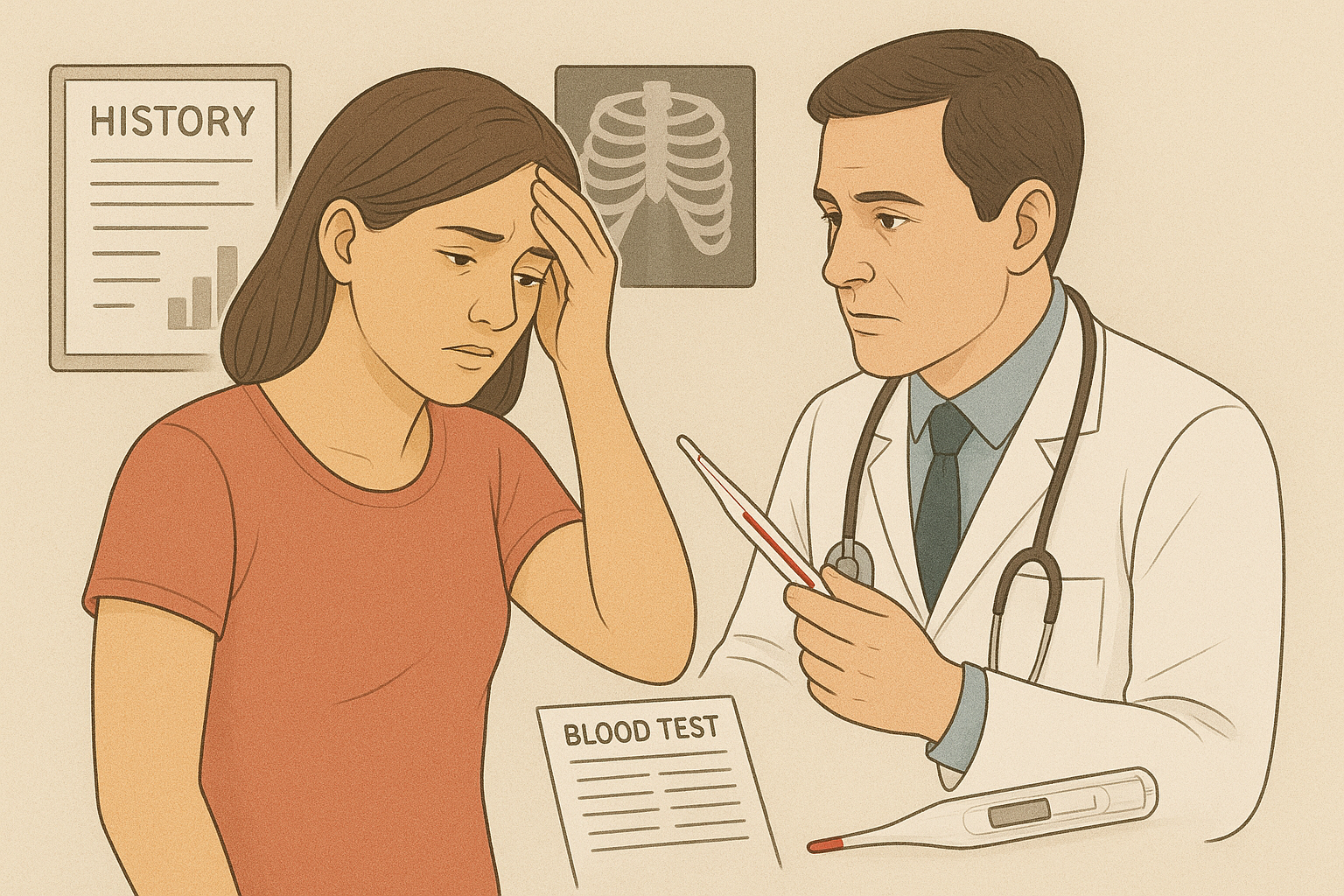
Diagnosis of Double Pneumonia
Doctors diagnose double pneumonia using:
- Chest X-ray (shows infection in both lungs)
- CT scan for detailed lung imaging
- Blood tests to detect infection
- Sputum tests to identify the causative organism
- Oxygen level monitoring
Treatment of Double Pneumonia
Treatment depends on the cause, severity, and patient’s overall health.
Medical Treatment
- Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia
- Antiviral medications for viral pneumonia
- Antifungal drugs if fungal infection is suspected
- Oxygen therapy in cases of low oxygen levels
- IV fluids and fever control
Hospitalization
Severe cases may require:
- Hospital admission
- Intensive care monitoring
- Mechanical ventilation (in critical cases)
Complications of Double Pneumonia
If not treated properly, double pneumonia can lead to:
- Respiratory failure
- Sepsis
- Lung abscess
- Pleural effusion
- Increased risk of death in high-risk individuals
Prevention Tips
You can reduce the risk of double pneumonia by:
- Getting vaccinated (pneumococcal and influenza vaccines)
- Avoiding smoking
- Maintaining good hygiene
- Managing chronic illnesses
- Seeking early medical care for respiratory infections
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing
- High or persistent fever
- Chest pain
- Confusion or extreme weakness
- Worsening cough
Recovery and Outlook
Recovery from double pneumonia may take weeks to months, depending on severity. Adequate rest, proper medication adherence, hydration, and follow-up visits are crucial for full recovery.
Conclusion
Double pneumonia is a serious but treatable condition when diagnosed early. Prompt medical care, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures can significantly improve outcomes and reduce complications.