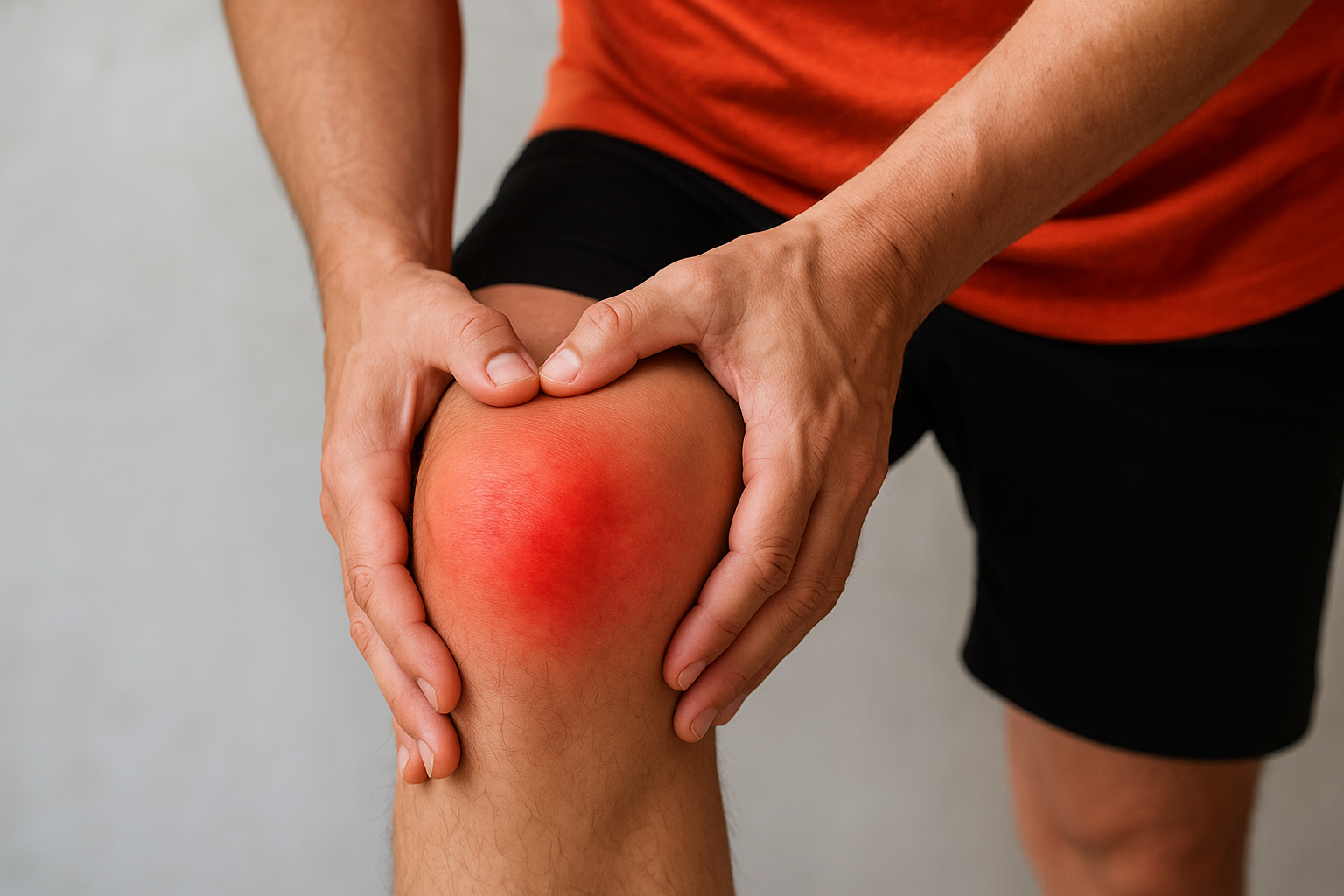
Knee pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal problems affecting people of all ages. From athletes to older adults, anyone can experience discomfort or stiffness in the knee that interferes with daily activities. Understanding the causes of knee pain and learning how to manage it properly can prevent long-term disability and improve quality of life.
This blog covers the causes of knee pain, symptoms, treatment options, and effective prevention strategies to help you maintain healthy knee joints.
What Is Knee Pain?
Knee pain refers to discomfort around the knee joint, which connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). The joint relies on ligaments, cartilage, tendons, and muscles for stability and movement. Damage or strain to any of these structures can result in pain, swelling, or limited motion.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
1. Injuries
Sudden trauma may damage ligaments or cartilage:
- ACL or PCL tears
- Meniscus injuries
- Knee dislocation or fractures
2. Osteoarthritis
Age-related wear and tear of cartilage leads to joint stiffness, pain, and reduced flexibility, commonly affecting people over 40 years of age.
3. Overuse & Strain
Repetitive movements such as running, jumping, or kneeling can cause:
- Tendinitis
- Runner’s knee (patellofemoral pain syndrome)
4. Inflammatory Conditions
Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or gout cause inflammation inside the knee joint, leading to:
- Joint swelling
- Redness
- Warmth
5. Obesity
Excess weight increases pressure on knee joints, accelerating cartilage breakdown and worsening arthritis-related pain.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
The symptoms depend on the cause but commonly include:
- Pain or aching
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Difficulty bending or straightening the knee
- Clicking or popping sounds
- Knee instability
- Limping
Diagnosis of Knee Pain
Doctors use:
- Physical examination
- X-rays (for arthritis or fractures)
- MRI scans (for ligament or cartilage injuries)
- Blood tests (for inflammatory disease)
These tests help identify the root cause and guide proper treatment.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
✅ 1. Rest, Ice, Compression & Elevation (RICE)
Ideal for early injury management:
- Rest the knee
- Apply cold packs
- Use compression bandages
- Elevate the leg
✅ 2. Medications
- Pain relievers (paracetamol)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Joint supplements (glucosamine, vitamin D)
✅ 3. Physical Therapy
Strengthens muscles around the knee to improve joint support and flexibility.
✅ 4. Weight Management
Losing even a small amount of weight reduces knee joint pressure and pain severity.
✅ 5. Knee Support Braces
Provides stability for weakened joints and prevents further strain.
✅ 6. Injections
- Corticosteroids for inflammation
- Hyaluronic acid for joint lubrication
✅ 7. Surgery
For severe knee damage:
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament reconstruction
- Partial or total knee replacement
Home Remedies for Knee Pain
- Gentle stretching exercises
- Warm compress for stiffness
- Turmeric or ginger supplementation
- Avoid sitting or standing for long periods
- Wear proper footwear
Preventing Knee Pain
🦵 Maintain a healthy weight
🦵 Warm up before exercise
🦵 Strengthen thigh and leg muscles
🦵 Wear knee protection in sports
🦵 Avoid repetitive knee strain
🦵 Follow good posture techniques
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical care if you experience:
🚨 Severe swelling
🚨 Persistent pain longer than 7 days
🚨 Fever with knee redness
🚨 Difficulty walking
🚨 Knee deformity after injury
Early treatment prevents permanent joint damage.
Living With Knee Pain
Lifestyle changes such as routine low-impact exercises (walking, swimming, yoga) and balanced nutrition can help preserve knee health. Working closely with healthcare providers ensures proper diagnosis, safe therapy, and improved mobility.
Final Thoughts
Knee pain should never be ignored. Early recognition, correct diagnosis, and timely management can stop disease progression and help you return to an active, pain-free life. Whether your pain is caused by injury, arthritis, or overuse, the right treatment makes recovery possible.