A lipid profile test is a commonly performed blood test used to assess the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. It measures different types of fats (lipids) in the blood, helping doctors diagnose and monitor cholesterol disorders. Understanding the tests included in a lipid profile allows patients to take better control of their heart health.
What Is a Lipid Profile Test?
A lipid profile, also called a lipid panel, is a group of blood tests that evaluate cholesterol and triglyceride levels. It can be done as a fasting or non-fasting (random) test, depending on clinical need.
This test is essential for early detection of dyslipidemia, a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
Tests Included in a Lipid Profile
1. Total Cholesterol (TC)
Total cholesterol measures the overall cholesterol present in the blood, including both good and bad cholesterol.
Normal Value:
- Less than 200 mg/dL
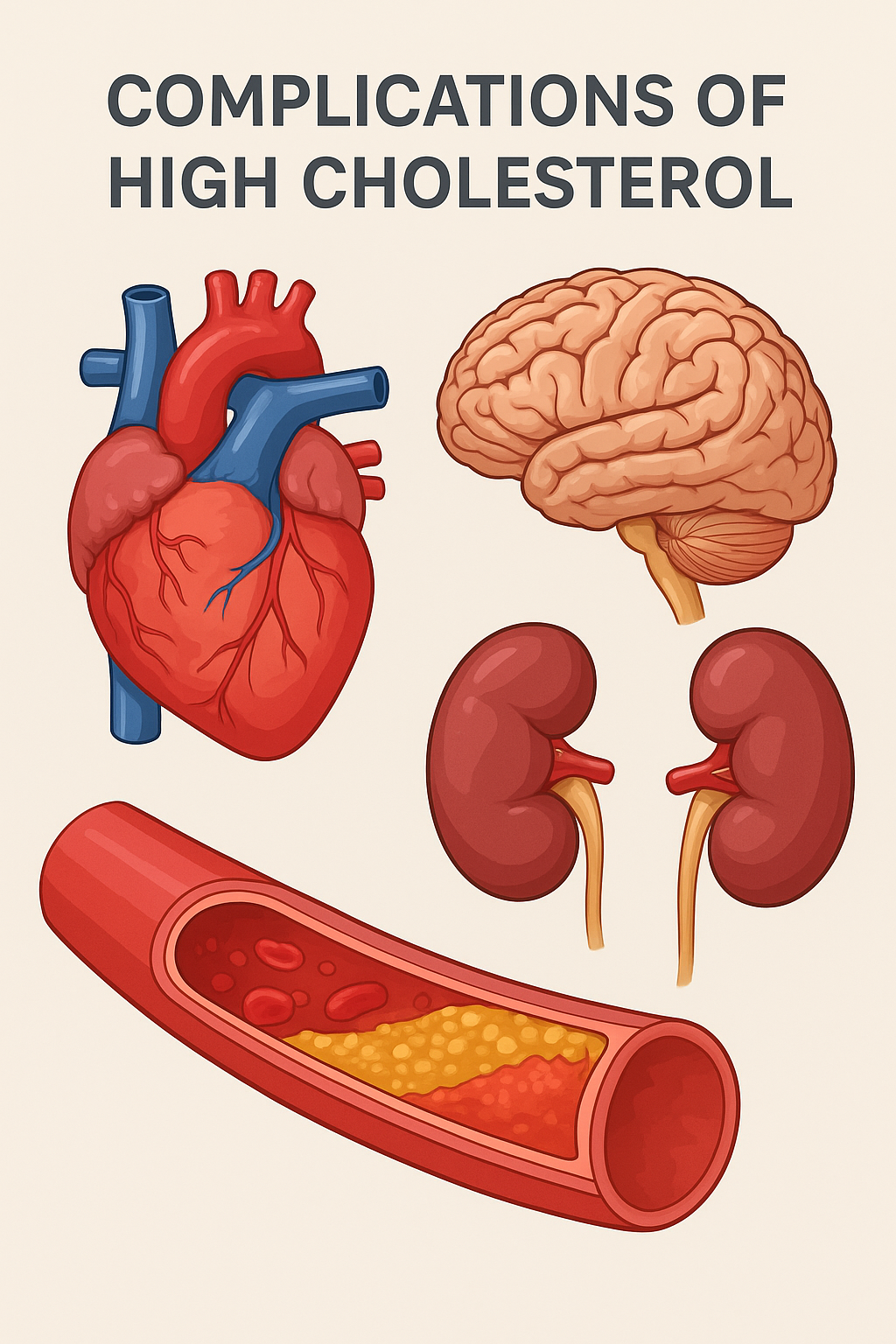
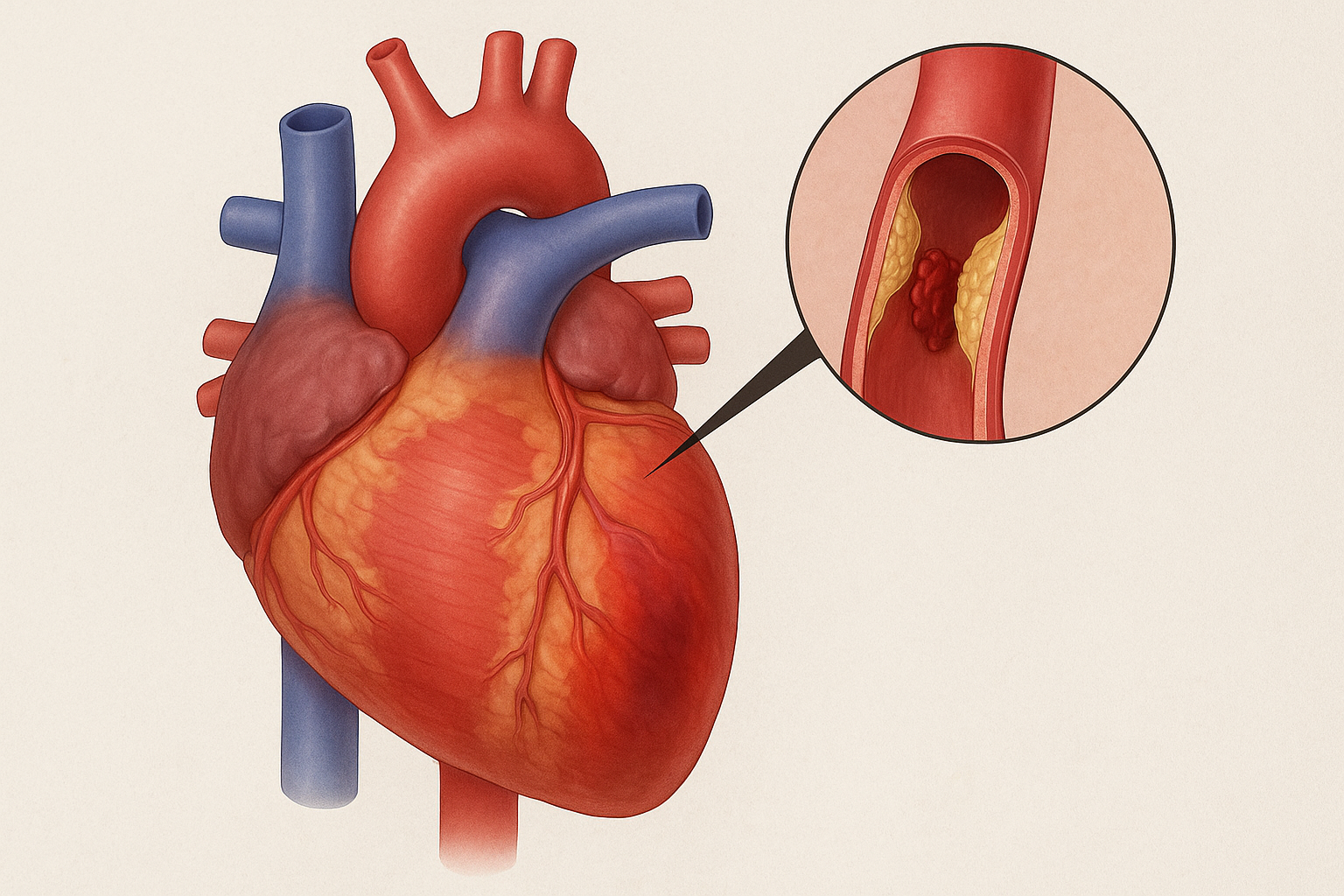
High total cholesterol increases the risk of heart disease and blocked arteries.
2. Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Cholesterol – “Bad Cholesterol”
LDL cholesterol is considered harmful because it deposits cholesterol in the arterial walls, leading to atherosclerosis.
Optimal Level:
- Less than 100 mg/dL
Lower LDL levels reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
3. High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Cholesterol – “Good Cholesterol”
HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and protects against heart disease.
Desirable Level:
- ≥ 40 mg/dL (men)
- ≥ 50 mg/dL (women)
Higher HDL levels are beneficial for cardiovascular health.
4. Triglycerides (TG)
Triglycerides are fats formed from excess calories and sugar intake. High levels are linked to diabetes, obesity, and pancreatitis.
Normal Level:
- Fasting: < 150 mg/dL
- Non-fasting: < 175 mg/dL
5. Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) Cholesterol
VLDL carries triglycerides in the blood and contributes to plaque formation in arteries.
Normal Range:
- 5–40 mg/dL
Elevated VLDL increases cardiovascular risk.
6. Non-HDL Cholesterol
Non-HDL cholesterol is calculated by subtracting HDL from total cholesterol. It represents all atherogenic (harmful) lipoproteins.
Ideal Level:
- Less than 130 mg/dL
It is especially useful in non-fasting lipid profiles.
7. Cholesterol Ratios (Optional)
Some laboratories report ratios for better risk assessment:
- Total Cholesterol / HDL Ratio
- LDL / HDL Ratio
Lower ratios indicate lower cardiovascular risk.
Why Are Lipid Profile Tests Important?
Lipid profile tests help in:
- Early detection of heart disease
- Monitoring response to cholesterol-lowering medications
- Assessing risk in diabetics and hypertensive patients
- Preventing heart attack and stroke
- Guiding lifestyle and dietary changes
Who Should Get a Lipid Profile Test?
A lipid profile is recommended for:
- Adults above 20 years
- Patients with diabetes mellitus
- People with high blood pressure
- Overweight and obese individuals
- Smokers
- Patients with a family history of heart disease
How to Prepare for a Lipid Profile Test
- Fasting test: Avoid food for 8–12 hours
- Non-fasting test: No preparation needed
- Avoid alcohol and heavy meals before testing
- Inform your doctor about ongoing medications
Conclusion
The tests included in a lipid profile provide valuable information about cholesterol and fat levels in the blood. Regular lipid testing plays a key role in preventing cardiovascular diseases through early diagnosis and proper management. Maintaining healthy lipid levels through diet, exercise, and medical care can significantly improve long-term heart health.