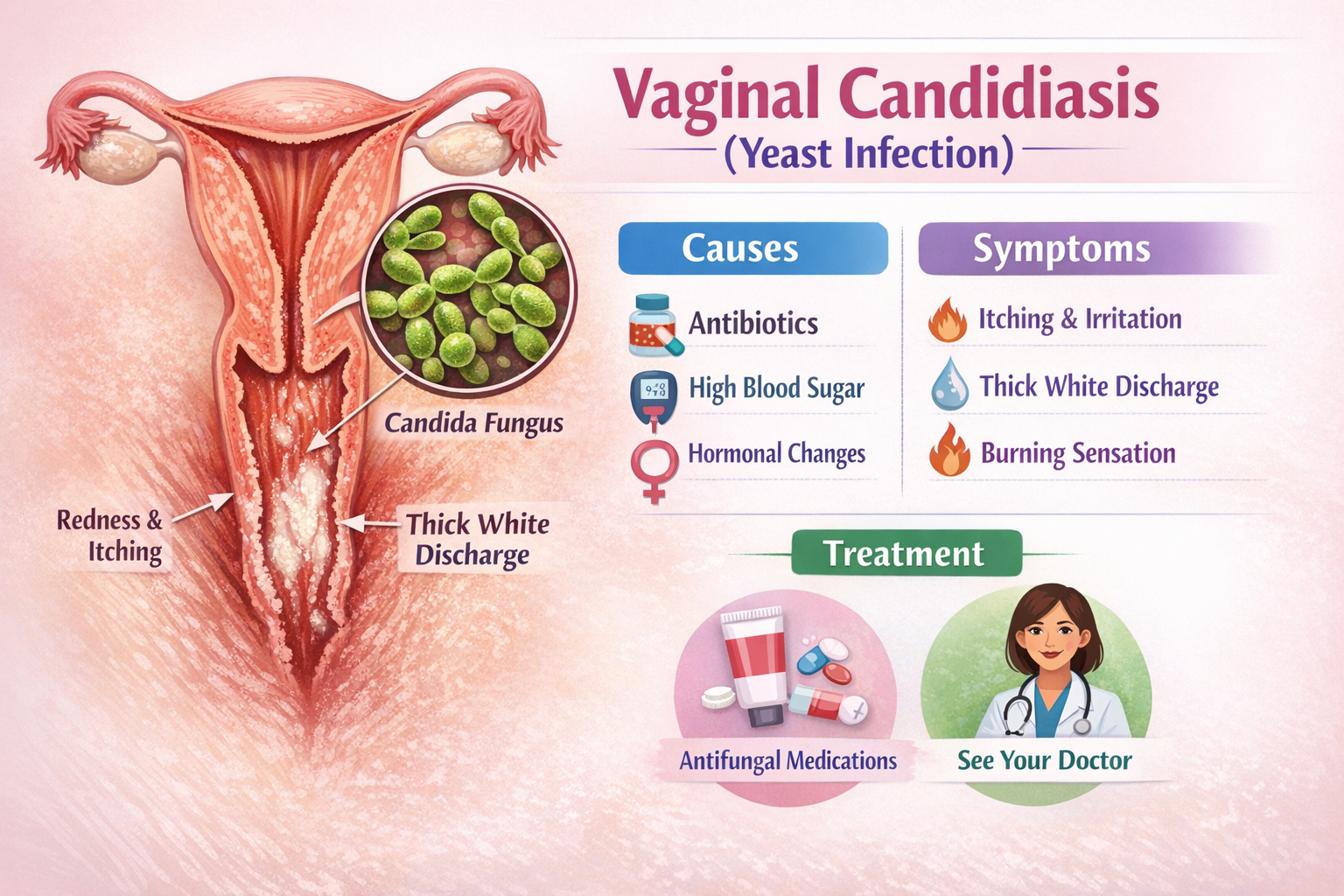
Vaginal candidiasis, commonly known as vaginal yeast infection, is a frequent fungal infection affecting women of all ages. It is mainly caused by an overgrowth of Candida albicans, a yeast that normally lives in small amounts in the vagina. When the natural balance of vaginal flora is disturbed, Candida can multiply and cause uncomfortable symptoms.
What Is Vaginal Candidiasis?
Vaginal candidiasis is a fungal infection of the vagina that leads to irritation, abnormal discharge, itching, and discomfort. Although it is not considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI), sexual activity and other factors can increase the risk.
According to medical studies, nearly 75% of women experience at least one episode of vaginal candidiasis during their lifetime.
Causes of Vaginal Candidiasis
Several factors can disrupt the normal vaginal environment and promote yeast overgrowth:
- Antibiotic use (kills protective bacteria)
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
- Pregnancy
- Weak immune system
- Hormonal changes (oral contraceptives, hormone therapy)
- Tight or synthetic underwear
- Poor genital hygiene
- Excessive vaginal douching
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of vaginal candidiasis may range from mild to severe and include:
- Intense vaginal itching
- Thick, white, curd-like vaginal discharge
- Redness and swelling of the vulva
- Burning sensation, especially during urination
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Vaginal soreness or irritation
Unlike bacterial infections, yeast infections usually do not produce a foul smell.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually made through:
- Detailed medical history
- Pelvic examination
- Microscopic examination of vaginal discharge
- Vaginal swab or culture (in recurrent or resistant cases)
Proper diagnosis is important, as symptoms may mimic other vaginal infections.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity and recurrence of infection:
1. Antifungal Medications
- Topical antifungal creams or suppositories (clotrimazole, miconazole)
- Oral antifungal tablets (fluconazole)
2. Recurrent Vaginal Candidiasis
Women with frequent infections may require:
- Long-term antifungal therapy
- Strict blood sugar control in diabetic patients
- Lifestyle and hygiene modifications
⚠️ Self-medication should be avoided, especially in recurrent cases.
Vaginal Candidiasis in Pregnancy
Vaginal candidiasis is common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. Topical antifungal treatments are preferred, while oral antifungals should only be used under medical supervision.
Prevention Tips
You can reduce the risk of vaginal candidiasis by following these preventive measures:
- Maintain good genital hygiene
- Avoid unnecessary antibiotic use
- Wear cotton, breathable underwear
- Keep blood sugar levels under control
- Avoid vaginal douching and scented products
- Change wet clothes promptly
- Eat a balanced diet to support immunity
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if:
- Symptoms persist despite treatment
- Infections occur more than 4 times a year
- You are pregnant or diabetic
- You experience severe pain or fever
Conclusion
Vaginal candidiasis is a common and treatable condition when diagnosed early. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting preventive measures can help women maintain optimal vaginal health. Timely medical consultation ensures effective treatment and prevents complications.