Metformin is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). It has been in use for decades and remains the first-line treatment due to its proven safety, effectiveness, and ability to improve blood sugar control without causing weight gain.
Beyond diabetes, Metformin has gained attention for its potential roles in weight management, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and even anti-aging research.
What Is Metformin?
Metformin belongs to a class of drugs known as biguanides. It helps lower blood glucose levels by:
- Reducing glucose production in the liver (hepatic gluconeogenesis)
- Improving insulin sensitivity in muscle cells
- Decreasing glucose absorption from the intestines
Unlike many other antidiabetic drugs, Metformin does not stimulate insulin release, which is why it rarely causes hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) when used alone.
Uses of Metformin
Metformin is primarily used for managing Type 2 Diabetes, but it also has several off-label and additional benefits supported by clinical research.
1. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Metformin helps control fasting and post-meal blood sugar levels.
- It is often prescribed as a first-line therapy in new diabetes cases.
- It can be used alone or in combination with other oral antidiabetic medications or insulin.
- Long-term use has been linked with reduced cardiovascular risk and diabetes-related complications.
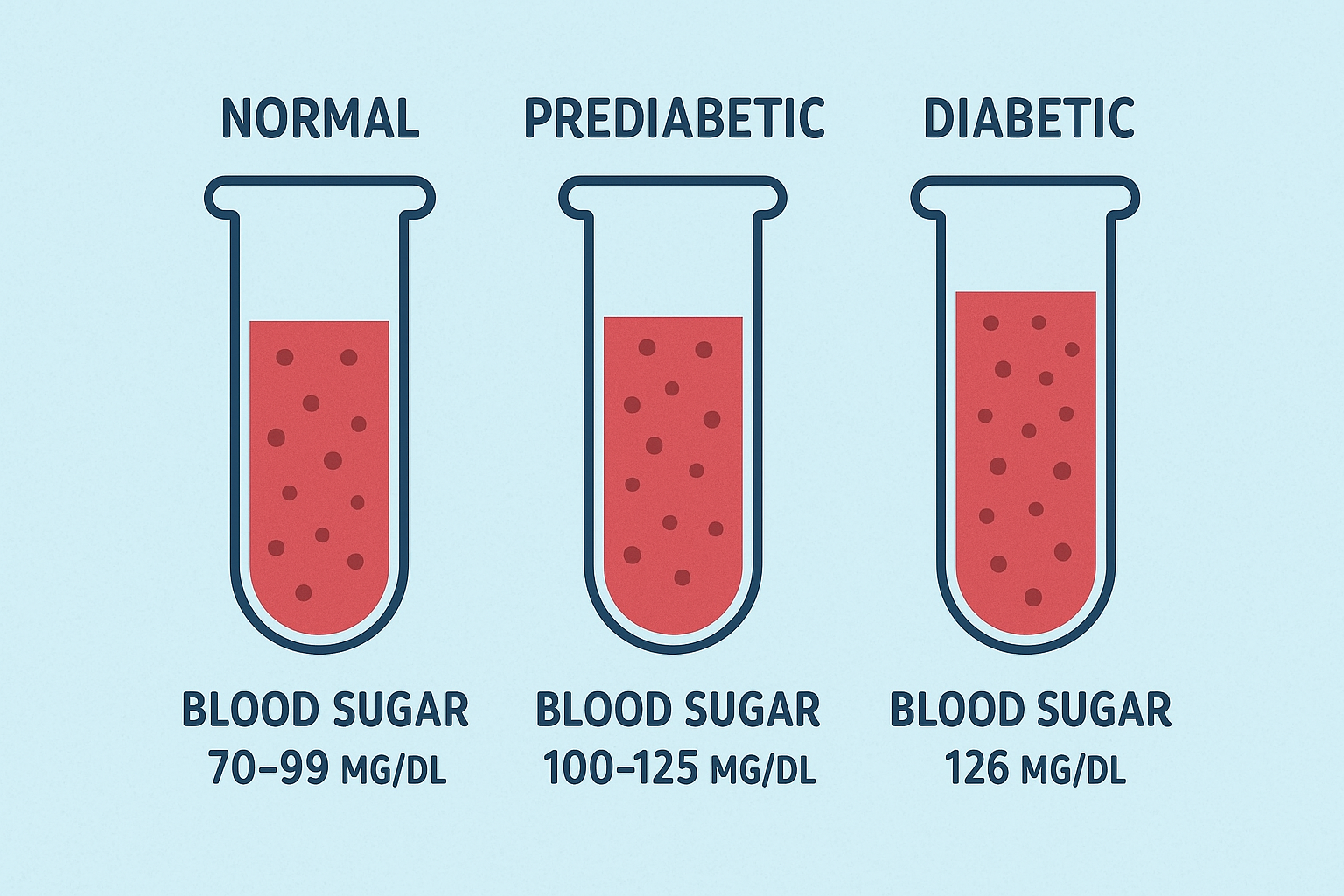
2. Prediabetes
In patients with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose, Metformin can delay or prevent the onset of Type 2 diabetes, especially in those who are overweight or obese.
3. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Metformin helps in regulating menstrual cycles, reducing insulin resistance, and improving fertility in women with PCOS. It also helps lower androgen levels, which can reduce acne and excessive hair growth.
4. Weight Management
Although not a weight-loss drug, Metformin can lead to modest weight reduction by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing appetite. It is sometimes used in obese patients with insulin resistance even without diabetes.
5. Anti-Aging and Longevity
Recent studies have explored Metformin’s potential anti-aging properties. Researchers believe it may help reduce the risk of age-related diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular disease, by improving cellular metabolism and reducing oxidative stress.
How Metformin Works (Mechanism of Action)
Metformin primarily targets the liver and muscle tissues:
- Decreases hepatic glucose production
- Enhances insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues
- Promotes glucose uptake by cells
- Improves gut microbiome balance, which indirectly supports metabolism
This combination of effects makes Metformin unique and effective in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Common Dosage and Forms
Metformin is available in several formulations:
- Immediate-release tablets: 500 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg
- Extended-release tablets (Metformin XR): 500 mg, 750 mg, 1000 mg
Typical starting dose:
- 500 mg once daily with meals
- Gradually increased to 1500–2000 mg/day based on tolerance and blood sugar control
Always take Metformin with food to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
Side Effects of Metformin
While generally safe, Metformin can cause some side effects, especially when starting treatment.
Common Side Effects:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal discomfort
- Diarrhea
- Metallic taste in mouth
These side effects are usually mild and temporary and improve as the body adjusts.
Serious but Rare Side Effect:
- Lactic acidosis: A rare but potentially dangerous condition caused by buildup of lactic acid in the blood.
It’s more likely to occur in patients with kidney or liver problems, heart failure, or heavy alcohol use.
Regular monitoring of kidney function (creatinine, eGFR) is important for safe Metformin use.
Who Should Avoid Metformin?
Metformin is not recommended in:
- Patients with severe kidney or liver disease
- Heart failure or recent heart attack
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Severe dehydration or infection
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting or continuing Metformin therapy.
Benefits of Metformin
- Proven safety record and cost-effective
- Reduces risk of diabetes complications
- May improve cholesterol profile and heart health
- Supports weight control
- Possible anti-aging benefits
Latest Research and Future Insights
Recent studies suggest that Metformin may:
- Improve gut microbiota composition, enhancing metabolic health
- Reduce the risk of certain cancers
- Delay age-related diseases by regulating cellular energy pathways (AMPK activation)
Large-scale trials like the TAME (Targeting Aging with Metformin) study are exploring whether Metformin can extend lifespan and promote healthy aging.
Conclusion
Metformin remains a cornerstone medication in diabetes management and continues to surprise researchers with its wide-ranging health benefits. Whether for blood sugar control, PCOS, or potential longevity effects, Metformin has proven to be a safe, effective, and affordable therapy backed by decades of clinical experience.
Always consult your doctor before starting or changing your Metformin dose, especially if you have kidney, liver, or heart conditions.