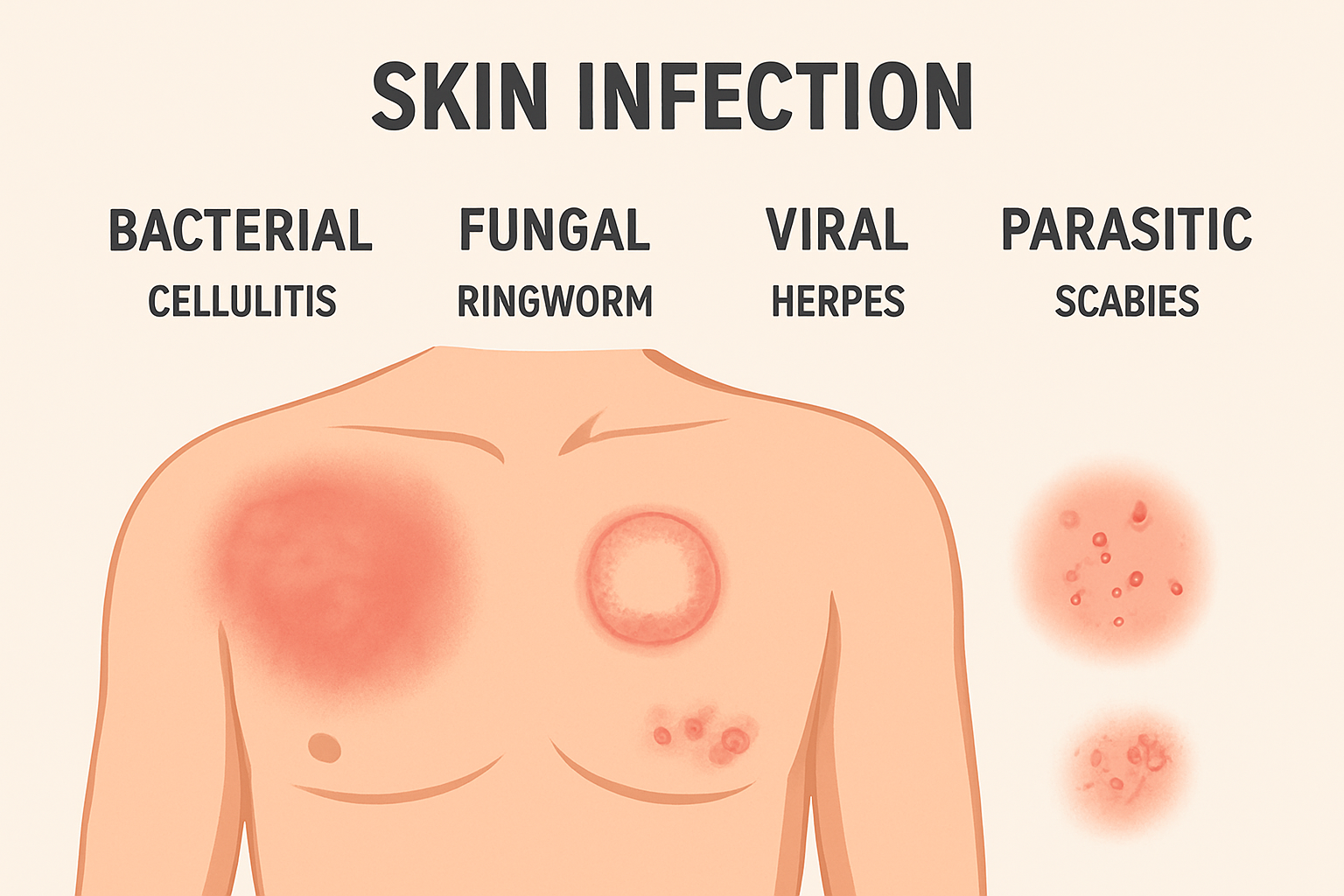
Skin infections are common and can affect anyone—children, adults, and older individuals. While many infections are mild and treatable at home, some can spread quickly and require medical attention. This guide explains types of skin infections, causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention tips, all in a simple and SEO-friendly way.
What Is a Skin Infection?
A skin infection occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites enter the skin and begin to multiply. This leads to symptoms such as redness, swelling, pain, warmth, itching, or pus formation.
Depending on the cause, skin infections can range from mild to severe.
Types of Skin Infections
Skin infections are classified into four main categories:
1. Bacterial Skin Infections
These usually start as small red bumps but can become serious if untreated.
Common bacterial infections:
- Cellulitis
- Impetigo
- Boils (Furuncles)
- Folliculitis
- Erysipelas
Causes:
Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus enter through cuts, insect bites, or cracked skin.
2. Fungal Skin Infections
Fungi grow in warm, moist areas of the body.
Common fungal infections:
- Ringworm
- Athlete’s foot
- Jock itch
- Candidiasis (Yeast infection)
Risk factors:
Excess sweating, diabetes, obesity, poor hygiene, tight clothing.
3. Viral Skin Infections
These spread easily from person to person.
Examples:
- Herpes simplex (Cold sores)
- Herpes zoster (Shingles)
- Warts
- Molluscum contagiosum
4. Parasitic Skin Infections
Parasites invade the skin or lay eggs.
Common examples:
- Scabies
- Lice infestation
- Cutaneous larva migrans
Common Symptoms of Skin Infections
Symptoms depend on the type of infection but may include:
- Redness or rash
- Swelling
- Pain or tenderness
- Warmth in the affected area
- Pus or fluid discharge
- Itching or burning
- Fever (in severe infections)
If an infection spreads quickly, or if you have diabetes, weakened immunity, or heart/kidney disease, seek medical help immediately.
Causes & Risk Factors
Skin infections can occur due to:
- Poor hygiene
- Scratches, cuts, or insect bites
- Sharing towels or personal items
- Weakened immune system
- Excess sweating
- Diabetes or obesity
- Close contact with infected people
Treatment of Skin Infections
Treatment depends on the organism causing the infection.
1. Treatment for Bacterial Infections
- Topical antibiotics (mupirocin, fusidic acid)
- Oral antibiotics (cephalexin, cloxacillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate)
- Warm compress for boils
- Drainage of pus by a doctor if needed
2. Treatment for Fungal Infections
- Antifungal creams (clotrimazole, terbinafine, miconazole)
- Oral antifungals (fluconazole, itraconazole) for severe cases
- Keeping skin dry and clean
3. Treatment for Viral Infections
- Antivirals (acyclovir, valacyclovir)
- Pain relief
- Avoid scratching to prevent spreading
4. Treatment for Parasitic Infections
- Permethrin lotion for scabies
- Medicated shampoos for lice
- Treating close contacts to prevent reinfection
When to See a Doctor?
Seek medical evaluation if you notice:
- Rapidly spreading redness
- Severe pain or swelling
- Fever
- Pus-producing wounds
- Infection not improving with home treatment
- Recurrent infections
People with diabetes must be extra careful because infections can progress rapidly.
Prevention Tips for Healthy Skin
✔ Maintain good hygiene
✔ Wash hands regularly
✔ Keep skin dry, especially skin folds
✔ Avoid sharing personal items
✔ Use clean towels and clothes
✔ Keep nails trimmed
✔ Manage blood sugar if diabetic
✔ Treat small cuts immediately
✔ Avoid walking barefoot in damp areas
Conclusion
Skin infections are common but preventable and treatable with proper care. Understanding the types, symptoms, and treatment options helps you take action early and avoid complications. If symptoms worsen or spread quickly, consult a healthcare professional promptly.