Managing blood sugar levels is essential for overall health, especially for people living with diabetes or prediabetes. However, blood sugar targets are not the same for everyone. Age plays a major role in determining safe and effective glucose goals. Keeping sugar levels within the recommended range according to age helps prevent complications while maintaining quality of life.
In this blog, we will explain how blood sugar targets change with age, why these differences matter, and the effects of achieving or missing those age-based goals.
What Are Blood Sugar Targets?
Blood sugar targets are the recommended glucose ranges considered safe for daily life and long-term health. They include:
- Fasting blood sugar levels
- Before-meal glucose levels
- After-meal (post-prandial) levels
- HbA1c (3-month average glucose)
These targets shift with age because children, adults, and elderly individuals face different risks and needs.
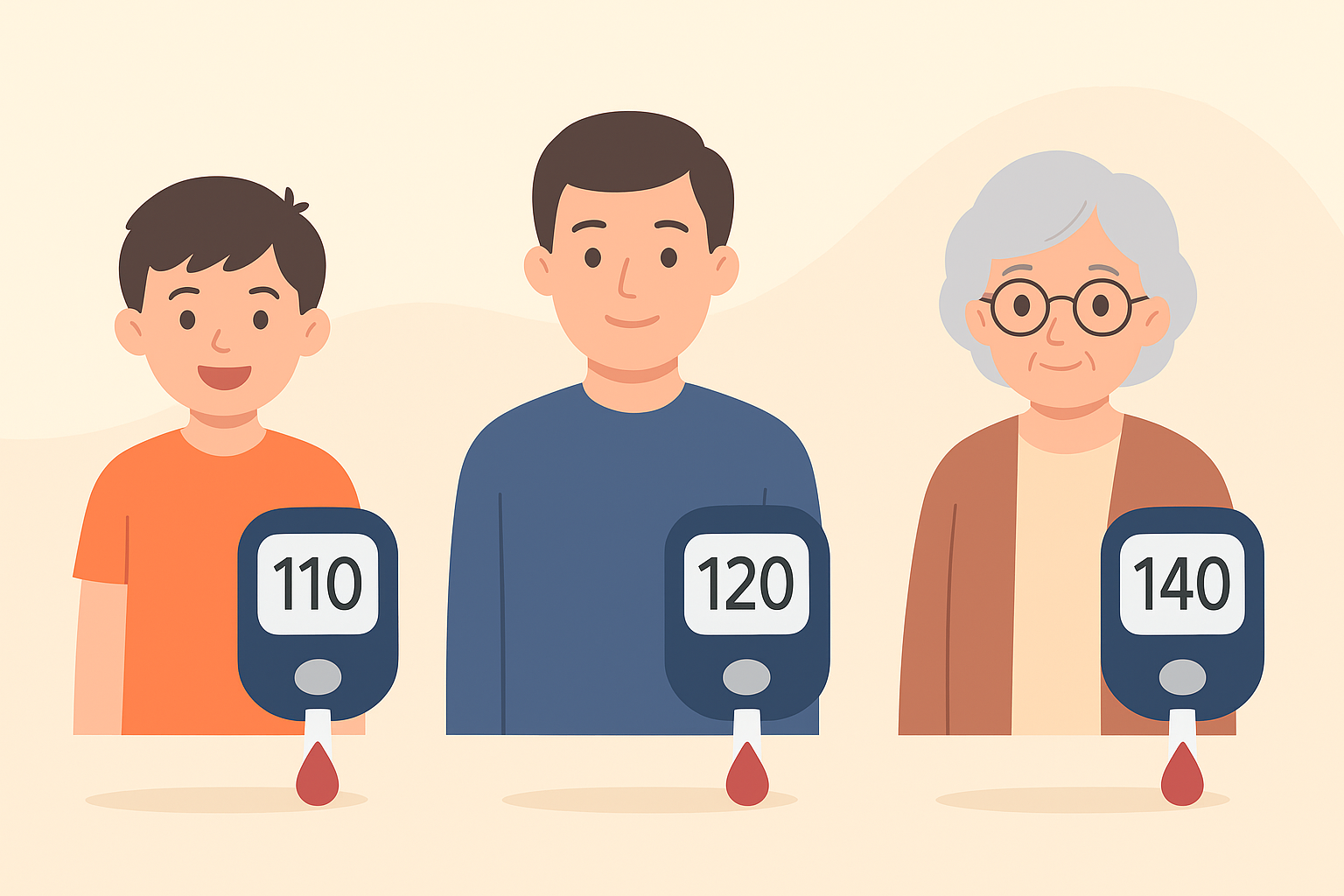
Blood Sugar Targets by Age Group
1. Children & Adolescents (0–18 Years)
Children need slightly higher targets than adults to avoid dangerous low blood sugar episodes.
Recommended targets:
- Fasting: 90–130 mg/dL
- After meals: Less than 180 mg/dL
- HbA1c: Below 7.5%
Effects of meeting targets:
- Supports healthy growth and development
- Prevents fatigue and mood swings
- Reduces future diabetes-related complications
Effects of poor control:
- Delayed growth
- Learning and concentration problems
- Increased risk of hypoglycemia
2. Adults (19–64 Years)
This age group aims for stricter glucose targets to limit long-term complications.
Recommended targets:
- Fasting: 80–130 mg/dL
- After meals: Less than 180 mg/dL
- HbA1c: Below 7%
Effects of meeting targets:
- Lower risk of heart disease and stroke
- Better energy levels and focus
- Reduced risk of kidney, nerve, and eye damage
Effects of poor control:
- Vision problems
- Nerve damage
- Frequent urination and fatigue
- Sexual dysfunction and chronic infections
3. Older Adults (65+ Years)
Elderly individuals often have other medical conditions, so targets are slightly relaxed to avoid dangerous hypoglycemia.
Recommended targets:
- Fasting: 90–150 mg/dL
- After meals: Less than 200 mg/dL
- HbA1c: 7.5% – 8%
Effects of age-adjusted targets:
- Lower risk of falls and fainting
- Better independence and safety
- Reduced medication side effects
Effects of overly strict control:
- Severe low blood sugar episodes
- Dizziness and confusion
- Increased fall and injury risk
Why Age-Based Targets Matter
Different age groups respond differently to blood sugar fluctuations:
- Children are sensitive to lows that affect learning and safety.
- Adults face more long-term complications from high levels.
- Seniors are vulnerable to medication side effects and hypoglycemia.
Age-adjusted targets keep blood sugar control balanced between safety and protection from complications.
Health Benefits of Achieving Proper Blood Sugar Targets
✅ Reduces risk of heart attacks and strokes
✅ Protects kidney function
✅ Maintains healthy eyesight
✅ Prevents nerve damage
✅ Stabilizes mood and energy
✅ Improves sleep quality
Effects of Ignoring Blood Sugar Targets
Uncontrolled sugar levels can lead to:
❌ Diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain)
❌ Kidney failure
❌ Vision loss
❌ Frequent infections
❌ Foot ulcers and amputations
❌ Memory problems in older adults
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar at Any Age
- Monitor blood glucose regularly
- Follow age-appropriate meal plans
- Stay physically active
- Take medicines as prescribed
- Avoid sugary drinks and junk foods
- Manage stress and sleep well
- Schedule regular checkups
HbA1c: The Universal Target Marker
HbA1c reflects your average blood sugar over 3 months and is used to guide treatment goals for every age group.
- Children: <7.5%
- Adults: <7%
- Seniors: 7.5–8%
Regular HbA1c testing supports early detection of dangerous trends.
Conclusion
Blood sugar targets according to age are essential for safe and effective diabetes care. Children need protection from hypoglycemia, adults need stricter control to avoid complications, and seniors require gentler goals to maintain safety and independence. Understanding and following age-specific glucose targets ensures better health and a longer, more active life.