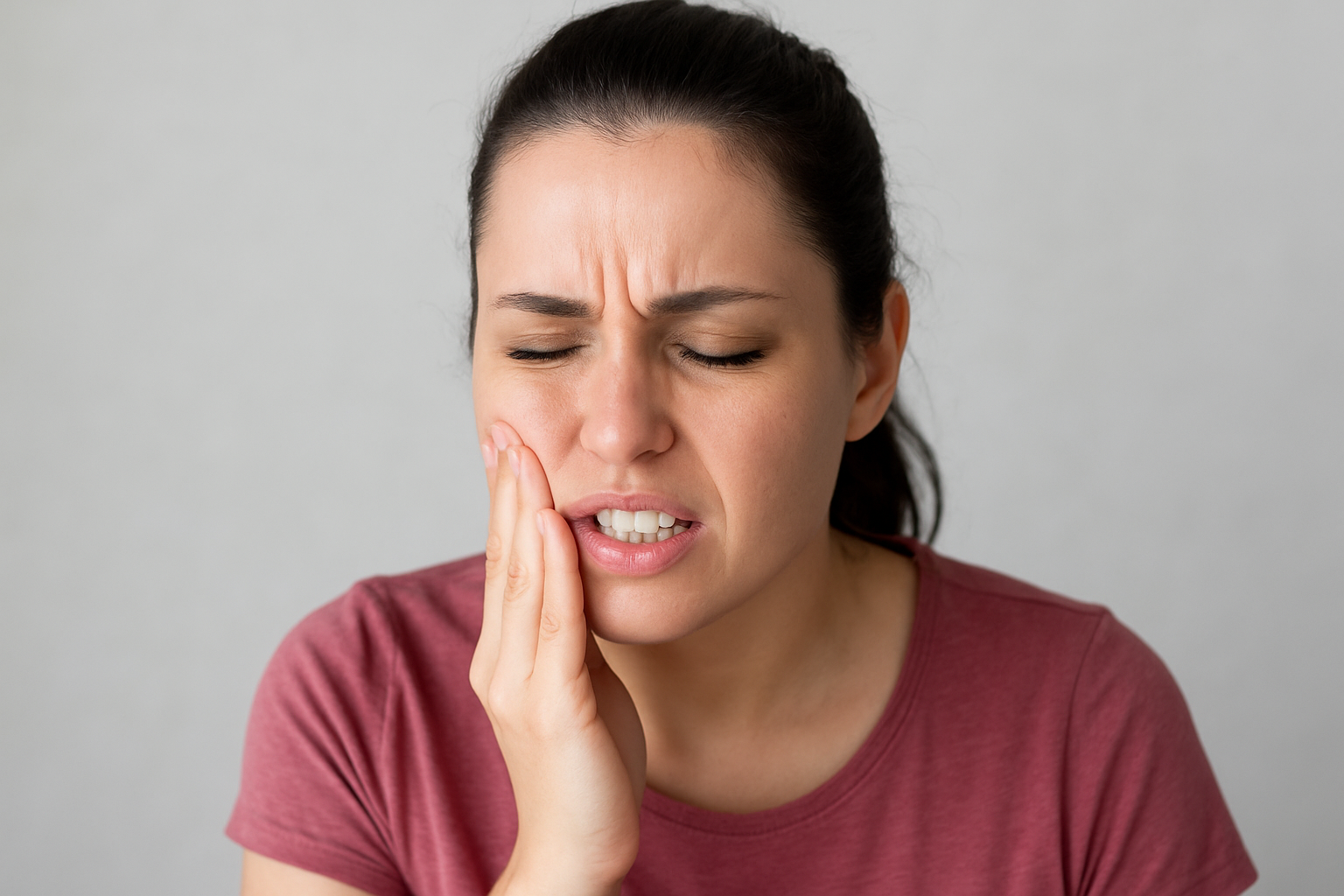
A tooth infection—also called a dental abscess—is a painful and potentially serious dental condition caused by bacteria entering the tooth or surrounding tissues. It often begins as untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or a cracked tooth and can spread quickly if not managed in time. Recognizing early symptoms and seeking timely treatment can prevent complications, including bone infection or facial swelling.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection occurs when bacteria reach the inner part of the tooth (pulp), causing inflammation, pus formation, and severe pain. The infection can spread to the gums, jawbone, and surrounding tissues.
Common types include:
- Periapical abscess – infection at the root tip
- Periodontal abscess – infection in the gums
- Gingival abscess – infection on the gum surface
SEO Keywords for Tooth Infection Blog
Causes of Tooth Infection
1. Untreated Dental Cavities
Deep cavities allow bacteria to reach the pulp, causing infection.
2. Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
Inflamed and infected gums can harbor bacteria that spread to the tooth roots.
3. Cracked or Broken Tooth
Cracks provide a pathway for bacteria to enter the tooth.
4. Poor Oral Hygiene
Irregular brushing and flossing increase plaque buildup and bacteria growth.
5. Previous Dental Work
If not properly sealed, fillings or crowns may allow bacteria to enter the tooth.
Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
Common symptoms include:
- Throbbing or sharp tooth pain
- Swollen gums or cheeks
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods
- Bad breath or foul taste in the mouth
- Fever
- Redness or swelling in jaw or neck
- Pus around the tooth
- Difficulty chewing
Emergency symptoms (seek immediate care):
- Severe swelling
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- High fever
Diagnosis of Tooth Infection
A dentist will perform:
- Oral examination to check swelling or pus
- X-rays to identify root infection or bone involvement
- Sensitivity tests to assess nerve damage
Early diagnosis prevents the infection from spreading to other parts of the body.
Treatment Options for Tooth Infection
1. Antibiotics
Used to control the infection, especially if swelling or fever is present.
2. Root Canal Treatment (RCT)
The infected pulp is removed, cleaned, and sealed to save the tooth.
3. Abscess Drainage
The dentist drains pus to relieve pressure and pain.
4. Tooth Extraction
If the tooth is severely damaged, removal may be necessary.
5. Pain Management
OTC pain relievers help reduce discomfort while receiving dental care.
Home Remedies for Temporary Relief
(These do NOT cure the infection but help relieve pain temporarily.)
- Warm saltwater gargles
- Cold compress on swollen side
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Avoiding very hot, cold, or sweet foods
Always remember: Home remedies cannot replace dental treatment.
Complications of Untreated Tooth Infection
If ignored, the infection may spread to:
- Jawbone
- Neck and throat
- Sinuses
- Bloodstream (sepsis — a medical emergency)
Early treatment prevents life-threatening complications.
Prevention Tips
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily
- Reduce sugar intake
- Treat cavities early
- Visit the dentist every 6 months
- Use antibacterial mouthwash
- Avoid smoking and tobacco
Conclusion
A tooth infection is a serious dental condition that requires immediate attention. With proper diagnosis, antibiotics, root canal treatment, or extraction, the infection can be effectively controlled. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups is the key to preventing future infections and protecting your oral health.